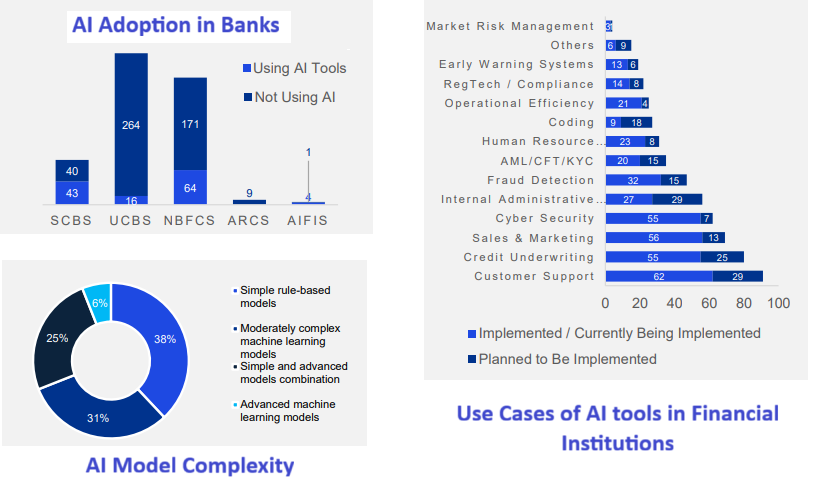
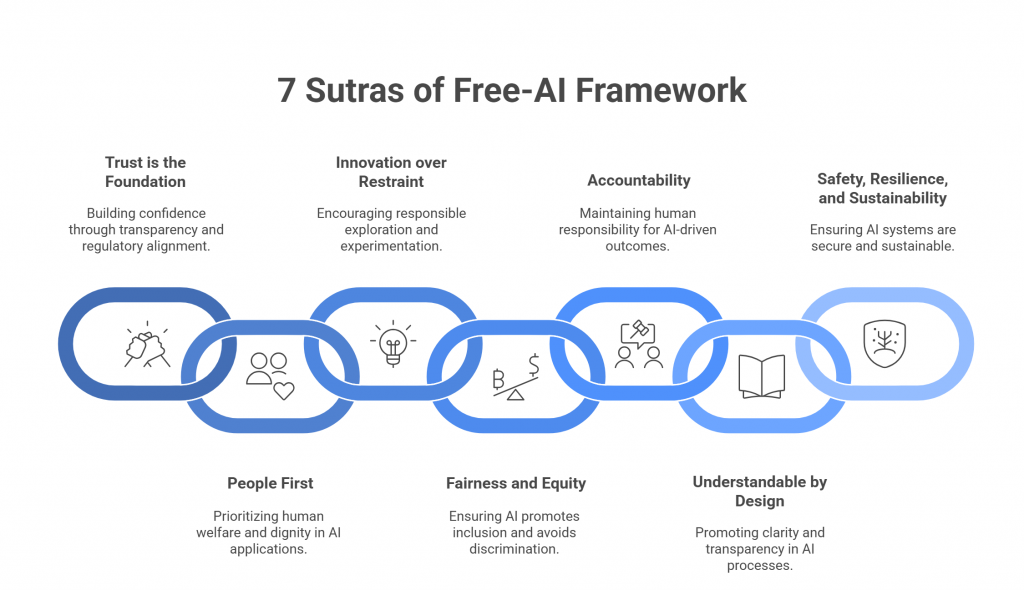
