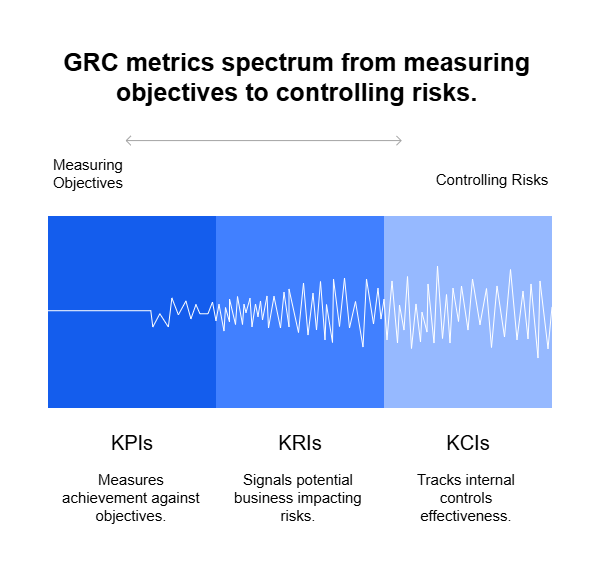
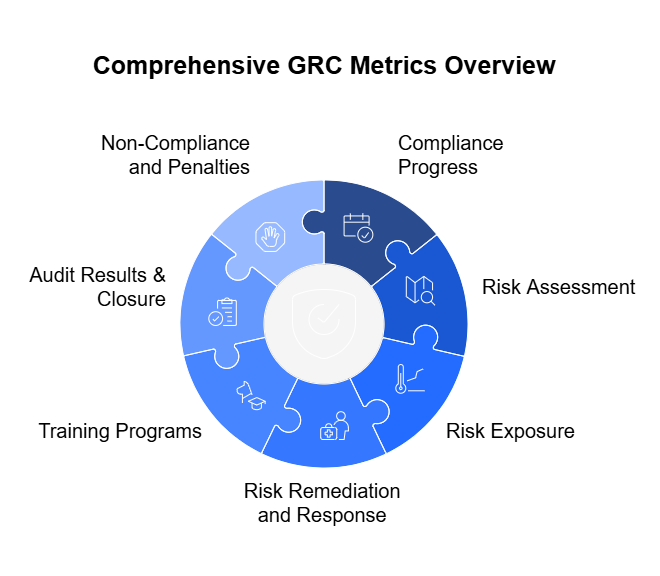
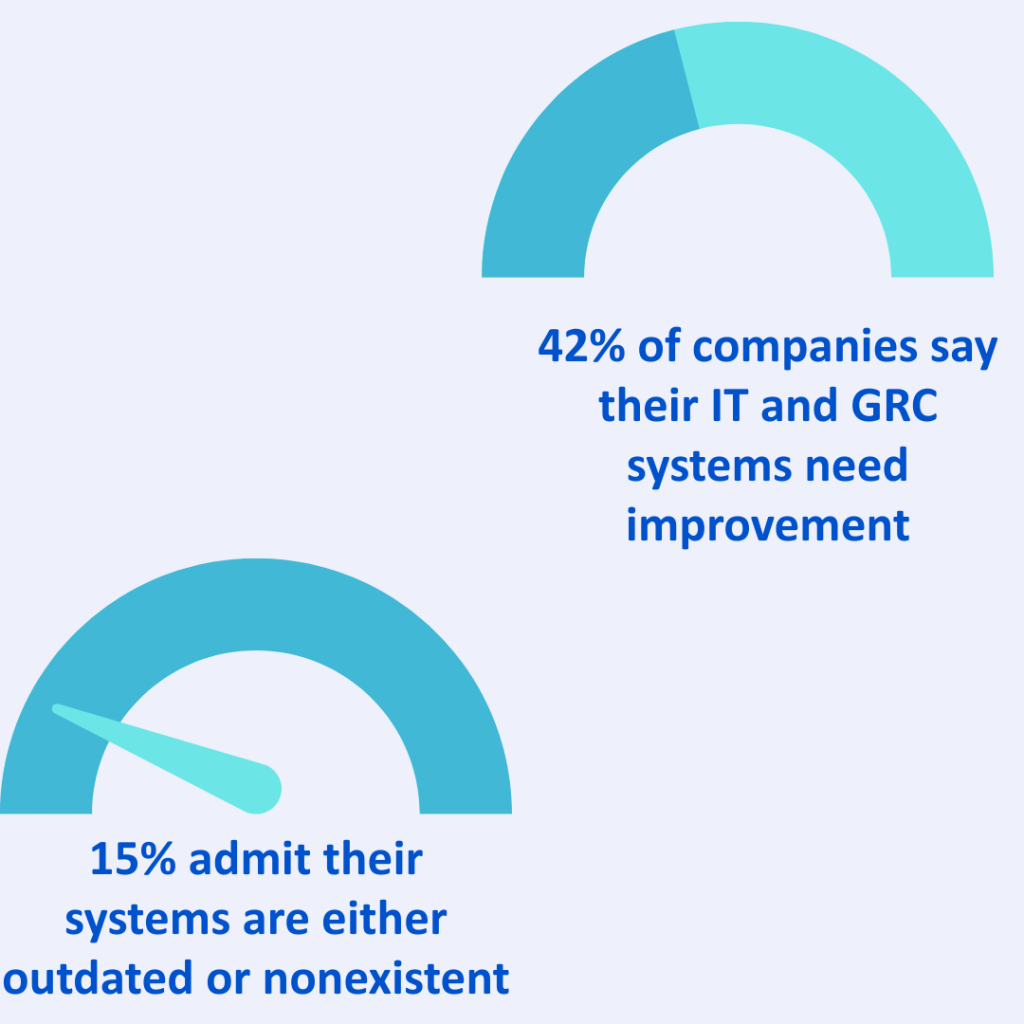
For years, spreadsheets have been the go-to tool for managing governance, risk, and compliance (GRC). They’re familiar, easy to set up, and cost nothing more than a license most businesses already own. At first glance, they seem like the simplest way to track policies, controls, risks, and compliance obligations.
According to a survey curated by Ayoub Fandi, founder of GRC Engineer Podcast and Newsletter, nearly one in four GRC practitioners rely on spreadsheets plus productivity tools like JIRA, Notion, Google Docs, Asana, etc. Several other reports also cite that companies predominantly use spreadsheets for internal audit and compliance management.

