Manual testing falls short in this reality. Teams chase evidence, sample only a fraction of activity, and often discover issues months too late. Consequently, risk grows while trust erodes. In contrast, automated controls testing closes this gap. It monitors systems in real time, gathers evidence automatically, and highlights exceptions before they become costly failures.
Moreover, automation does more than improve efficiency. It strengthens security, accelerates audits, and gives executives confidence in their risk posture. Research shows that automation can reduce compliance review time by up to 50%, freeing teams to focus on higher-value analysis.
What Is Automated Controls Testing?
Automated controls testing is the practice of using technology to check whether an organization’s policies, procedures, and safeguards work as intended—without relying solely on manual reviews. Instead of auditors sampling a handful of transactions or IT teams chasing screenshots, automation continuously validates controls in real time.
For example, a manual process might involve checking ten user accounts each quarter to confirm that only authorized employees have access to sensitive systems. In contrast, automated testing scans all user accounts every day, flags anomalies instantly, and generates evidence for auditors automatically. This approach not only saves time but also eliminates the blind spots left by sampling.
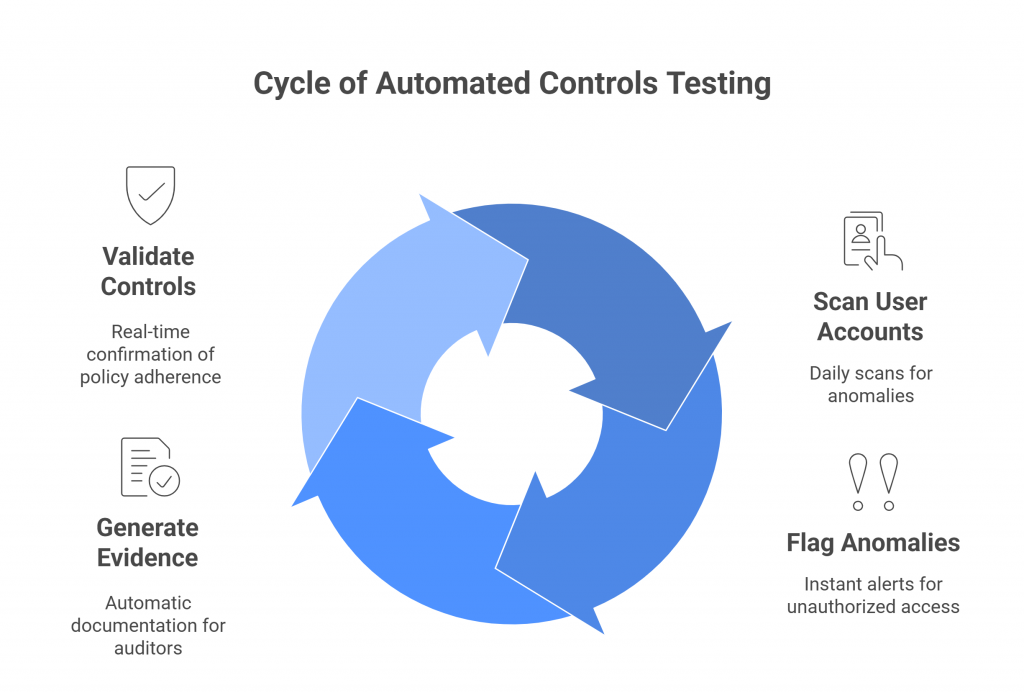
Key Elements
- Continuous Monitoring – Automated tools keep watch over systems, processes, and configurations, detecting deviations as they occur.
- Automated Evidence Collection – Instead of pulling reports by hand, the system stores logs, tickets, and configurations as audit-ready evidence.
- Exception Handling – When a control fails, workflows route alerts to the right teams, ensuring quick remediation.
- Audit Readiness – Dashboards and reports provide auditors with complete, verifiable data—without disrupting business operations.
This shift is crucial because modern IT environments change rapidly. Cloud workloads spin up and down in seconds, and new regulatory requirements emerge each year. Without automation, organizations risk falling behind, leaving gaps in compliance and increasing exposure to penalties or breaches. Automated controls testing ensures that compliance remains continuous, scalable, and reliable, rather than static and reactive.
The Business Value of Automation
Automated controls testing does more than streamline compliance tasks. It delivers speed, scale, and assurance that manual methods cannot match. Below are the key areas where organizations see the greatest impact.

1. Speed and Agility
Manual audits often require weeks of preparation, evidence gathering, and back-and-forth with auditors. These delays leave organizations vulnerable, as risks can evolve faster than reports. Automation changes this dynamic. By running control tests continuously, systems can detect deviations within minutes and provide instant alerts.
