According to a 2024 report by Verizon, 83% of data breaches involve sensitive data like payment information or personal health records. Despite the staggering numbers, many organizations still treat compliance as a one-time project rather than a continuous process. Imagine if you only changed your car’s oil once and expected it to run smoothly forever. Just like your vehicle, compliance needs regular maintenance to keep your organization safe and efficient.
Maintaining compliance with standards like PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is more than just checking a box. It’s an ongoing cycle of assessing, implementing, monitoring, and improving. Treating compliance as a continuous cycle helps protect sensitive data, sustain customer trust, and reduce risks.
In this article, we’ll explore the principles of cyclical compliance management, focusing on PCI-DSS and HIPAA. We’ll also discuss how to perform regular gap assessments and control validations while leveraging cross-framework synergies to streamline your efforts.
Principles of Cyclical Compliance Management
Compliance is not a one-time achievement but an ongoing commitment. To effectively manage compliance with frameworks like PCI-DSS and HIPAA, organizations need to adopt a cyclical approach. This method ensures that compliance efforts evolve alongside changes in regulations, technologies, and organizational practices.
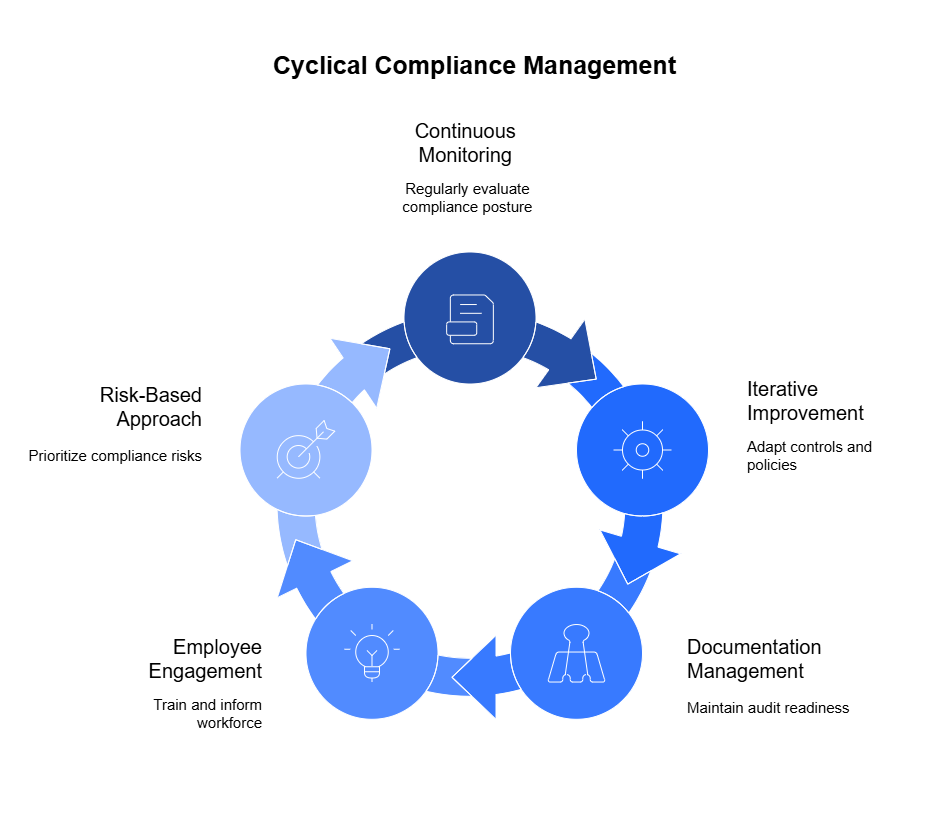
Here are the core principles that form the foundation of cyclical compliance management:
1. Continuous Monitoring and Assessment
You can’t just set up compliance controls and forget about them. You need to regularly check your organization’s compliance status through automated monitoring. Automated tools can track system configurations, network activity, and data access in real time. They alert you when something goes wrong, like unauthorized access or a security breach.