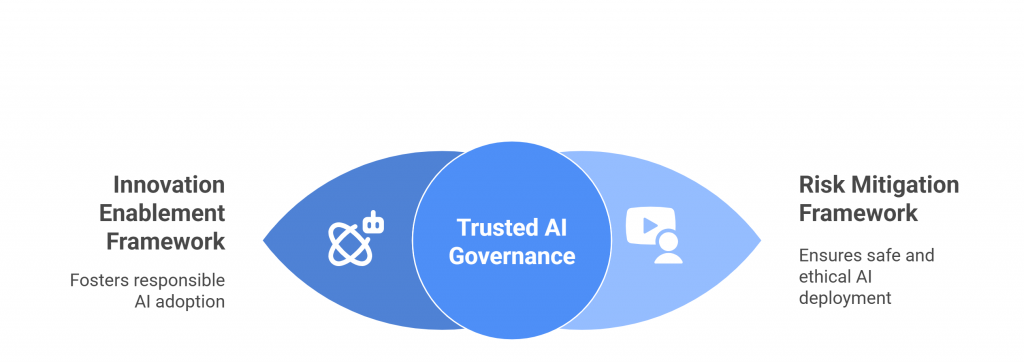
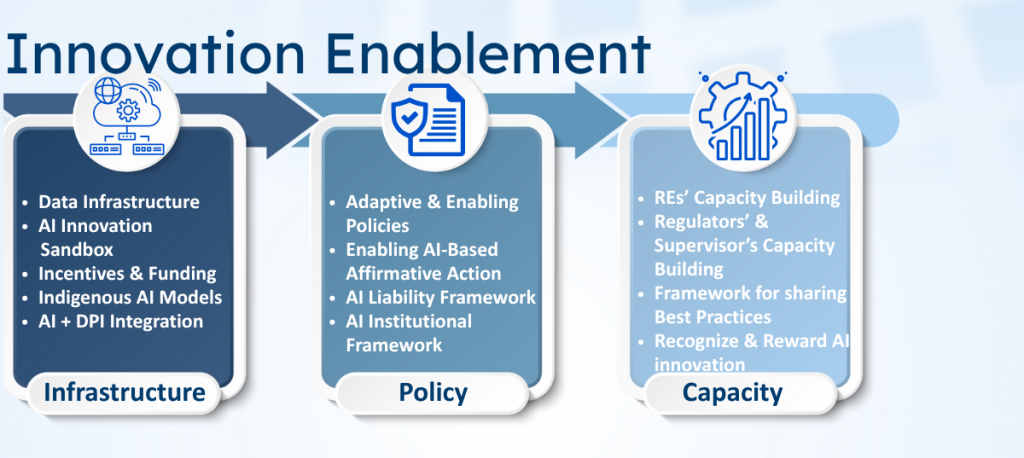
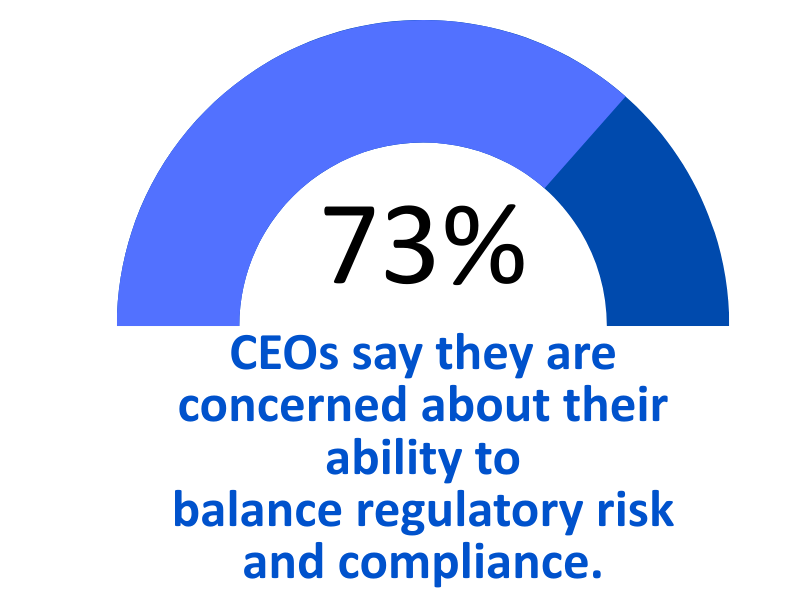