For example, if a user gains unauthorized access to a financial system, an automated test can flag the issue the same day—rather than months later during a quarterly review. As a result, businesses no longer wait for audit cycles to know if they are compliant; they gain real-time assurance that their safeguards are working.
2. Scalability Across Complex Environments
Today’s enterprises operate across multiple geographies, business units, and IT platforms. Cloud services spin up and down daily, and third-party vendors introduce additional risks. Manual testing cannot cover this complexity without becoming prohibitively expensive or inconsistent.
Automated controls testing, however, scales seamlessly. It can monitor thousands of controls across different environments at once, applying consistent logic and standards. This ensures that a new cloud server in Singapore, a partner application in Europe, and an ERP system in the U.S. are all tested under the same framework. The result is unified compliance across the entire enterprise, regardless of size or complexity.
3. Accuracy and Reliability
Humans are prone to fatigue and error, especially when dealing with repetitive tasks like log reviews or access checks. A missed screenshot or misfiled report can lead to failed audits and regulatory penalties.
Automation eliminates these risks by executing tests consistently, with no variation in logic or diligence. Research highlights that organizations adopting automated compliance solutions report 35% fewer audit findings compared to those relying on manual processes. By ensuring accuracy, automation not only reduces regulatory exposure but also builds confidence with auditors and stakeholders.
4. Cost Efficiency
Manual testing consumes valuable time and resources. Skilled compliance staff often spend hours collecting screenshots, reconciling reports, and answering audit requests instead of focusing on strategic risk management.
Automation reduces this burden significantly. By automating evidence collection and test execution, organizations lower labor costs while improving productivity. Compliance professionals can then redirect their efforts to higher-value tasks, such as strengthening governance frameworks, analyzing risk trends, and advising leadership. Over time, this shift lowers the total cost of compliance while delivering better results.
5. Executive Confidence and Transparency
In many organizations, executives only receive compliance updates during quarterly board meetings or after an audit. This lag creates blind spots, leaving leadership uncertain about the company’s current risk posture.
Automated controls testing solves this by providing real-time dashboards and continuous reporting. Executives can log in at any time to see the status of controls, exceptions, and remediation progress. This visibility builds confidence, improves decision-making, and demonstrates accountability to regulators, investors, and customers alike.
Core Capabilities of an Automated Controls Framework
Automated controls testing is not a single tool—it is a framework made up of interconnected capabilities. Together, these capabilities ensure that compliance is not only efficient but also continuous, scalable, and resilient.
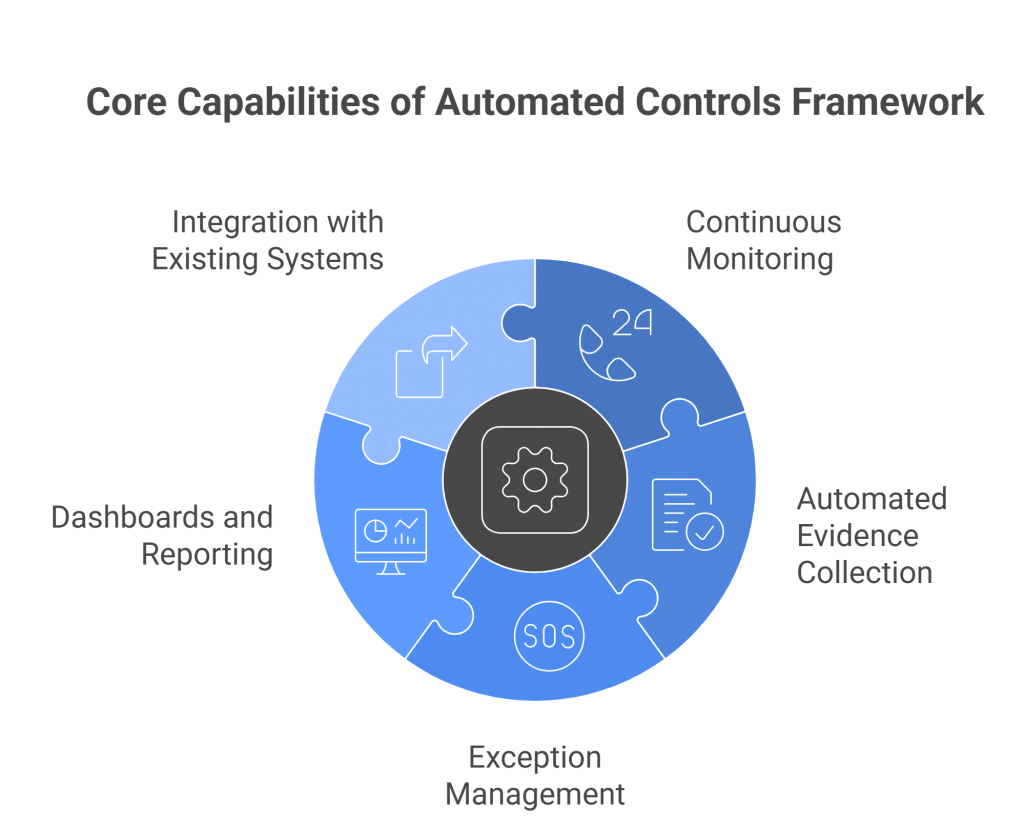
1. Continuous Monitoring
Manual reviews happen at fixed intervals, leaving blind spots between audits. Continuous monitoring closes this gap. Automated systems run in the background 24/7, tracking user activity, configuration changes, and system logs.
