Cyber threats are escalating at an unprecedented rate. Studies indicate that organizations were facing an average of 1,876 cyberattacks per week in Q3 2024. That’s a whopping 75% increase from last year.
Thus, businesses can no longer afford a reactive approach to security. The latest update to ISO 27001, the global standard for information security management, is designed to address modern cyber risks with a more streamlined and proactive compliance framework.

The transition deadline is October 31, 2025, but companies that start preparing now will be in a stronger position to defend against emerging threats, align with other compliance frameworks, and avoid last-minute compliance chaos.
Let’s break down the key changes, what they mean for your compliance strategy, and the pitfalls to avoid.
A Deep Dive into the new changes in ISO 27001:2002
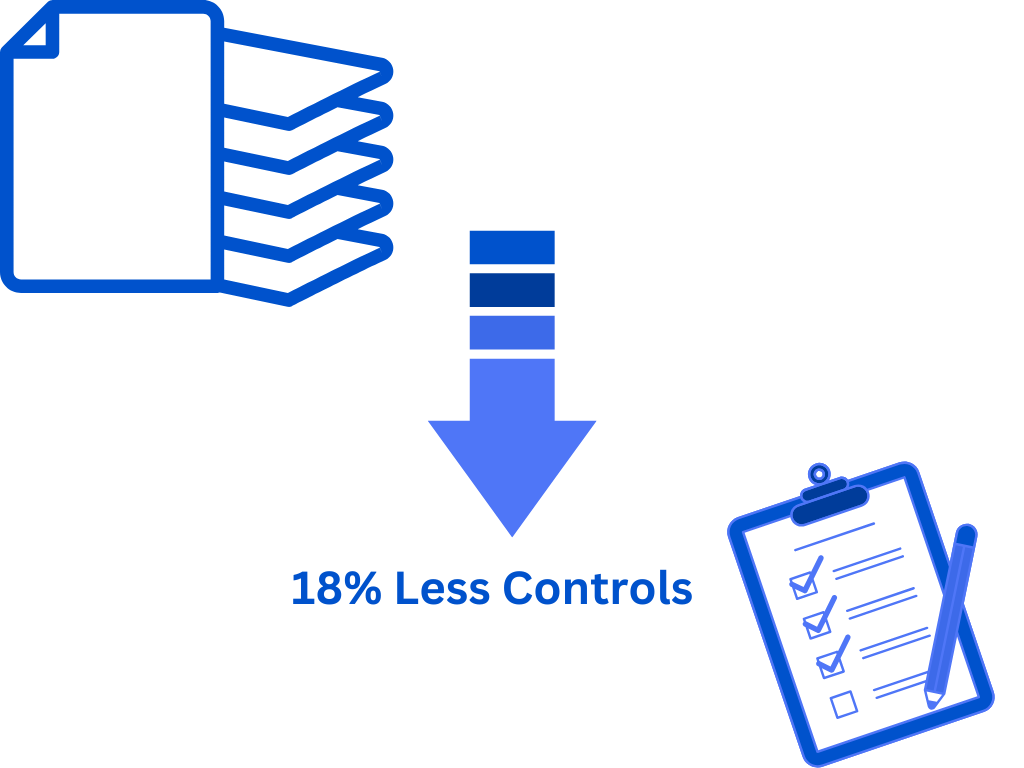
New Control Structure: From 114 to 93 Controls
One of the most significant changes in ISO 27001:2022 is the restructuring of Annex A security controls. The number of controls has been reduced from 114 to 93, consolidating overlapping controls and improving clarity.
These controls are now categorized into four logical groups:
- Organizational Controls – These focus on governance, risk management, and policy implementation. Organizations must ensure that security is embedded at a strategic level, with leadership playing a central role in risk management.
- People Controls – Human error remains one of the biggest security risks. These controls emphasize the importance of security awareness, employee training, and clearly defined security responsibilities.
- Physical Controls – These address physical security measures such as facility access control, environmental protections, and security of on-premise data centers.
- Technological Controls – These focus on cybersecurity best practices, including data encryption, endpoint security, and network monitoring.
Why does this matter?
- Easier implementation – The revised structure makes it easier for organizations to map controls to their business processes.
- Better risk alignment – With clearer categorization, businesses can focus on the controls that matter most to their specific risk environment.
- Less redundancy – Consolidating controls eliminates overlap, reducing the effort needed for compliance management.
11 New Controls for Today’s Security Challenges
The evolving cyber threat landscape has introduced new challenges that weren’t adequately covered in the previous version of ISO 27001. The 2022 update adds 11 new security controls designed to enhance threat detection, improve data protection, and secure cloud environments.
