Security questionnaires are structured assessments that work both ways for vendor assessments as well for enterprises that need their own posture evaluated by their clients.
They provide a standardized way to gather details about security policies, technical controls, regulatory compliance, and risk management practices.
Organizations use them to evaluate whether a third party can be trusted with sensitive data or access, while vendors rely on them to demonstrate their maturity and readiness to prospective clients. This makes security practices transparent, helping both sides identify and mitigate risks before they become issues.

The Current State of Third-Party Risk Assessments
Third-party risk assessments typically follow a predictable workflow: enterprises distribute questionnaires, vendors complete and return responses, and security teams validate the information against internal standards and compliance requirements. While this process is straightforward in theory, in practice it creates significant friction on both sides.
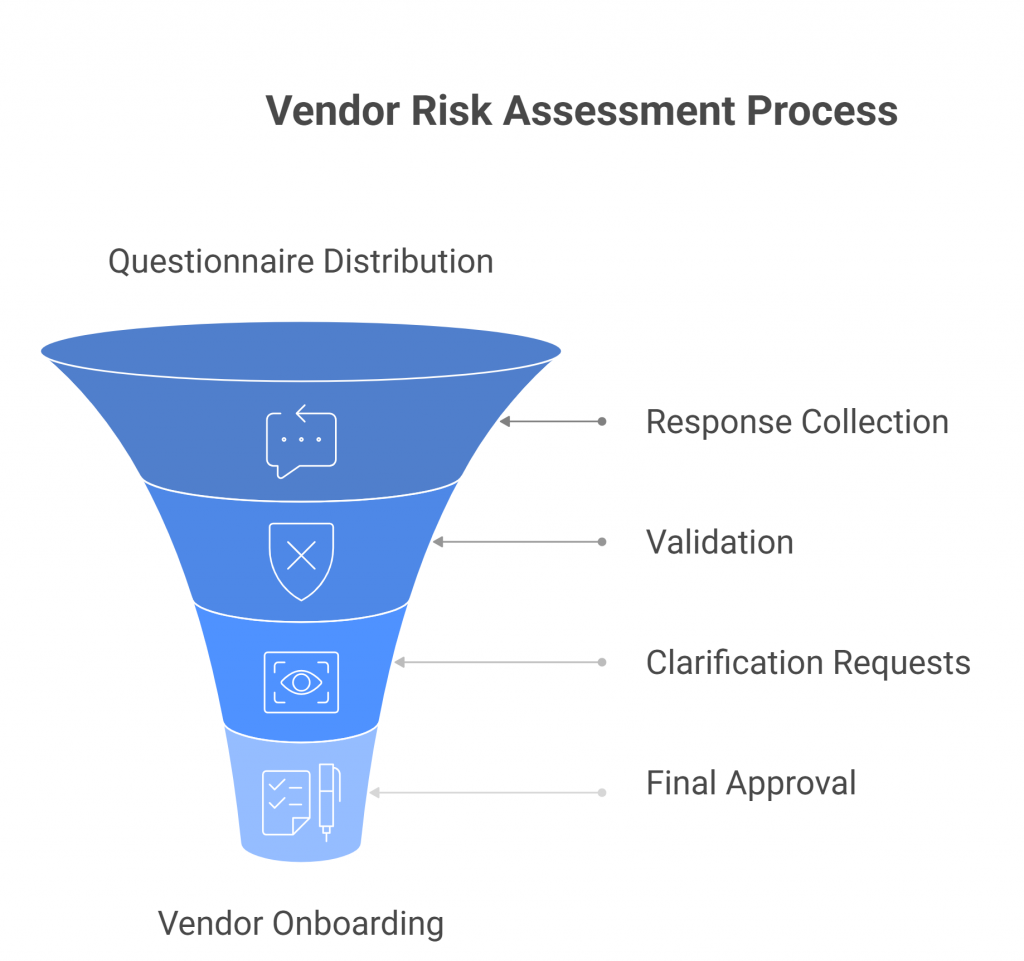
Typical Workflow
- Questionnaire Distribution – Enterprises send vendors standardized or custom questionnaires, often hundreds of questions long, covering security, compliance, and operational practices.