For instance, if a cloud server is launched without encryption enabled, continuous monitoring tools detect the misconfiguration immediately. Instead of waiting for the next audit cycle, the system alerts IT teams to correct the issue at once. This constant vigilance shifts compliance from reactive to proactive.
2. Automated Evidence Collection
Collecting evidence for audits is one of the most time-consuming parts of compliance. Screenshots, access logs, and approval tickets often require days of effort. Automated frameworks simplify this by gathering and storing evidence as soon as events occur.
Imagine an access request approved through an identity management system. The automated framework records the request, the approver’s identity, and the timestamp automatically. When auditors later ask for proof, the system provides ready-to-use documentation—without any manual effort.
3. Exception Management
Even with the strongest controls, exceptions will occur. The key is how quickly an organization can detect and remediate them. Automated frameworks route exceptions into workflows, often integrating with IT service management (ITSM) platforms such as ServiceNow or Jira.
This integration ensures accountability: when a control fails, the right team receives an alert, a remediation ticket opens, and progress is tracked until resolution. By closing the loop, organizations not only fix issues faster but also demonstrate to regulators that they have strong corrective measures in place.
4. Dashboards and Reporting
Executives, regulators, and auditors need visibility. Automated frameworks deliver this through real-time dashboards and customizable reports. Instead of static spreadsheets, leadership can view compliance posture across systems, geographies, or business units with a few clicks.
Dashboards can highlight which controls are passing, which are failing, and where remediation is in progress. This transparency gives leaders confidence, helps auditors trust the process, and fosters a culture of accountability throughout the organization.
5. Integration with Existing Systems
The most effective frameworks do not operate in isolation. They integrate with identity management systems, cloud platforms, ERP applications, and security tools. This interoperability ensures comprehensive coverage and reduces duplication of effort.
For example, a framework integrated with a cloud provider can automatically validate encryption, firewall rules, and identity policies. By pulling data directly from source systems, it ensures accuracy and reduces reliance on error-prone manual reporting.
These core capabilities together form the backbone of an effective automated controls testing program. They not only strengthen compliance but also embed assurance into the daily operations of the organization.
Automated Controls: Use Cases Across Domains
Automated controls testing applies across industries and risk areas. By tailoring the framework to specific domains, organizations gain stronger compliance, faster response times, and greater assurance.
1. Regulatory Compliance
Industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail face strict oversight. Regulations like SOX, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR require consistent proof that controls are working. Manual testing often struggles to keep up with these demands.
With automation, organizations can continuously test access controls, transaction monitoring, and data protection measures. For example, a bank can automatically validate that only authorized traders have access to high-risk systems and generate reports for regulators at any time. This not only satisfies audit requirements but also reduces the risk of costly non-compliance penalties.
2. Cybersecurity Controls
Cybersecurity threats evolve daily, making real-time validation critical. Automated testing ensures that safeguards like identity and access management (IAM), endpoint protections, and vulnerability management work as designed.
Consider IAM as an example. Automated controls can check every login attempt against predefined rules—flagging unauthorized access, enforcing multi-factor authentication, and blocking inactive accounts. These measures not only reduce breach risk but also strengthen defense in depth.
3. Cloud Governance
Cloud adoption brings speed and flexibility but also introduces new risks. Misconfigured cloud resources are a leading cause of data breaches. Automated controls testing helps by continuously scanning cloud environments for compliance with security policies and regulatory standards.