No one doubts Excel’s strength as a business tool. However, when it comes to compliance and risk management—areas that demand precision—its limitations are becoming a growing concern in particular in sectors like BFSI.
Version conflicts, hidden errors, and limited scalability turn what once seemed like a practical solution into a serious liability. Instead of helping teams stay in control, spreadsheets often create confusion, wasted effort, and even compliance gaps.
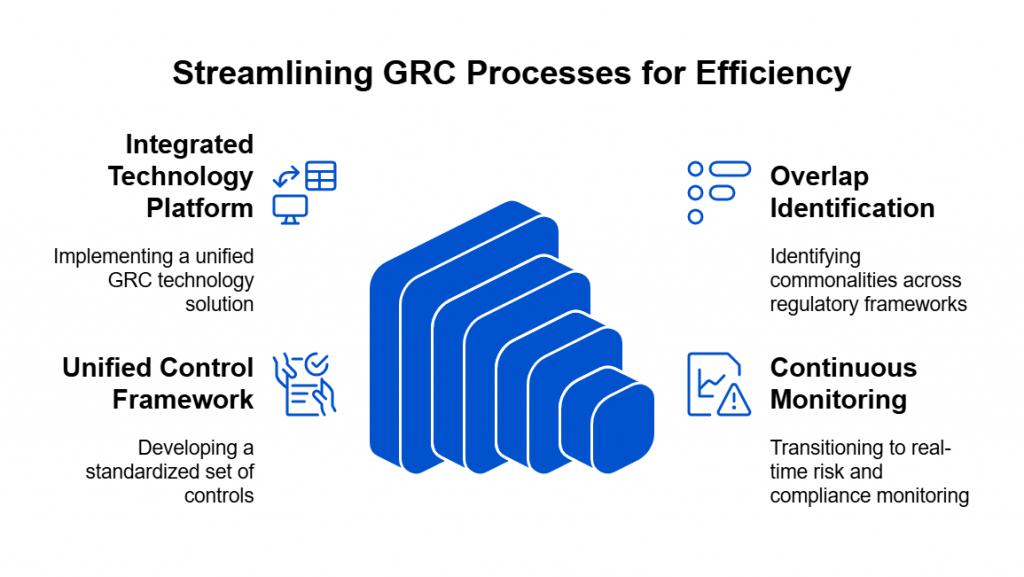
That’s where dedicated GRC tools come in. Designed specifically to handle the complexity of modern compliance, these platforms offer automation, transparency, and collaboration features that spreadsheets simply can’t match.
