Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the game across industries, bringing incredible efficiencies and innovation. But with great power comes great responsibility. As AI adoption skyrockets, so do concerns around ethics, bias, transparency, and accountability.
That’s why AI compliance frameworks are becoming a must-have. They help businesses ensure their AI systems are fair, secure, and legally compliant while also protecting users and society at large.
And the numbers tell the story. In 2024, 72% of companies reported using AI in at least one business function, up from just 55% the previous year. AI is no longer a futuristic concept. It is here, and it is everywhere.
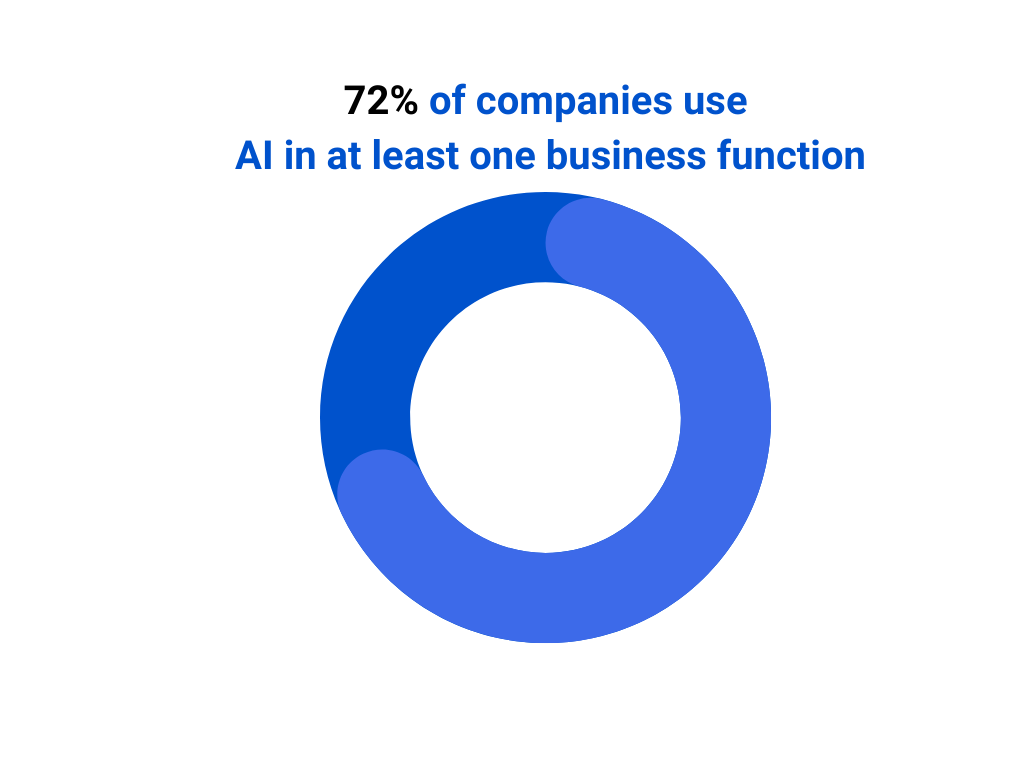
But here’s the catch. 81% of Americans believe AI poses more risks than benefits, especially when it comes to data privacy. That is a trust gap businesses cannot afford to ignore.
So, what is the solution? Strong AI compliance frameworks. Companies that take AI governance seriously will not only avoid regulatory headaches but also build trust with their customers and stakeholders.
AI is not slowing down, and neither should compliance. The question is, is your AI strategy keeping up.
Benchmark AI Regulatory and Compliance Frameworks you need to know
- EU AI Act (European Union Artificial Intelligence Act)
Region: European Union
Focus: AI risk classification and regulation
The first comprehensive AI law, classifying AI systems into four risk categories:
- Unacceptable Risk – Banned AI applications (e.g., social scoring).
- High Risk – Strictly regulated AI systems (e.g., medical AI, biometric surveillance).
- Limited Risk – AI applications requiring transparency (e.g., chatbots).
- Minimal Risk – Low-risk AI applications with no regulatory restrictions.
Businesses operating in the EU or providing AI services to EU citizens must comply with this framework to avoid penalties.