- Response Collection – Vendors provide answers, often copying and pasting from previous questionnaires or assembling inputs from multiple internal teams.
- Validation – Security teams review the responses, cross-check evidence, and request clarifications, leading to multiple rounds of revisions before approval.
Common Pain Points
- Time-consuming back-and-forth
The review process rarely ends with the first submission. Vendors often provide partial answers or generic responses that fail to meet an enterprise’s requirements. Security teams then need to chase additional details, evidence, or clarifications through lengthy email chains or portal requests. This back-and-forth can stretch out over weeks, delaying decision-making and straining both vendor and enterprise resources. - Inconsistent formats (Excel, PDF, portals)
There is little standardization across industries. Some enterprises use massive Excel spreadsheets, others rely on static PDFs, and many have adopted vendor risk management portals with custom formats. Vendors must adapt to each format, while enterprises waste time consolidating data into a central system. The lack of uniformity not only slows down the process but also increases the likelihood of misinterpretation. - High potential for human error
Manual entry and review processes leave plenty of room for mistakes. A miscopied response, an unchecked control, or a missed attachment can introduce blind spots in risk assessments. On the vendor side, rushed or inconsistent answers may not accurately reflect security practices, leading to misrepresentation. Over time, these errors accumulate, creating hidden risks that undermine the integrity of the entire assessment process. - Slow turnaround impacting vendor onboarding
Lengthy questionnaire cycles can stall business operations. Procurement teams often cannot finalize contracts until risk assessments are complete, meaning business units must wait to onboard critical vendors. This delay frustrates stakeholders who want to move quickly, and in fast-moving industries, it can even cause enterprises to lose competitive advantage by slowing down projects or initiatives. - Regulatory and compliance pressures (GDPR, HIPAA, ISO, SOC 2, etc.)
Regulations place increasing responsibility on enterprises to ensure their vendors meet specific security and privacy standards. GDPR requires strict data handling protocols, HIPAA enforces protections on healthcare data, and ISO 27001 and SOC 2 demand documented proof of information security practices. Non-compliance exposes enterprises to fines, reputational damage, and legal liability. Vendors, in turn, must maintain detailed records and provide evidence of compliance across multiple frameworks, which only adds to the workload.
The Outcome
The result is a process that consumes excessive time and resources, frustrates stakeholders, and still leaves organizations vulnerable to oversights. Enterprises wait too long for reliable answers, and vendors waste significant effort providing them. In today’s business environment, where speed and trust are critical, the current state of third-party risk assessments remains inefficient and unsustainable.
Why Automate Security Questionnaires?
The inefficiencies in today’s third-party risk assessments make a strong case for automation. As vendor ecosystems grow and regulatory demands intensify, enterprises and vendors alike need a smarter, faster, and more consistent approach. Automation addresses the key pain points by reducing manual work, improving accuracy, and ensuring compliance at scale.