The Spreadsheet Trap: Convenience Today may Cost Consequences Tomorrow
Although Excel remains one of the most widely used business tools, it also carries a track record of expensive errors. High-profile cases have shown how simple mistakes such as copy-paste missteps, inaccurate data, or flawed formulas can create serious problems.
- Metro Bank, UK — Risk-Weighted Assets Misreporting
In 2021, Metro Bank was fined about £5.3 million after errors in its regulatory reporting. They used complex Excel spreadsheets to aggregate data from multiple systems, and a broken link deep in the workbook had caused hundreds of millions of pounds of high-risk exposures to be omitted. This led to materially inaccurate capital calculations and regulatory breaches.
- JPMorgan’s “London Whale” scandal –
A series of faulty formulas in a risk model spreadsheet, combined with manual copy-paste processes, caused the bank to underestimate losses in its synthetic credit portfolio. The error ultimately contributed to more than $6.5 billion in losses and fines.
- Fidelity Investment’s missing minus sign –
A simple transcription error—dropping a negative sign while transferring figures to a spreadsheet—turned a $1.3 billion loss into a gain. This inflated dividend projections by $2.6 billion, forcing the firm to cancel the distribution.
5 Reasons to Ditch Spreadsheets
1. Scalability and Complexity
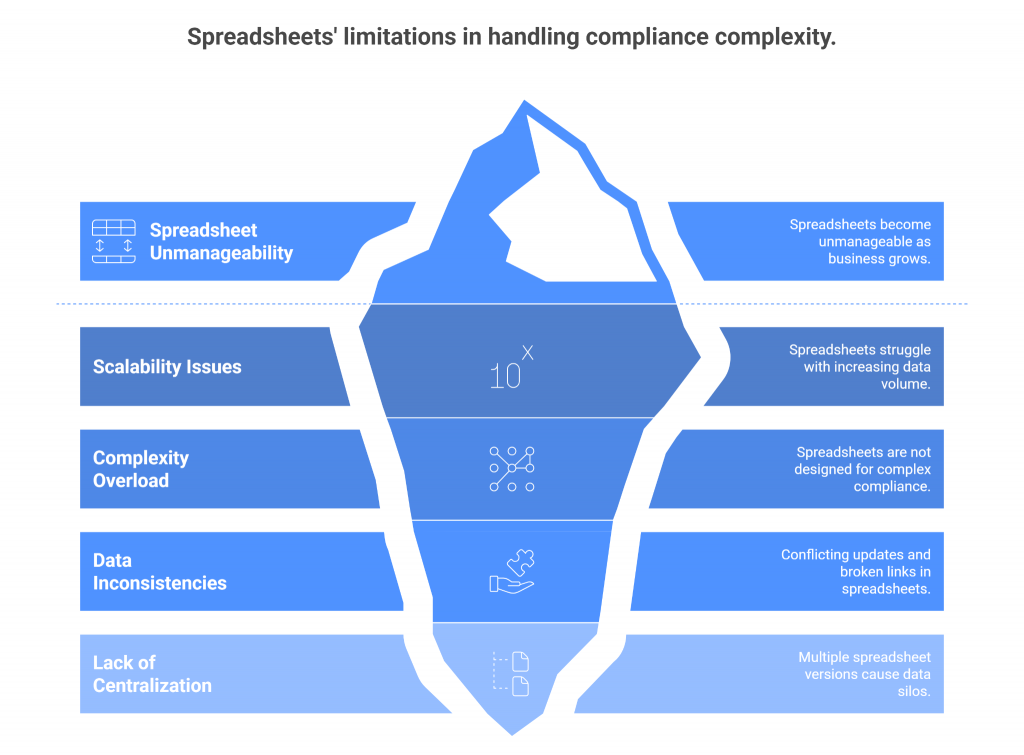
Spreadsheets may work well when an organization is small and compliance requirements are limited, but they quickly become unmanageable as the business grows. What starts as a simple tracker with a handful of tabs can balloon into dozens of versions passed between departments—each with conflicting updates, broken links, and missing information.