- NIST AI RMF (National Institute of Standards and Technology AI Risk Management Framework)
Region: United States
Focus: AI risk management and trustworthiness
This voluntary framework provides a structured approach to:
- Identifying AI risks
- Ensuring fairness and transparency
- Mitigating biases
- Enhancing accountability
It is widely adopted by enterprises and government agencies in the U.S. for building responsible AI systems.
- ISO/IEC 42001 (AI Management System Standard)
Region: Global
Focus: AI governance and risk management
The first international AI governance standard, helping businesses:
- Develop AI policies aligned with compliance regulations
- Implement risk mitigation strategies
- Improve AI model security and ethics
Enterprises building AI-driven solutions globally must adhere to ISO/IEC 42001 to maintain industry standards.
4️. OECD AI Principles (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development AI Principles)
Region: Global
Focus: Ethical AI development and accountability
These international AI governance principles focus on:
- AI transparency and explainability
- Human-centric AI development
- AI accountability and governance
Adopted by over 40 countries, influencing AI policies worldwide.
5. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) & AI Compliance
Region: European Union (Global Impact)
Focus: Data privacy and AI regulation
GDPR applies to AI systems processing personal data, ensuring:
- AI decision-making is explainable (Right to Explanation)
- Users can opt-out of automated decision-making
- AI-driven data processing is lawful and transparent
Non-compliance can lead to fines of up to €20M or 4% of global revenue.
6. CCPA & CPRA (California Consumer Privacy Act & California Privacy Rights Act)
Region: United States (California)
Focus: AI-driven consumer data protection
Why It Matters:
- CCPA/CPRA regulate AI-based profiling and automated decision-making
- Businesses must provide consumers transparency and control over AI-driven processes
Companies handling California residents’ data must comply or face penalties
7. IEEE 7000 Series
Region: Global
Focus: Ethical AI design
It covers AI bias mitigation, transparency, and security, making it essential for organizations designing AI-driven products.
8️. Singapore Model AI Governance Framework
Region: Asia-Pacific
Focus: AI governance and ethical AI adoption
It provides practical AI governance guidelines, emphasizing:
- AI fairness and accountability
- Risk-based AI deployment
- AI transparency for consumers
Used as a reference by businesses in Asia and beyond.
Why do you need to Implement AI GRC frameworks now?
In a recent report commissioned by Prove AI and conducted by Zogby Analytics, 96% of organizations are already using AI to support business operations, with the same percentage planning to increase their AI budgets in the coming year.
And yet, only 5% of these organizations have implemented an AI governance framework, while the majority intend to implement one soon.
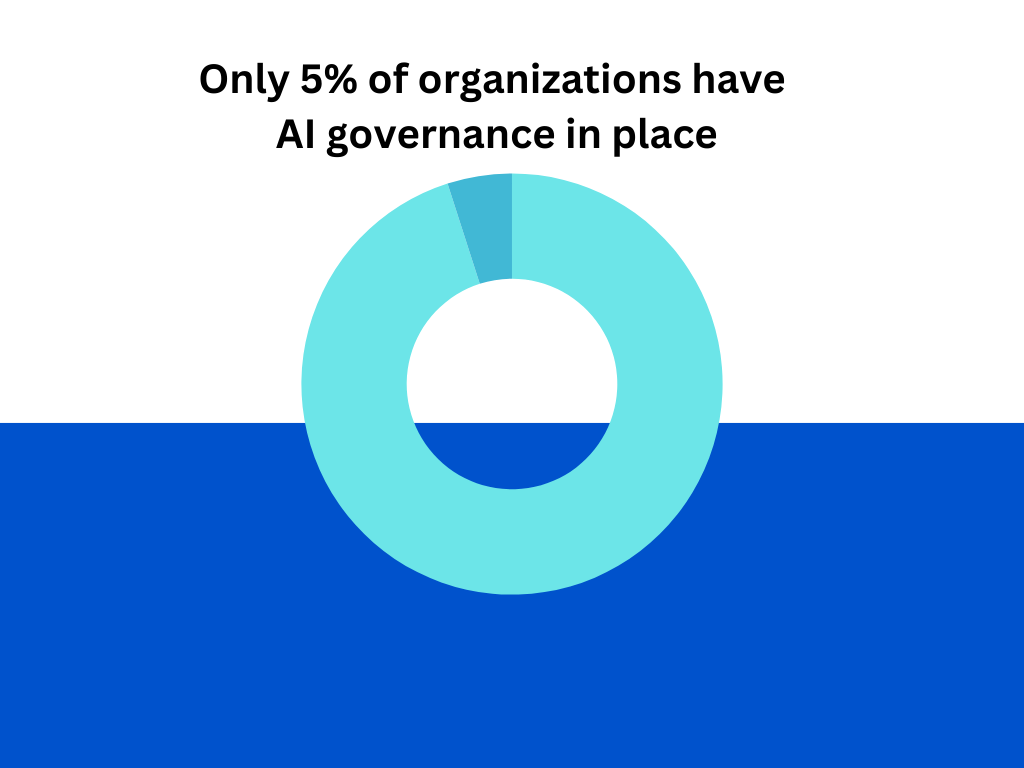
This gap between AI adoption and governance poses a serious risk.