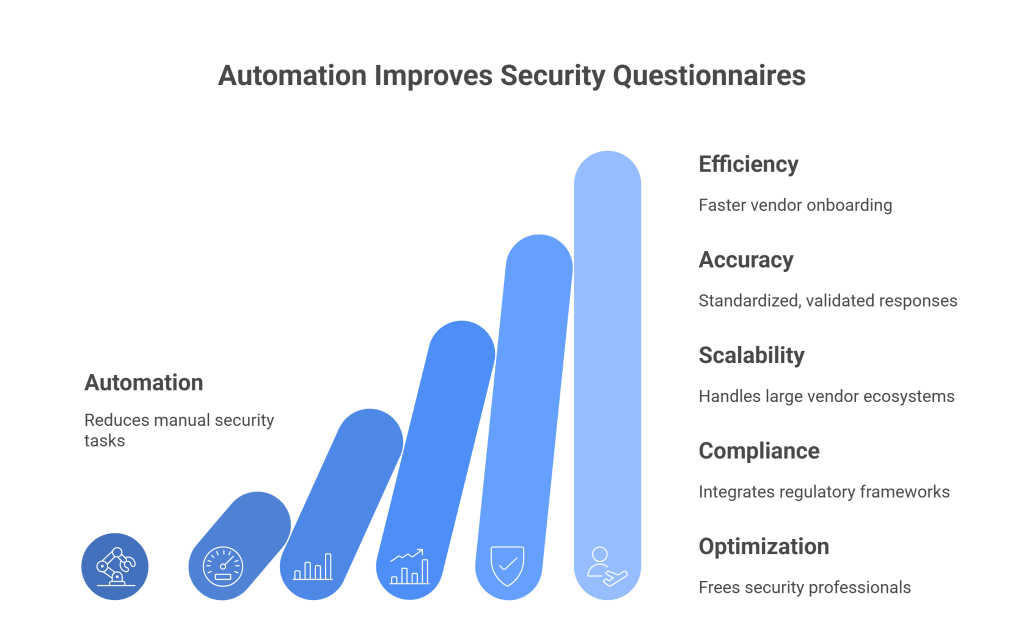
Efficiency and Speed
Automation eliminates repetitive tasks such as data entry, manual tracking, and repeated follow-ups. Enterprises can automatically distribute questionnaires, track completion, and flag missing responses without constant oversight. Vendors can auto-populate answers from a centralized response library, reducing the time required to complete assessments and speeding up the entire cycle. The result is faster vendor onboarding and quicker time-to-value for business relationships.
Accuracy and Consistency
With automated systems, responses can be standardized and validated in real time. Enterprises gain consistent, comparable data across all vendors, making it easier to spot gaps or risks. Vendors benefit by reusing approved answers from prior assessments, ensuring accuracy while maintaining consistency across multiple clients. This reduces the risk of errors, misrepresentations, and compliance gaps that often plague manual processes.
Scalability
As organizations expand, the number of vendor assessments multiplies. What may be manageable with ten vendors quickly becomes overwhelming with hundreds. Automation scales effortlessly, enabling enterprises to assess large vendor ecosystems without adding headcount. Vendors can also handle incoming questionnaires more efficiently, even when client demand spikes.
Compliance and Auditability
Automation platforms can integrate compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 directly into workflows. Enterprises can map responses to specific regulatory requirements and generate audit-ready reports instantly. Vendors can demonstrate compliance with standardized, well-documented evidence, reducing the burden of proving security posture to every client.
Resource Optimization
Perhaps the most important benefit is freeing security and compliance professionals from administrative work. Instead of chasing incomplete answers or manually scoring spreadsheets, they can focus on analyzing real risks, building stronger defenses, and strengthening vendor partnerships. Vendors can reallocate staff time from repetitive questionnaire completion to higher-value initiatives like product security improvements.
The Business Advantage
By embracing automation, enterprises accelerate decision-making, reduce onboarding delays, and strengthen compliance oversight. Vendors improve customer trust, shorten sales cycles, and reduce the cost of responding to assessments. Ultimately, automation transforms third-party risk management from a bottleneck into a business enabler.
Best Practices to Streamline Security Questionnaires with Automation
Security questionnaires remain one of the most time-consuming aspects of third-party risk management. While automation can transform how enterprises and vendors handle them, the key lies in implementing automation thoughtfully. Below are best practices that apply directly to the lifecycle of security questionnaires.
1. Standardize on Core Questionnaires
Instead of allowing every business unit or client to invent its own template, enterprises should adopt widely recognized standards such as the SIG (Standardized Information Gathering Questionnaire), CAIQ (Consensus Assessments Initiative Questionnaire), or sector-specific frameworks like HITRUST for healthcare. These frameworks cover 70–80% of what most organizations need to assess, dramatically cutting down on redundant or custom questions.
- Enterprise benefit: Easier comparison of vendors across a single standard.
- Vendor benefit: The ability to prepare once and reuse responses across multiple clients.
- Example: A vendor responding to a standardized SIG Lite questionnaire may be able to complete 60% of the questions from its pre-approved library, rather than starting from scratch with every new client.