The problem is scale. Modern compliance programs don’t just track a few risks; they manage hundreds of controls, multiple regulatory frameworks, third-party assessments, and evolving audit requirements. Spreadsheets were never designed to handle this level of complexity. The more data you add, the more fragile and error-prone they become.
By contrast, dedicated GRC tools are purpose-built to centralize and scale compliance operations. Instead of juggling multiple files, teams work from a single source of truth that updates in real time. Complex frameworks like SOX, GDPR, or PCI DSS can be mapped directly to controls, with built-in workflows that ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
2. Accuracy and Risk Reduction
One of the biggest weaknesses of spreadsheets is their vulnerability to human error. A misplaced decimal, an overwritten formula, or a wrong cell reference can go unnoticed until it snowballs into a costly mistake. In fact, research shows that the majority of complex spreadsheets contain errors, and those errors often surface in critical areas like financial reporting, regulatory submissions, or risk assessments.
GRC tools reduce these risks by automating calculations, standardizing processes, and enforcing validation checks. Instead of relying on manual data entry and scattered formulas, they provide structured workflows, built-in controls, and real-time accuracy.
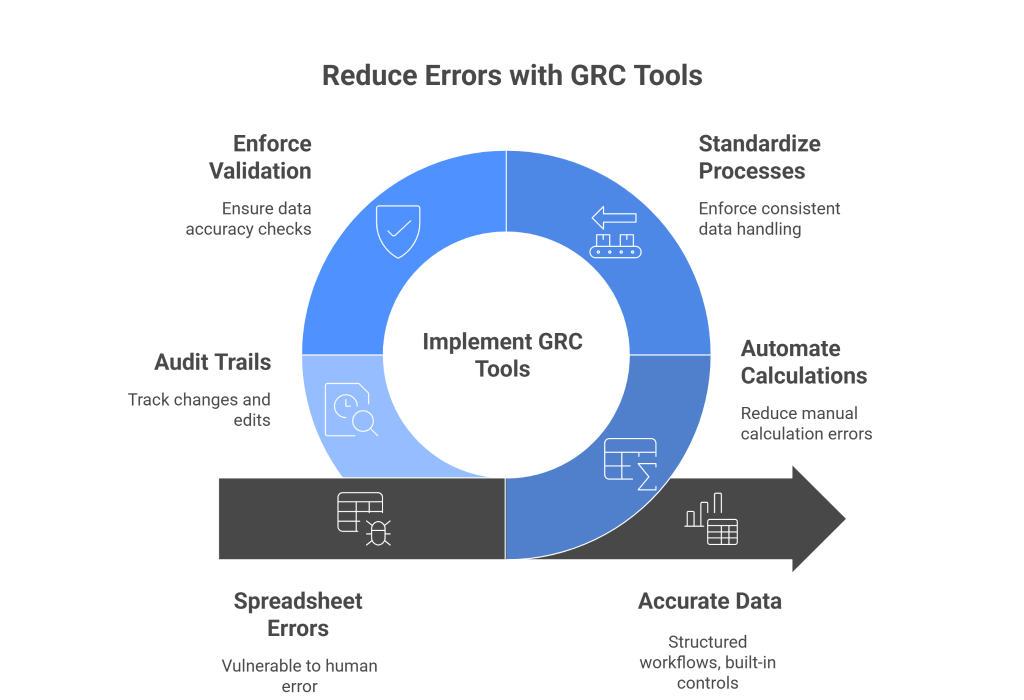
Audit trails ensure that every change is visible and traceable, eliminating the guesswork of “who edited this cell?”