AI systems influence hiring, lending, healthcare, security, and even legal decisions, but without proper oversight, they can lead to biased outcomes, data privacy violations, and security vulnerabilities.
That is why AI Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) frameworks are essential. These frameworks help organizations ensure AI systems are ethical, secure, and legally compliant while mitigating risks.
Here’s why AI GRC frameworks are critical:
1. Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory landscape for AI is intensifying. The European Union’s AI Act, expected to be enforced by 2026, will introduce stringent requirements for AI systems, with non-compliance potentially leading to fines of up to €35 million or 7% of global revenue.
Additionally, nearly 90% of enterprises express concerns about regulatory non-compliance in AI environments.
2. Bias and Fairness Mitigation
AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases present in their training data. For instance, a study revealed that AI tools favored white-associated names 85% of the time over Black-associated names in resume screenings.
Implementing robust GRC frameworks helps detect and mitigate such biases, ensuring fair and responsible AI.
3. Data Privacy and Security
AI’s reliance on vast datasets raises significant data privacy concerns. A 2023 Pew Research Center survey found that 81% of Americans believe the risks of AI outweigh its benefits, particularly regarding data privacy.
GRC frameworks enforce stringent data protection policies, aligning AI operations with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, thereby safeguarding sensitive user information.
4. Trust and Transparency
Public trust in AI systems is paramount. However, 52% of individuals reported feeling nervous about AI products and services, an increase from previous years.
A well-implemented AI GRC framework ensures auditability, traceability, and governance, fostering transparency and building trust in AI-driven decisions.
5. Operational Resilience
AI-related failures can lead to significant operational disruptions. In fact, 44% of organizations have experienced negative consequences from the use of generative AI, including issues like inaccuracy and cybersecurity threats.
AI GRC frameworks help businesses build resilient AI systems capable of withstanding such risks and uncertainties.
In summary, AI GRC frameworks are not just regulatory checkboxes; they are essential for responsible innovation. Now is the time for organizations to buck up and implement AI governance frameworks and stay ahead of the race.
Organizations that proactively implement these frameworks will not only stay compliant but also gain a competitive edge by building trustworthy and future-proof AI solutions.
AI Compliance Best Practices for Organizations
For mid-market companies and large enterprises, AI can be both a boon and a bane. While it drives efficiency, innovation, and automation, it also introduces significant compliance risks. The challenge is not just developing AI models but ensuring they operate ethically, transparently, and within regulatory boundaries.
With AI regulations evolving rapidly, organizations need a structured approach to compliance monitoring and automation to minimize risks and ensure long-term sustainability.
Here are key best practices to follow:
1. Continuous Compliance Monitoring is Non-Negotiable
Relying on periodic compliance checks is risky, especially as AI systems make real-time decisions that can impact users, customers, and stakeholders. Organizations must ensure:
- Regulatory updates are continuously tracked – AI governance standards such as GDPR, ISO/IEC 42001, and the EU AI Act are evolving, requiring businesses to stay ahead of compliance requirements.