The goal of continuous monitoring is to detect compliance failures early, before they escalate into significant security incidents or regulatory breaches. By keeping a pulse on your compliance status, you can implement timely corrective actions and maintain a robust security posture. Regular monitoring helps you catch problems before they turn into costly breaches or violations.
2. Iterative Improvement
Compliance isn’t static. As regulations change or new threats emerge, your policies and controls need to adapt. You can’t just set it and forget it. Instead, take an iterative approach.
Start by reviewing the results from your monitoring. Identify where your controls are weak or outdated. For example, if PCI-DSS updates its encryption standards, make sure your data encryption methods meet the new requirements. Involve your IT, legal, and risk management teams to evaluate the changes. Then, make improvements in a prioritized way, focusing on the biggest risks first. Document what you changed and why, so you have a clear record for future audits.
3. Documentation and Evidence Management
Accurate documentation is essential for proving compliance. You need to keep detailed records of your policies, procedures, and any changes you make. Also, gather evidence like system logs, training records, and reports from automated monitoring tools.
Use a centralized, automated repository to gather and organize evidence. Automation ensures that documents, logs, and reports are collected and updated consistently without manual intervention. This method makes it easy to retrieve data during an audit or when reviewing compliance status. Clearly label each record with version numbers and update dates to maintain accuracy and clarity. Regularly update your documentation as your processes change. Keeping accurate and current records helps you demonstrate your compliance at any time.
4. Employee Engagement and Training
Your employees play a big role in maintaining compliance. They’re often the first line of defense when handling sensitive data. Make sure they know their responsibilities through regular training. Teach them how to handle personal information securely, whether it’s payment data (PCI-DSS) or health records (HIPAA).
Don’t just train them once. Keep compliance awareness fresh with ongoing sessions, quizzes, and real-life scenarios. Tailor the training to fit different roles, since not everyone handles data the same way. Create a culture where employees understand that compliance isn’t just a rule—they’re a key part of keeping data safe.
5. Risk-Based Approach
Not every compliance issue carries the same risk. You need to focus your efforts on the areas that pose the biggest threat. Start by identifying your most critical data—like payment information for PCI-DSS or health records for HIPAA. Determine what would happen if this data got compromised.
Once you know your biggest risks, put stronger controls in place to protect them. For example, use multi-factor authentication for accessing sensitive data and encrypt it both in transit and at rest. Reassess these risks regularly, especially if your organization adopts new technologies or services. Prioritizing your efforts helps you protect what matters most without spreading resources too thin.
Specific Considerations for PCI-DSS and HIPAA
When managing compliance, it’s essential to understand the unique requirements of different frameworks. PCI-DSS and HIPAA are two of the most critical standards, especially for organizations handling payment information and protected health information (PHI). Let’s break down the specific considerations for each:
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI-DSS is crucial for businesses that handle card payments. Its primary goal is to protect cardholder data from breaches and fraud. Here are some key considerations:
1. Data Encryption:
You must encrypt cardholder data both in transit and at rest. Use strong encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) to protect data when it’s being transmitted. For data at rest, consider using AES-256 encryption. Always store encryption keys securely and limit access to authorized personnel only.
2. Secure Network Architecture:
Build and maintain a secure network by implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS). Segment networks to isolate cardholder data environments (CDE) from other networks. Regularly test your network to identify vulnerabilities and apply patches as soon as they become available.
3. Access Control Measures:
Restrict access to cardholder data on a need-to-know basis. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for users accessing the CDE. Monitor and log all access attempts to detect unauthorized activities.
4. Regular Testing and Monitoring:
Continuously monitor your systems for vulnerabilities and perform regular penetration testing. Log and track all access to network resources and cardholder data. Implement automated monitoring tools to detect unusual behavior in real time.
5. Incident Response Plan:
Have a clear plan for responding to data breaches involving cardholder information. This should include immediate containment, forensic investigation, and customer notification. Test your plan regularly to ensure effectiveness.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA focuses on the security and privacy of protected health information (PHI). Organizations that handle PHI, such as healthcare providers and their business associates, must comply with strict regulations. Here’s what you need to consider:
1. PHI Handling:
Identify and classify PHI within your systems. Ensure that all PHI is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Use strong access controls to limit who can view or handle sensitive health data.