Let’s break down the key additions:
- Threat Intelligence – Helps organizations proactively detect and respond to security threats by gathering intelligence from external and internal sources. This aligns with the broader industry shift toward proactive cybersecurity rather than reactive compliance.
- Data Masking – Strengthens data protection by obfuscating sensitive information, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. This is crucial for GDPR compliance and helps reduce exposure in case of data breaches.
- Cloud Security – Addresses the growing reliance on cloud services and ensures that organizations implement security best practices for cloud-based environments. This control is particularly relevant as 83% of enterprise workloads are now in the cloud.
- Web Filtering – Blocks access to malicious or unauthorized websites, reducing the risk of phishing attacks and malware infections. Given that 91% of cyberattacks start with phishing, this control is essential for modern security strategies.
- Security Monitoring – Implements real-time monitoring of security events to detect and mitigate threats before they escalate. This supports continuous compliance and aligns with SOC 2 and NIST CSF requirements.
- Secure Coding Practices – Encourages organizations to integrate security into the software development lifecycle (SDLC), reducing vulnerabilities in applications before deployment.
- Data Leakage Prevention (DLP) – Helps prevent accidental or malicious data exfiltration by monitoring and controlling sensitive data transfers.
- Information Security for Cloud Services – Expands beyond general cloud security to focus on vendor security assessments and shared responsibility models for cloud security management.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM) – Reinforces strong authentication and authorization measures to prevent unauthorized access.
- Configuration Management – Ensures IT systems are securely configured and maintained to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring Activities – Enhances log management and analysis to improve visibility into potential security incidents.
Why do these new controls matter?
- They reflect real-world risks – Cyberattacks are more sophisticated than ever, and these new controls tackle modern security challenges like cloud security, data protection, and real-time monitoring.
- They align with global compliance standards – Many of these additions strengthen ISO 27001’s alignment with SOC 2, GDPR, and NIST CSF, reducing the burden of managing multiple frameworks.
- They support continuous security – The emphasis on real-time monitoring and proactive defense ensures organizations can stay ahead of threats, rather than just checking compliance boxes.
ISO 27001:2022: The Compliance Bridge You Didn’t Know You Needed
We understand that compliance can feel like a never-ending obstacle course. You jump through hoops for ISO 27001, then SOC 2, then GDPR, and before you know it, you’re drowning in security frameworks, each demanding its own set of controls, audits, and documentation.
But here’s the thing. ISO 27001:2022 isn’t just another certification to check off. If you use it the right way, it can actually simplify compliance across multiple frameworks.
Think of it like a universal adapter for security standards. Instead of managing separate security programs for every regulation, you can use ISO 27001 as your single source of truth – one framework that aligns with SOC 2, NIST, GDPR, and more.
How does that work? Let’s break it down.
ISO 27001 Helps You Stop Doing the Same Work Twice
Most security frameworks overlap. They all require risk assessments, access controls, incident response plans, and vendor security reviews. The only difference is how they phrase it and who’s asking.
- SOC 2 says, “Show me you protect customer data.”
- GDPR says, “Show me you protect personal data.”
- NIST says, “Show me your entire security program.”
At their core, they’re asking for the same thing. The problem is, companies often treat them as separate projects, leading to duplicate efforts, wasted resources, and compliance fatigue.
ISO 27001:2022 helps cut through the noise by aligning with these frameworks. Instead of creating three different risk management policies, you document one that meets all their requirements. Instead of running separate security audits for each standard, you map them to a single control set.