3. Audit Readiness and Transparency
For organizations relying on spreadsheets, audit season often feels like a scramble. Teams spend weeks gathering files, reconciling inconsistent versions, and chasing down missing evidence. Even then, auditors frequently uncover gaps—unclear ownership, untraceable edits, or outdated data—that undermine confidence in the results.
Spreadsheets simply don’t provide the transparency regulators and auditors demand. There’s no reliable audit trail, version control is limited, and critical context is often buried in hidden tabs or undocumented formulas. This not only slows down the audit process but also exposes organizations to compliance risks and potential fines.
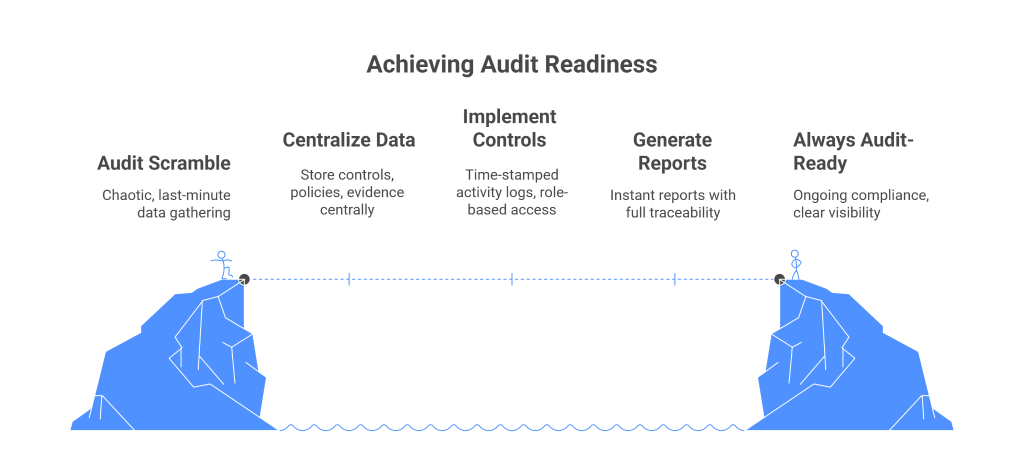
GRC tools eliminate this chaos by making audit readiness an ongoing state rather than a last-minute exercise. Every control, policy, and piece of evidence is stored in a centralized system with time-stamped activity logs and role-based access. Reports can be generated instantly, showing auditors exactly what they need with full traceability.
The result is greater confidence on both sides. Organizations save time and resources, while auditors gain clear visibility into compliance practices. Instead of fire drills at audit time, GRC platforms make “always audit-ready” a reality.
4. Collaboration and Accountability
Spreadsheets were never designed for collaborative compliance work. Once multiple stakeholders get involved—compliance officers, risk managers, legal teams, IT, and auditors—version control issues and ownership confusion quickly arise.
Who last updated the file? Which version is the source of truth? And who is responsible for reviewing and approving changes? These questions often create delays, miscommunication, and frustration.
Without clear accountability, tasks can fall through the cracks. For example, a risk assessment may be logged in a spreadsheet, but without automated reminders or ownership tags, it can sit unnoticed until an auditor asks for evidence. Similarly, approvals may be tracked by email, creating disconnected records that are nearly impossible to reconcile.

GRC tools resolve these problems by embedding collaboration into the platform itself. Tasks can be assigned with deadlines and reminders, responsibilities are clearly documented, and workflows route items to the right people at the right time. Role-based access ensures that sensitive information is only visible to those who need it, while still enabling cross-functional teams to work together seamlessly.