2. Data Integrity and Availability:
Implement measures to protect data from unauthorized alteration or destruction. Use backup solutions to maintain data availability, even in the case of a security incident. Regularly verify the integrity of stored data and ensure it hasn’t been tampered with.
3. Access Controls:
Grant access to PHI only to those who need it to perform their job duties. Use role-based access controls (RBAC) to manage permissions. Require strong authentication, including MFA, to access PHI.
4. Audit Controls:
Implement automated logging to track access to PHI. Regularly review these logs to detect any suspicious activity. Store logs securely and ensure they are tamper-proof.
5. Employee Training on Privacy Rules:
Educate employees on how to handle PHI securely. Include training on identifying phishing attempts and securing devices that access PHI. Regularly update training materials to cover emerging threats and regulatory updates.
6. Breach Notification:
Have a defined process for notifying affected parties in case of a data breach. This includes notifying individuals whose PHI was compromised, as well as relevant regulatory bodies. Document every step taken to respond to the breach.
Commonalities Between PCI-DSS and HIPAA
While PCI-DSS and HIPAA focus on different types of data, they share some common principles:
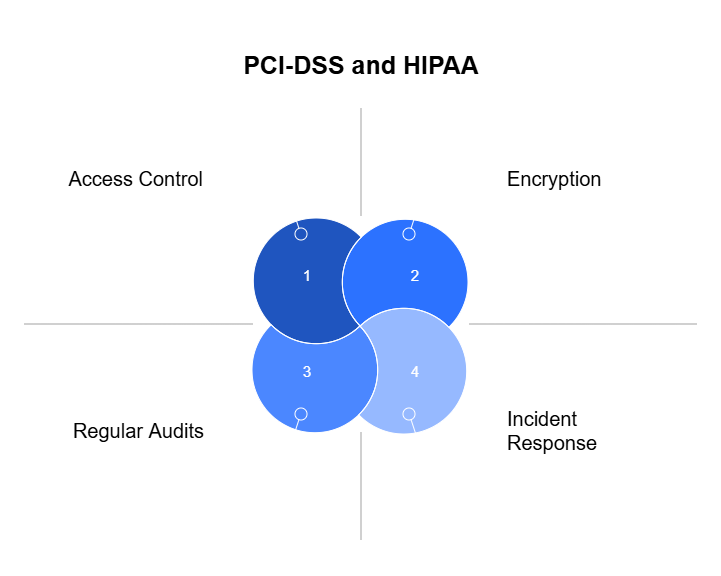
- Encryption: Both require encryption of sensitive data to protect against unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Limit data access based on the principle of least privilege.
- Incident Response: Both frameworks mandate having a clear plan for addressing data breaches.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic reviews to ensure compliance with the latest standards and to identify potential gaps.
By understanding the unique and shared requirements of PCI-DSS and HIPAA, you can build a more resilient compliance strategy. Integrating these standards helps reduce redundancy and enhances your overall data security posture.
Regular Gap Assessments and Control Validations
Maintaining compliance is an ongoing process that requires regular assessments and validations. Even if your organization has achieved compliance, risks can evolve due to changing regulations, new technologies, or emerging threats. Regular gap assessments and control validations help you identify areas where your compliance measures might fall short and ensure your controls remain effective.
1. Conducting Gap Assessments
A gap assessment helps you compare your current compliance status against the requirements of standards like PCI-DSS and HIPAA. The goal is to identify where your practices don’t meet regulatory expectations. Here’s how to conduct an effective gap assessment:
- Step 1: Define the Scope:
Start by identifying which standards you need to assess, such as PCI-DSS for payment data or HIPAA for healthcare information. Clearly outline the systems, processes, and data types involved. - Step 2: Gather Documentation:
Collect policies, procedures, system configurations, and audit logs. Ensure your data collection is automated where possible, using centralized compliance management tools to streamline the process. - Step 3: Identify Compliance Gaps:
Compare your current practices against the latest version of the standard. For PCI-DSS, check encryption protocols and access controls. For HIPAA, examine data handling and breach notification processes. Highlight areas where your current setup deviates from the requirements. - Step 4: Prioritize Findings:
Rank the gaps based on the risk they pose. Address critical issues like unencrypted PHI or outdated firewall configurations first. This risk-based approach helps you allocate resources effectively. - Step 5: Develop a Remediation Plan:
Outline the steps needed to close the gaps. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and document the remediation efforts. Continuously monitor the progress and update stakeholders on improvements.