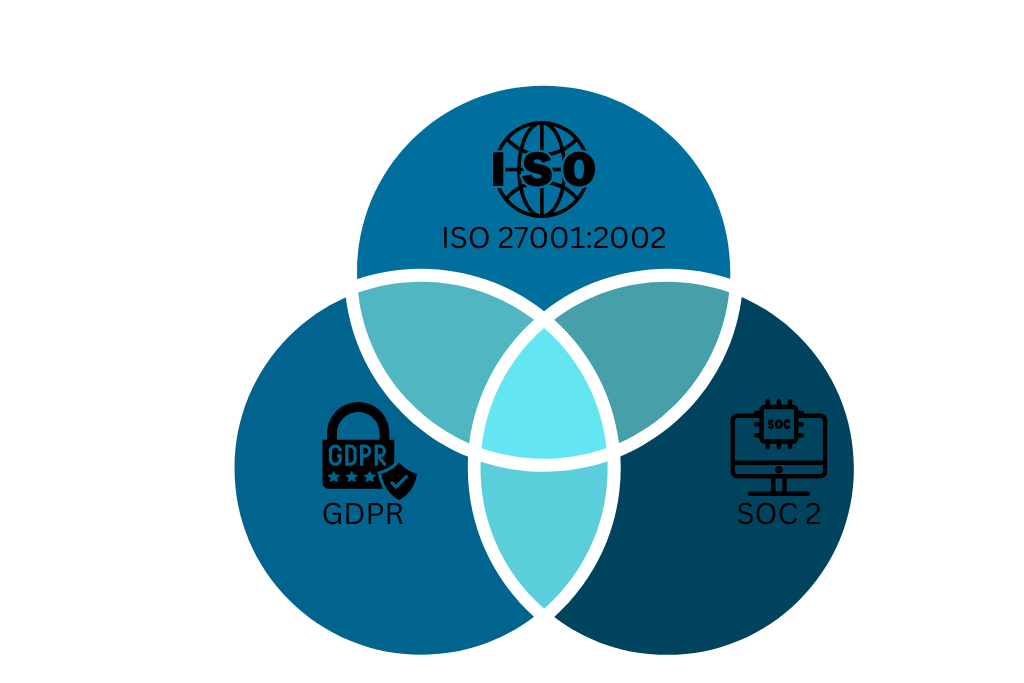
Most security standards share at least 70-80% of their requirements. They all focus on:
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating security threats
- Access controls: Ensuring only authorized users handle sensitive data
- Incident response: Having a plan when things go wrong
- Continuous monitoring: Tracking threats and vulnerabilities over time
Rather than implementing separate processes for SOC 2, GDPR, and NIST, you can streamline security efforts by creating one core security framework such as the ISO 27001:2002 to satisfy multiple regulations.
A compliance management tool can help you map overlapping controls, automate evidence collection, and maintain continuous compliance across multiple frameworks without duplicating efforts.
Instead of managing separate security programs and redoing the same work for every regulation, a tool can align ISO 27001 controls with SOC 2, NIST, and GDPR requirements, ensuring that one framework satisfies many.
With automation, you can reduce human error, cut down compliance fatigue, and maintain continuous security monitoring rather than scrambling before an audit. A well-implemented system can pull compliance evidence directly from IT systems, ensuring tamper-proof documentation and real-time compliance.
By leveraging ISO 27001 as your security foundation and integrating it with a compliance management tool, you’re not just ticking boxes; you’re creating a scalable, efficient security strategy that grows with your business and keeps you ahead of evolving regulations.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in the ISO 27001:2022 Transition
Transitioning to ISO 27001:2022 is not just a box to check. It is a strategic move that strengthens your security posture and ensures regulatory compliance. However, many organizations stumble during this transition due to poor planning, outdated processes, and underestimating the depth of changes. Below are some critical mistakes to avoid and how to stay ahead.
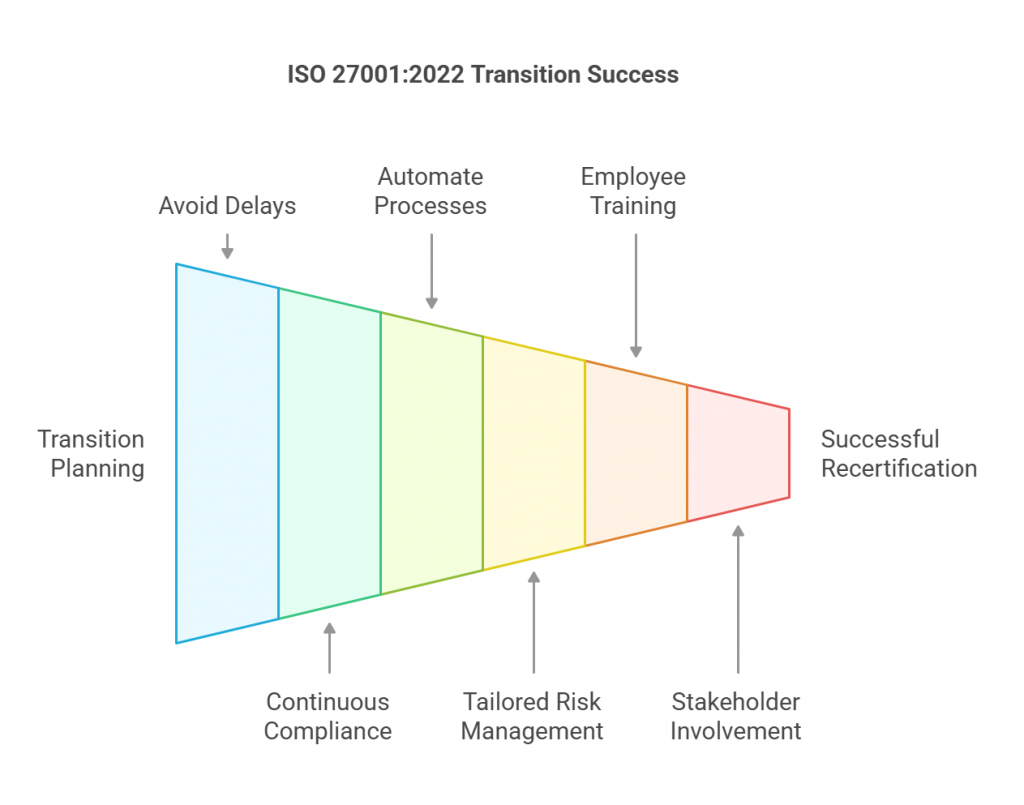
1. Delaying the Transition Process
Procrastination is a compliance killer. Many organizations assume they have plenty of time before the October 31, 2025, deadline. The reality is that a rushed transition increases the likelihood of gaps, failed audits, and compliance penalties. Updating documentation, implementing new controls, and training employees takes time.