The result is a culture of accountability. Everyone knows their role, progress is visible in real time, and compliance processes move forward without the bottlenecks and confusion that plague spreadsheet-based systems.
5. Efficiency and Automation
Managing compliance in spreadsheets is almost always a manual effort. Data must be copied, pasted, and reformatted; evidence has to be hunted down; and updates often require painstaking reconciliation across multiple files. This repetitive, error-prone work drains valuable time and keeps compliance teams stuck in reactive mode.
GRC tools transform this process by introducing automation at every step. Routine tasks, such as control testing, evidence collection, and risk scoring, can be automated, reducing manual workload and human error. Dashboards provide real-time visibility into compliance status, so teams don’t waste hours assembling reports from scattered spreadsheets.
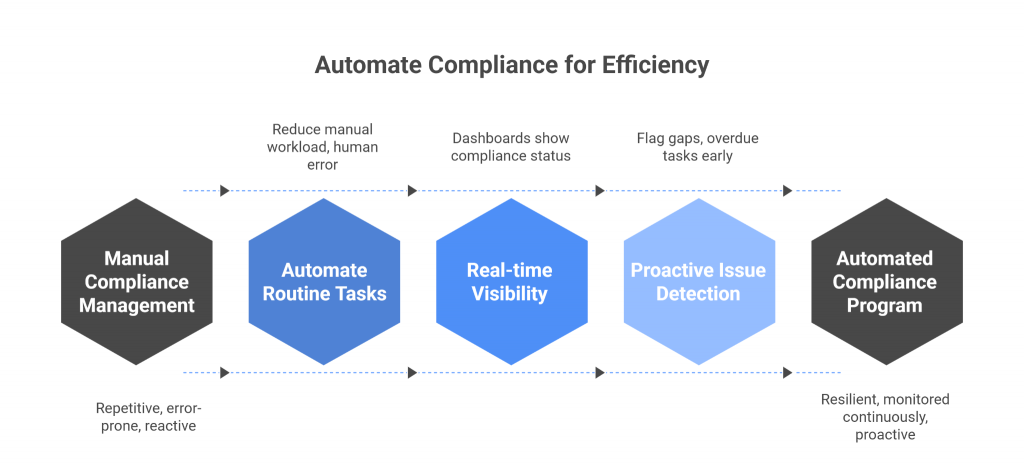
Automation also enables teams to be proactive rather than reactive. Instead of scrambling to identify issues after they’ve surfaced, GRC platforms flag gaps, overdue tasks, or unusual risk patterns as they happen. This allows compliance teams to focus their energy on high-value activities like analyzing risk trends, strengthening controls, and advising leadership.
The payoff is not just time saved, but also a more resilient compliance program. Organizations can operate with confidence knowing that compliance is monitored continuously, not just when someone has time to update a spreadsheet.