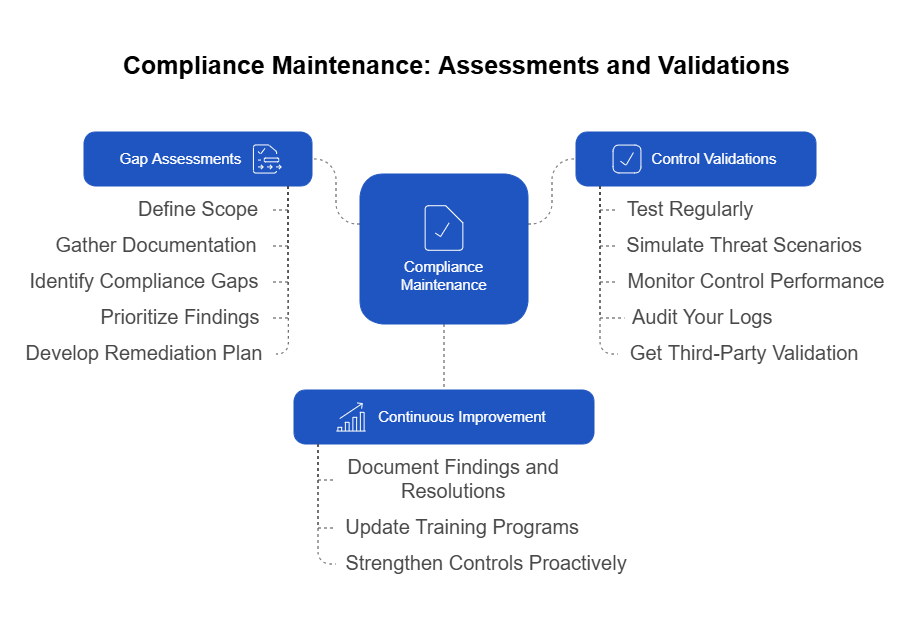
2. Validating Controls
After identifying gaps, it’s crucial to validate the effectiveness of your compliance controls. Controls are the specific practices, systems, and policies you put in place to meet compliance requirements. Here’s how to validate them effectively:
- Test Regularly:
Regular testing ensures that your controls work as intended. Use automated tools to test network security, data encryption, and access controls. Manual checks can supplement automated tests for areas requiring human oversight, like policy adherence. - Simulate Threat Scenarios:
Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses in your systems. Simulating real-world attack scenarios helps you understand how your controls respond under pressure. - Monitor Control Performance:
Set key performance indicators (KPIs) to track how well your controls are working. For example, measure the number of unauthorized access attempts detected or the speed at which data breaches are contained. - Audit Your Logs:
Review logs generated by automated monitoring tools. Look for any deviations from expected behavior. Ensure your logging practices align with compliance standards, such as keeping logs secure and unaltered. - Get Third-Party Validation:
Engage external auditors or consultants to validate your controls. An objective, third-party perspective can uncover issues that internal assessments might miss.
3. Continuous Improvement Through Feedback
Gap assessments and control validations shouldn’t just be a periodic exercise. Use the insights from these processes to refine your compliance strategy continuously. Develop a feedback loop that captures the lessons learned from each assessment and validation.
- Document Findings and Resolutions:
Maintain a record of identified gaps, the steps taken to resolve them, and the final outcomes. This documentation not only helps during audits but also informs future compliance initiatives. - Update Training Programs:
If assessments reveal gaps related to human error or misunderstanding, update your training materials. Make sure employees are aware of the changes and understand their role in maintaining compliance. - Strengthen Controls Proactively:
Use the data gathered from validations to anticipate potential vulnerabilities. If a control fails under a specific scenario, develop alternative strategies or strengthen the existing control to handle similar situations in the future.