- AI decision-making is transparent and auditable – Monitoring AI behavior to detect potential bias, discrimination, or unintended consequences is critical.
- Security and risk controls are proactive – AI models must be assessed for vulnerabilities, including adversarial attacks and data privacy risks.
2. AI Audits and Risk Assessments Should be Proactive, Not Reactive
Most organizations conduct AI compliance assessments only when required by auditors or regulators. Instead, compliance should be an ongoing process that includes:
- Automated risk assessments to detect potential compliance gaps before they become liabilities.
- Explainability frameworks (XAI) that ensure AI-driven decisions can be interpreted and justified.
- Bias detection and mitigation tools to safeguard fairness in AI models.
Proactively addressing compliance risks reduces exposure to regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
3. Compliance Documentation and Reporting Need to be Automated
AI compliance is not just about following regulations—it is about proving adherence. When an audit or investigation occurs, organizations need:
- Real-time compliance tracking to generate up-to-date reports.
- Tamper-proof audit logs that provide a transparent record of AI decisions and actions.
- Automated policy enforcement to prevent non-compliant AI models from being deployed.
Without automated compliance documentation, organizations may struggle to provide the necessary proof of compliance.
4. Employee Awareness and AI Governance Must be Integrated
While automated compliance tools can minimize risks, human oversight remains critical. Organizations should:
- Implement AI ethics training programs to ensure employees understand regulatory obligations.
- Use automated policy management systems to track employee acknowledgment and adherence.
- Embed compliance guardrails within AI development pipelines to prevent regulatory breaches at the source.
Action Plan: Implementing AI Compliance in Your Organization
AI compliance is not a one-time effort. It is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and automation. Organizations that embrace AI governance today will reduce regulatory risks, enhance trust, and drive responsible AI innovation.
Here’s a step-by-step checklist to help organizations establish a strong AI compliance framework:
1. Assess Your AI Compliance Readiness
☑ Identify where AI is being used across your organization.
☑ Map relevant AI regulations (e.g., EU AI Act, GDPR, ISO/IEC 42001).
☑ Conduct a risk assessment of AI models for bias, security, and transparency gaps.
2. Establish AI Governance Policies and Roles
☑ Define clear accountability—assign AI compliance ownership (Legal, IT, Compliance teams).
☑ Develop ethical AI guidelines aligned with industry standards.
☑ Implement Explainable AI (XAI) principles to ensure decision-making transparency.
3. Automate Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement
☑ Deploy real-time AI monitoring to track compliance violations.
☑ Use automated risk assessments to detect potential non-compliance early.
☑ Maintain immutable audit logs for AI decision-making and regulatory reporting.
4. Strengthen AI Security and Data Privacy Controls
☑ Apply encryption and access controls to protect AI-generated data.
☑ Conduct regular penetration testing for AI systems.
☑ Ensure privacy-by-design principles are embedded in AI models.
5. Train Employees and Build a Compliance-First Culture
☑ Educate teams on AI ethics, bias mitigation, and regulatory requirements.
☑ Implement automated compliance training with tracking and certification.
☑ Encourage cross-functional collaboration between Compliance, IT, and AI teams.
6. Regularly Audit and Update Compliance Frameworks
☑ Schedule periodic internal AI audits and gap analyses.
☑ Adapt AI compliance strategies based on new regulations and evolving risks.
☑ Continuously refine AI models to improve fairness, accuracy, and compliance.
Final Thoughts
As AI adoption accelerates, compliance cannot be treated as an afterthought. Relying on manual compliance tracking, siloed risk assessments, or periodic audits is no longer sustainable. Organizations need real-time monitoring, automated enforcement, and scalable governance frameworks to manage AI risk effectively.
SPOG.AI enables enterprises to achieve this by providing a Single Pane of Glass (SPOG) for AI governance. With its centralized compliance monitoring, automated risk assessments, and real-time enforcement capabilities, SPOG.AI ensures that organizations can maintain AI integrity, mitigate risks proactively, and align with evolving regulatory requirements.
To future-proof AI deployments, businesses must embrace solutions like SPOG.AI that offer continuous compliance, transparency, and trust in AI-driven decisions.