10 Common Spreadsheet Risks for GRC
While spreadsheets are flexible, their use in governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) exposes organizations to a wide range of issues that go beyond simple errors. In the context of GRC, the risks are amplified because regulatory obligations demand accuracy, transparency, and accountability. Here are ten of the most common spreadsheet risks compliance teams face:
- Version Control Failures
Multiple users saving different copies leads to conflicting data. In GRC, this can mean regulators are shown outdated or inconsistent compliance records. - Lack of Audit Trails
Spreadsheets rarely capture who changed what and when. Without a proper audit log, organizations struggle to demonstrate accountability during audits. - Formula and Logic Errors
A single broken formula can misstate risk exposure, control effectiveness, or compliance scores, leading to faulty decision-making. - Hidden Data and Formatting Issues
Rows hidden instead of deleted or formatting glitches can surface incorrect or incomplete information in regulatory reports. - Manual Data Entry
GRC often involves collecting evidence, test results, and control assessments. Manual entry increases the likelihood of typos, omissions, and inconsistencies. - Poor Access Controls
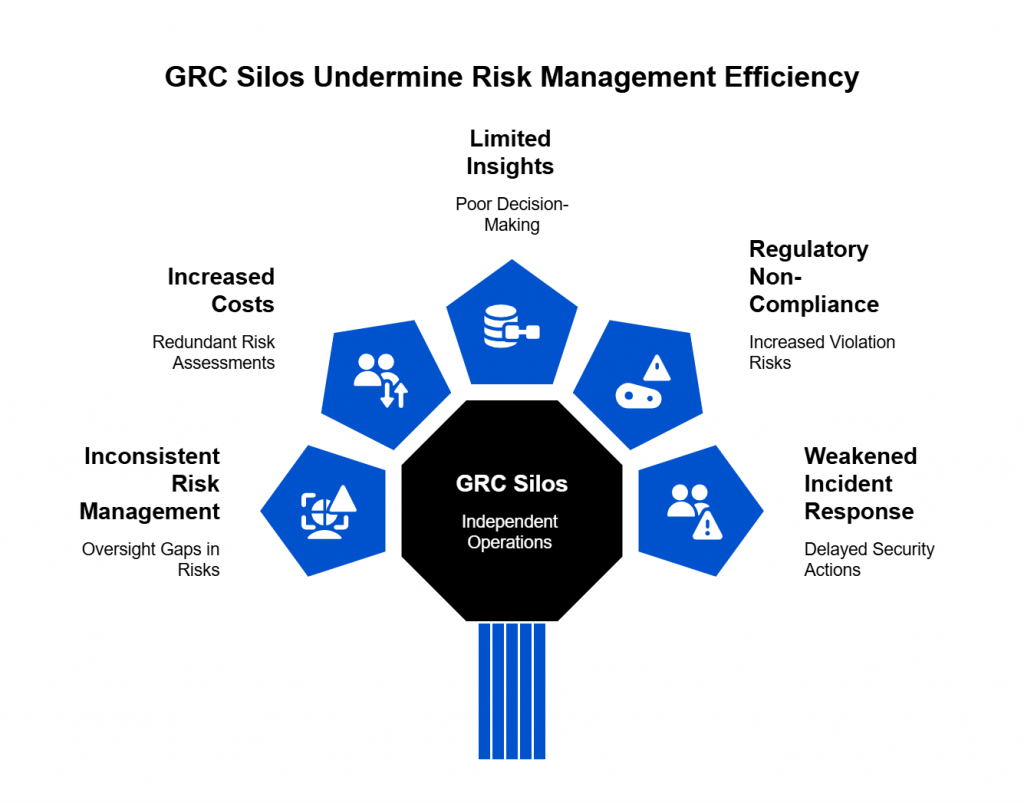
Sensitive compliance data stored in spreadsheets can be shared too widely, creating privacy breaches and failing to meet regulatory requirements for restricted access. - Data Fragmentation
Different departments maintain their own compliance spreadsheets, resulting in silos that make enterprise-wide risk visibility nearly impossible. - Limited Scalability
As obligations grow (e.g., multiple frameworks like GDPR, SOX, PCI DSS), spreadsheets collapse under the weight of hundreds of controls and thousands of rows of evidence. - Inconsistent Methodologies
Risk ratings, control evaluations, and scoring systems are often applied inconsistently across spreadsheets, undermining comparability and reliability. - Difficulty in Reporting
Regulators, boards, and auditors demand clear, timely reporting. Spreadsheets require manual consolidation, which delays reporting and increases the risk of errors in final submissions.
Conclusion
Spreadsheets will always have a place in business, but they’re no longer enough to manage the complexity and scrutiny of modern compliance. Organizations need tools that provide clarity, adaptability, and a deeper understanding of risk.
Platforms like SPOG.AI illustrate how the future of compliance is shifting. By using AI to surface risk insights and prioritize actions, such solutions move beyond simple tracking and enable teams to focus on decision-making and resilience. For companies outgrowing spreadsheets, this represents a natural next step in evolving their compliance programs.