Why Regular Gap Assessments and Control Validations Matter
Regular gap assessments and control validations are vital in maintaining compliance and safeguarding your organization against data breaches. Neglecting these practices can lead to significant vulnerabilities. For instance, organizations with a high level of noncompliance with regulations experienced an average data breach cost of $5.05 million, which is 12.6% higher than the average breach cost. This underscores the financial risk of inadequate compliance measures.
By conducting regular assessments and validations, you proactively identify and address weaknesses, reducing the likelihood of costly incidents. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also strengthens your organization’s overall security posture.
Strategies for Cross-Framework Synergy
Organizations often face the challenge of complying with multiple standards simultaneously, such as PCI-DSS and HIPAA. Managing each framework independently can lead to redundant efforts, increased costs, and potential inconsistencies. Instead, adopting a unified compliance strategy helps streamline processes and reduces duplication. Here’s how to achieve cross-framework synergy:
1. Map Common Controls Across Frameworks
Many compliance frameworks share similar requirements, particularly in areas like data encryption, access control, and incident response. Start by mapping these overlapping controls. For instance:
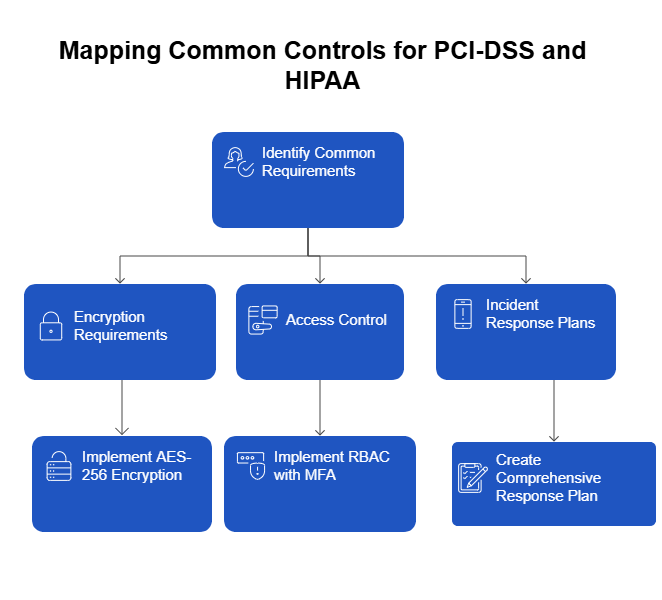
- Encryption Requirements: Both PCI-DSS and HIPAA require data encryption in transit and at rest. Implementing a robust encryption protocol, like AES-256, can satisfy both standards simultaneously.
- Access Control: Role-based access control (RBAC) with multi-factor authentication (MFA) meets the stringent access requirements for both PCI-DSS and HIPAA.
- Incident Response Plans: Both frameworks mandate having a documented plan for responding to data breaches. Creating a single, comprehensive incident response plan can address both standards.
By identifying these commonalities, you can develop a unified control set that covers multiple frameworks, saving time and resources.
2. Implement a Unified Compliance Management Platform
Using a centralized platform to manage multiple compliance frameworks makes it easier to track and update controls. Choose continuous compliance automation tools that support multi-framework integration, allowing you to monitor compliance metrics, track policy changes, and manage documentation from a single dashboard.
- Automation: Automate data collection, reporting, and evidence gathering. This reduces manual work and ensures consistency in how data is handled across different frameworks.
- Integrated Monitoring: Set up unified monitoring to detect compliance violations related to both PCI-DSS and HIPAA. For example, an integrated SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tool can track unauthorized access to both payment data and health records.
- Centralized Reporting: Generate cross-framework compliance reports automatically. This helps streamline internal audits and external certification processes.
3. Develop Cross-Functional Compliance Teams
Compliance should not be siloed within a single department. Form cross-functional teams that include IT, legal, risk management, and data governance experts. This collaborative approach ensures that compliance strategies consider diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Shared Responsibility: Assign specific roles and responsibilities for maintaining compliance across frameworks. For example, the IT team might handle technical controls, while the legal team manages policy updates.