2. Create a Centralized Response Library
Vendors should maintain a knowledge base of pre-approved answers, reviewed by internal stakeholders (security, legal, compliance). This repository should include answers to recurring questions like:
- “Do you encrypt customer data at rest and in transit?”
- “When was your last penetration test, and by whom was it conducted?”
- “What certifications (ISO, SOC 2, PCI DSS) do you maintain?”
Automation platforms can pull from this library to pre-fill answers, cutting response times from weeks to days and ensuring consistency across submissions.
- Enterprise benefit: Responses arrive more complete and standardized, reducing review cycles.
- Vendor benefit: Teams avoid “reinventing the wheel” for every client questionnaire.
- Best practice tip: Keep the response library current by reviewing it quarterly and tagging each answer with an “owner” responsible for updates.
3. Use AI to Map Questions to Existing Answers
One of the biggest challenges is that different clients often phrase the same control requirement in different ways. For example:
- Client A: “How do you monitor privileged accounts?”
- Client B: “What safeguards do you use to prevent misuse of administrator access?”
AI and natural language processing (NLP) engines can recognize these as equivalent and map both to the same pre-approved answer in the response library.
- Enterprise benefit: Reduces ambiguous answers by ensuring vendors respond consistently to similar questions.
- Vendor benefit: Saves hours of manual effort in finding and rewording answers to fit each client’s phrasing.
- Best practice tip: Train the AI model using past questionnaires to improve its ability to recognize variations.
4. Automate Evidence Attachment
Security questionnaires often require supporting documents such as SOC 2 Type II reports, ISO certifications, incident response playbooks, penetration test summaries, or data flow diagrams. Instead of manually attaching files each time, vendors can configure automation rules to pull in the most recent approved version.
- Enterprise benefit: Faster validation, since evidence arrives alongside the answer.
- Vendor benefit: Reduced chance of accidentally sending outdated or draft documents.
- Example: When answering a question about encryption, the system can automatically append the latest data security policy PDF without manual intervention.
5. Implement Workflow Automation for Follow-Ups
Security questionnaires almost always require collaboration across multiple teams—security operations, IT, legal, compliance, and sometimes HR. Instead of relying on email forwarding, vendors can configure workflows that automatically assign unanswered questions to the right subject matter expert.
On the enterprise side, automation can send reminders for incomplete questionnaires, escalate overdue items, and provide dashboards showing progress by vendor.
- Enterprise benefit: Reduced time spent chasing vendors.
- Vendor benefit: Faster internal coordination and fewer bottlenecks.
- Best practice tip: Use automated status dashboards to replace long email chains with real-time visibility.
6. Validate for Completeness and Accuracy
Before vendors submit a questionnaire, automated validation checks can flag issues such as:
- Unanswered questions
- Contradictory responses (e.g., claiming “encryption at rest” but attaching evidence that only covers “encryption in transit”)
- Expired certifications or missing dates
This reduces rework, avoids delays from clarification requests, and ensures vendors present themselves accurately.
- Enterprise benefit: Receives higher-quality responses with fewer follow-ups.
- Vendor benefit: Projects competence and professionalism, strengthening client trust.
- Best practice tip: Automate reminders to update evidence at fixed intervals (e.g., upload new SOC 2 report annually).
7. Map Responses to Compliance Frameworks
Automation tools should tag answers to relevant regulatory and compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and SOC 2. This allows enterprises to see how each response supports their compliance obligations, and enables vendors to demonstrate how a single control satisfies multiple frameworks.
- Enterprise benefit: Simplifies reporting for audits and regulatory reviews.
- Vendor benefit: Reduces duplication—one response can serve multiple compliance needs.
- Example: A vendor’s encryption policy might be mapped simultaneously to ISO 27001 Annex A, NIST 3.13.11, and SOC 2 CC6.1.
8. Track Metrics Specific to Questionnaires
Measuring success requires focusing on the unique challenges of security questionnaires, not just general GRC metrics.