For instance, automation can validate that all storage buckets are encrypted, firewalls are configured properly, and unused instances are shut down. In doing so, organizations prevent drift from secure baselines and maintain confidence that their cloud environment remains compliant.
4. Operational Resilience
Beyond compliance and security, organizations must also ensure resilience. Automated controls testing supports business continuity by validating disaster recovery plans, backup procedures, and vendor risk management.
Imagine a healthcare provider that relies on third-party services for patient records. Automated testing can verify vendor compliance with data protection standards and trigger alerts if a vendor falls short. This ensures continuity of service and protection of sensitive information.
5. Cross-Industry Applications
The value of automated controls testing extends beyond regulated industries. Retailers use it to protect customer payment data, technology companies apply it to secure software development pipelines, and manufacturers rely on it to safeguard supply chains. Wherever controls exist, automation strengthens their reliability.
What Challenges Do Organizations Face with Automated Controls and How to Overcome Them?
Automated controls testing offers tremendous value, but organizations often face roadblocks when implementing it. These challenges range from technical complexities to cultural resistance. By anticipating these barriers and applying best practices, companies can adopt automation more smoothly and achieve stronger, continuous compliance.
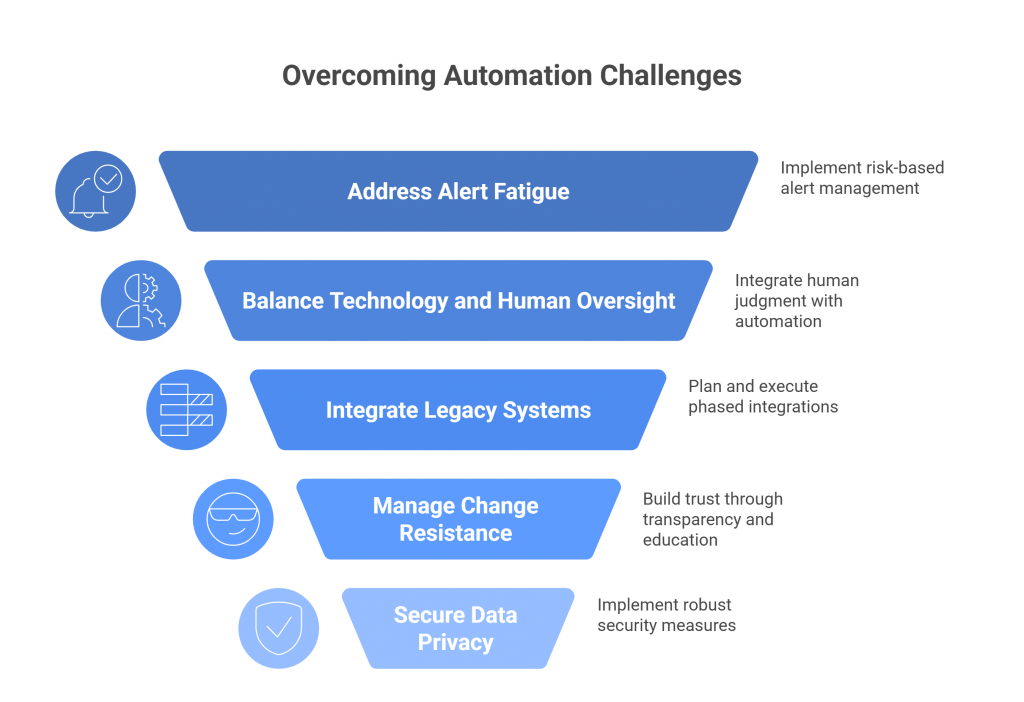
1. Alert Fatigue and False Positives
The Challenge: Automation can overwhelm teams with notifications. A control may trigger an alert for every small deviation, even when the risk is minor. Over time, teams become desensitized, increasing the chance of missing serious issues. For instance, a system that generates hundreds of daily alerts for password resets may hide a truly critical event—such as unauthorized access.
The Solution: Organizations should adopt a risk-based approach. By setting thresholds, categorizing alerts, and applying risk scoring, they can filter out noise and focus on the highest-priority issues. Tools that integrate with IT service management (ITSM) platforms, like ServiceNow or Jira, can also route alerts intelligently, ensuring accountability and faster remediation.
2. Overreliance on Technology
The Challenge: While automation handles repetitive checks well, it cannot replace human judgment. Controls that involve ethical considerations, regulatory interpretation, or business context require careful evaluation. Blindly trusting automation could create a false sense of security.