- Regular Meetings: Schedule meetings to discuss compliance changes, share insights from recent audits, and address any cross-framework conflicts.
- Unified Training Programs: Train employees on shared compliance principles, such as data protection and secure access practices, rather than providing separate training for each framework.
4. Adopt a Risk-Based Prioritization
Instead of addressing each framework individually, prioritize compliance efforts based on risk. Focus on areas where non-compliance would have the most significant impact, such as data breaches involving both payment data and PHI.
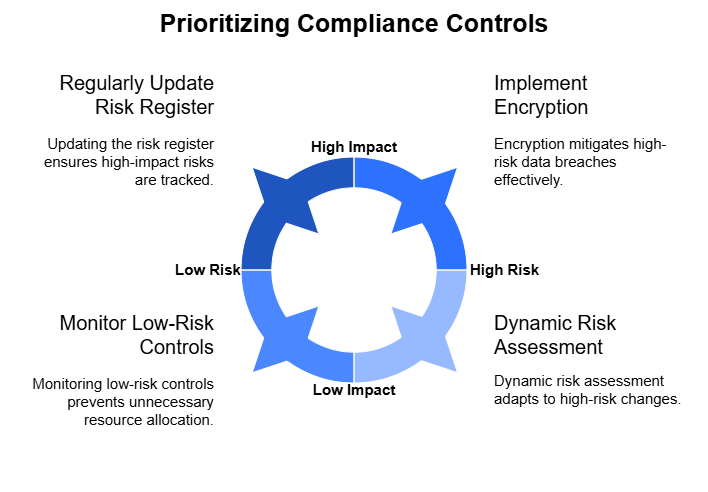
- Critical Control Implementation: Start with controls that mitigate the highest risks across both standards, like encryption and access management.
- Dynamic Risk Assessment: Continuously evaluate risks, especially when new technologies or processes are introduced. A change in one compliance area might impact others, so reassess as needed.
- Unified Risk Register: Maintain a single risk register that captures potential compliance issues related to multiple frameworks. Update it regularly as new risks emerge or regulations change.
Many organizations struggle with maintaining separate documentation and workflows for each standard. Use bridging tools and templates that align multiple frameworks into a single compliance matrix.
- Unified Policy Templates: Develop policies that address both PCI-DSS and HIPAA requirements simultaneously, such as those for data encryption and breach response.
- Control Mapping Tools: Utilize software that visually maps controls from one standard to another, highlighting overlaps and gaps.
- Compliance Calendars: Maintain a master calendar that tracks key compliance activities, like audits and training sessions, across all relevant frameworks.
Benefits of Cross-Framework Synergy
By integrating compliance efforts, you reduce redundancy and save resources. You also minimize the risk of conflicting policies or duplicate audits, which can confuse employees and auditors alike. A streamlined approach to managing multiple frameworks ensures consistency, simplifies reporting, and fosters a more holistic understanding of compliance throughout the organization.
Adopting cross-framework synergy not only makes compliance management more efficient but also helps maintain a stronger security posture by addressing shared vulnerabilities. This proactive approach supports long-term regulatory adherence and reduces the likelihood of compliance failures.
Conclusion
Compliance is not a destination; it’s a continuous journey. Treating compliance as a one-time project can leave your organization vulnerable to evolving risks and regulatory changes. Instead, adopting a cyclical approach ensures that your compliance efforts stay aligned with current standards, protect sensitive data, and support long-term security goals.
By implementing continuous monitoring, iterative improvements, and robust documentation practices, you build a proactive compliance strategy that evolves with your organization. Addressing the unique requirements of PCI-DSS and HIPAA while leveraging cross-framework synergies helps reduce redundancy and streamline your compliance management.
Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous compliance empowers employees to take ownership of data protection practices, making compliance an integral part of daily operations rather than a separate task. Regular gap assessments and control validations keep your program resilient, while real-time monitoring and automated systems enhance your ability to detect and respond to threats.
In the end, the key to successful compliance lies in consistency, collaboration, and a willingness to adapt. By embedding compliance into your organization’s culture and practices, you reduce risks, build customer trust, and stay ahead.