Start now with a comprehensive gap assessment to identify what needs to change and create a phased implementation plan.
2. Treating Compliance as a One-Time Project
If your compliance strategy is built around annual audits, you are already behind. Many companies focus on getting certified but fail to maintain compliance between audits. This reactive approach exposes your organization to security vulnerabilities and audit surprises.
Shift to continuous compliance by embedding security into everyday business operations. Real-time monitoring, automated alerts, and periodic internal audits can help maintain compliance year-round.
3. Relying on Manual Processes and Spreadsheets
Still managing compliance with spreadsheets and email threads? That is like navigating a cybersecurity minefield with a paper map. Manual tracking leads to inefficiencies, inconsistencies, and a lack of real-time visibility.
Leverage GRC automation tools to centralize compliance management, automate control checks, and generate audit-ready reports effortlessly.
4. Applying a One-Size-Fits-All Approach to Risk Management
Not all security risks are equal. Applying the same level of security controls across all assets can either overburden teams with unnecessary measures or leave critical areas exposed.
Prioritize based on risk assessments. Identify high-risk assets and apply security controls accordingly to maximize protection where it matters most.
5. Ignoring Employee Training and Awareness
Your security is only as strong as your weakest link. A well-crafted compliance program means nothing if employees are not aware of security policies and best practices. A single phishing email or weak password can compromise an entire network.
Regular security training is non-negotiable. Conduct phishing simulations, workshops, and refresher courses to ensure employees stay vigilant against cyber threats.
6. Overlooking the New Annex A Controls
ISO 27001:2022 introduces 11 new controls focusing on modern threats like cloud security, threat intelligence, and web filtering. Many organizations assume that their existing security measures automatically cover these areas, leading to gaps.
Conduct a detailed control mapping exercise to align your security framework with the new requirements and avoid missing critical updates.
7. Failing to Involve Key Stakeholders Early
Compliance is not just an IT responsibility. It requires coordination across legal, HR, operations, and executive leadership. Many companies fail because they treat compliance as a siloed IT project.
Engage leadership and cross-functional teams early in the process to ensure organization-wide buy-in and smoother implementation.
8. Not Having a Clear Roadmap for Recertification
The transition to ISO 27001:2022 is not just about updating policies. It requires a structured approach to implementation, testing, and recertification. Some companies rush to update documentation without testing the effectiveness of their controls.
Develop a clear transition roadmap that includes internal audits, third-party gap assessments, and pre-certification reviews to ensure a seamless transition.
Are you ready to Transition to ISO 27001:2022?
Transitioning to ISO 27001:2022 is not just about meeting a compliance deadline. It is about strengthening your security posture in a rapidly evolving threat landscape. The updates bring a more streamlined, risk-based approach, helping businesses stay resilient against modern cyber threats. But managing this transition manually can be overwhelming, especially when juggling multiple frameworks like SOC 2, NIST, and GDPR.
This is where Spog.ai comes in. Instead of drowning in spreadsheets and scrambling for audit evidence, Spog.ai automates control mapping, real-time compliance monitoring, and audit readiness all in one platform. It simplifies compliance, reduces redundant efforts, and ensures that your organization is always ahead of security and regulatory changes.
The clock is ticking. Are you ready to transition seamlessly to ISO 27001:2022? Let Spog.ai take the complexity out of compliance so you can focus on what truly matters, securing your business.