The Solution: The most effective programs blend automation with expert oversight. Automated tools should handle large-scale, repetitive checks—such as confirming encryption on cloud storage—while humans review exceptions and high-risk anomalies. This “human-in-the-loop” model balances efficiency with judgment.
3. Integration with Legacy Systems
The Challenge: Not all systems are built for automation. Legacy platforms often lack APIs, structured logs, or modern security features. This makes it difficult to connect them to automated frameworks, leading to partial coverage and manual workarounds.
The Solution: Organizations should plan integrations early and take a phased approach. Middleware, custom connectors, or hybrid workflows can bridge gaps while modernization initiatives progress. For example, logs from an old ERP system might be exported and normalized before being fed into an automation platform. Over time, as systems are upgraded, integration becomes smoother.
4. Change Management Resistance
The Challenge: People are often the biggest barrier to automation. Compliance and audit teams may distrust automated results, fearing loss of control or accountability. Others may resist change because they are comfortable with existing manual processes—even if those processes are inefficient.
The Solution: Leaders should build trust through transparency. This includes educating teams about how automation works, showing audit-ready reports generated by the system, and involving stakeholders from the start. Quick wins, such as automating repetitive access reviews, can demonstrate value and reduce skepticism. Clear communication that automation is an enabler—not a replacement—helps shift mindsets.
5. Data Privacy and Security Risks
The Challenge: Automated controls testing relies on collecting sensitive data such as access logs, approval workflows, and configuration details. If not properly secured, these repositories can become a target for attackers or an additional compliance liability.
The Solution: Organizations must secure the automation framework itself. This includes encrypting all stored evidence, enforcing least privilege on access, and maintaining audit trails of who interacts with the system. Regular penetration testing and compliance with standards such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2 strengthen trust that the automation platform is as secure as the systems it monitors.
What Does the Future of Automated Controls Testing Look Like?
The future of automated controls testing is moving far beyond compliance checklists. As technology matures and regulatory expectations evolve, automation will shift from a supporting tool into the backbone of enterprise risk management.
1. Autonomous Compliance Engines
In the coming years, organizations will see automated controls evolve into self-healing systems. Instead of simply flagging a failed control, these systems will take corrective action automatically—for example, disabling unauthorized accounts or reconfiguring a misaligned cloud resource. This shift from detection to correction will redefine compliance as a real-time, closed-loop process.
2. Deeper Integration With Business Operations
Automated controls will no longer sit in isolation within IT or audit functions. They will embed directly into daily workflows—from HR onboarding to software development pipelines—ensuring that compliance is part of every business process. This integration will make compliance invisible yet continuous, reducing friction while strengthening assurance.
3. AI-Driven Predictive Risk Management
Artificial intelligence will expand the role of automated controls from retrospective checks to predictive insights. By analyzing patterns across millions of data points, AI can forecast which controls are most likely to fail and which areas pose the highest emerging risks. This proactive approach will allow businesses to allocate resources more effectively and prevent issues before they occur.
4. Regulatory Acceptance of Automation
Regulators are already beginning to recognize the value of automation. In the future, audit and regulatory bodies may accept automated evidence directly, reducing the need for manual sampling and verification. This shift could shorten audit timelines from months to days and reshape how organizations prepare for compliance reviews.
5. Convergence of Cybersecurity and Compliance
As cyber threats grow more complex, the line between security monitoring and compliance testing will blur. Automated controls frameworks will increasingly serve both functions, validating technical safeguards while producing evidence for regulators. This convergence will create unified risk dashboards that give executives a complete picture of security, compliance, and resilience in one view.
The future of automated controls testing is not just about doing compliance faster—it’s about transforming compliance into a strategic advantage. Organizations that embrace these advancements will gain real-time visibility, stronger security, and greater trust with regulators, investors, and customers alike.
Conclusion
Automated controls testing marks a turning point in how organizations think about compliance. What was once a backward-looking exercise is now becoming a forward-facing capability that strengthens both trust and resilience. Instead of waiting for annual audits or scrambling to gather evidence, companies can demonstrate assurance every day, in real time.
This shift changes the role of compliance teams as well. Rather than being perceived as auditors who “slow things down,” they emerge as strategic partners who enable agility and confidence. Executives gain a clear, ongoing view of risk posture, while regulators and stakeholders see evidence of accountability baked into business operations.
The future belongs to organizations that see compliance not as a burden, but as an opportunity to differentiate. By embedding automated controls into daily processes, companies build stronger governance foundations, speed innovation, and create lasting trust with customers and investors alike.
The message is simple: compliance does not have to be reactive, fragmented, or painful. With automated controls testing, it can be continuous, integrated, and value-driven