- Average turnaround time for questionnaire completion
- Percentage of questions answered automatically from the response library
- Number of evidence files reused vs. manually attached
- Rate of clarification requests from enterprises
These metrics show whether automation is truly reducing questionnaire fatigue and help organizations refine their process over time.
- Enterprise benefit: Demonstrates improved vendor risk assessment efficiency to leadership and auditors.
- Vendor benefit: Quantifies ROI on automation tools and shows improved responsiveness to clients.
Are Security Questionnaires Enough?
Security questionnaires remain the backbone of third-party risk assessments, but on their own, they are no longer sufficient to provide a complete picture of vendor risk. While they deliver valuable insights into a vendor’s documented policies, certifications, and security practices, they represent only a snapshot in time. In today’s threat landscape, where risks evolve daily, relying exclusively on questionnaires leaves organizations exposed to blind spots.
Limitations of Security Questionnaires
- Point-in-time assessments – Vendors typically complete questionnaires annually or during onboarding, but security postures can change far more frequently. A compliant vendor today may face a breach or fail an audit tomorrow.
- Self-reported information – Questionnaires depend on vendors being transparent and accurate. Responses may be incomplete, overly generic, or even embellished to speed up approvals. Without independent validation, enterprises must take answers at face value.
- Lag in identifying emerging risks – Questionnaires cannot capture real-time changes such as new vulnerabilities, staffing changes, or vendor mergers that may impact security.
- Inconsistent depth – Some vendors provide detailed evidence, while others give minimal responses. This inconsistency makes it difficult for enterprises to compare vendors objectively.
The Need for Complementary Approaches
To address these gaps, enterprises increasingly combine questionnaires with additional tools and data sources:
1. Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of vendor environments through security rating services or threat intelligence feeds. A vendor that looked compliant six months ago may have since introduced critical vulnerabilities. Continuous monitoring highlights risks in real time, helping enterprises prioritize remediation before an incident occurs.
For instance, an enterprise may receive an alert that a vendor’s domain was associated with a phishing campaign.
2. Independent Attestations and Certifications
Third-party audits and certifications provide verified assurance that vendors follow industry best practices. Reports like SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, HIPAA, or FedRAMP attestations give enterprises confidence that vendor controls have been independently tested.
3. Automated Scanning and Penetration Testing
For vendors delivering technology services (e.g., SaaS providers), enterprises often require ongoing vulnerability scanning, application security testing, or independent penetration tests. Some assessments even include “shared results” portals where vendors upload findings from their most recent scans.
4. Contractual Obligations
Contracts remain a powerful complement to questionnaires. Written obligations hold vendors accountable and create legal recourse if they fail to meet agreed-upon standards. Enterprises can include specific clauses requiring vendors to:
- Report any breaches or incidents within 24–72 hours.
- Maintain certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2 throughout the contract term.
- Notify the enterprise of material changes such as mergers, acquisitions, or major system migrations.
- Permit audits or security assessments upon request.
A Balanced Approach
Security questionnaires remain critical because they formalize due diligence and establish accountability between enterprises and vendors. However, they should serve as the foundation—not the entirety—of vendor risk management. Enterprises that combine questionnaires with continuous oversight, independent validations, and strong contractual controls gain a more accurate and dynamic view of their third-party risk posture.
Enterprises can no longer treat vendor risk assessments as a one-off checkbox exercise. The sheer scale of third-party ecosystems, coupled with the speed of emerging threats, demands a more agile and intelligent approach. Security questionnaires still provide the foundation for due diligence, but their true value emerges when organizations integrate them into a broader, automated risk management strategy.
Automation shifts questionnaires from being static documents into dynamic tools that drive faster decisions, clearer accountability, and stronger trust between enterprises and vendors. When paired with continuous oversight and independent validation, they evolve from paperwork into a living framework for resilience.
Organizations that act now to modernize this process not only cut friction and delays but also position themselves as partners who take security seriously. Vendors that embrace automation gain a competitive edge by demonstrating transparency and responsiveness at scale. Together, both sides build stronger, more secure business relationships—fit for the realities of today’s threat landscape.