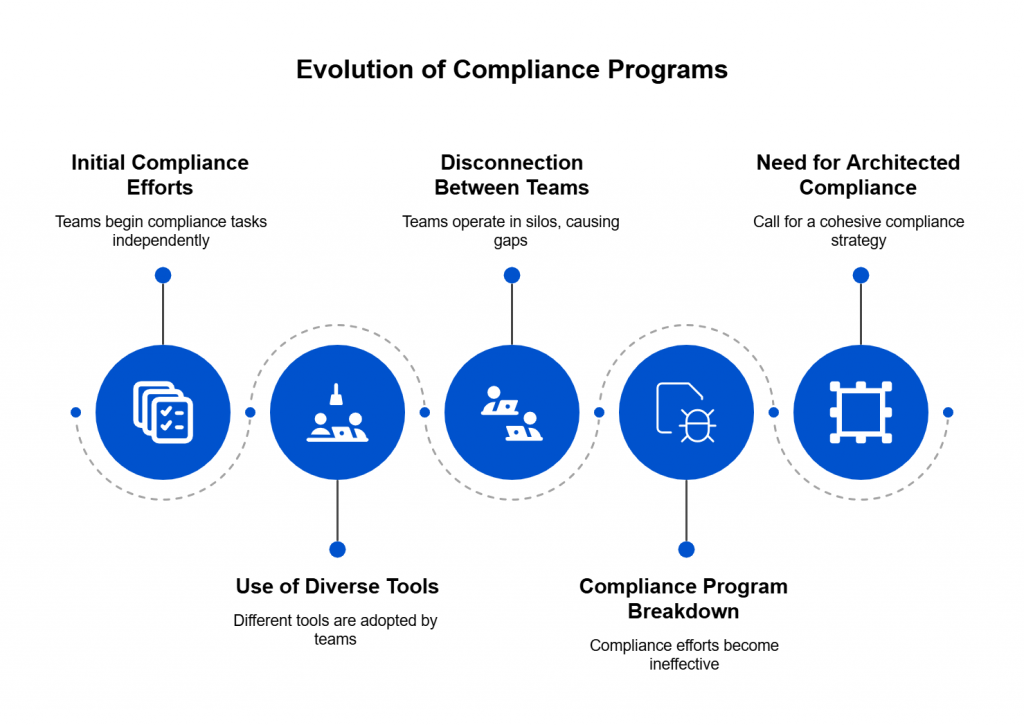
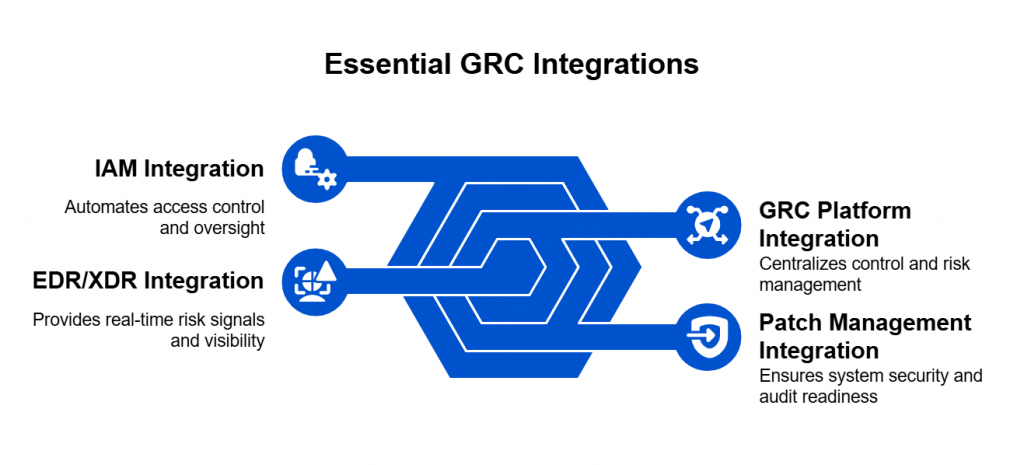
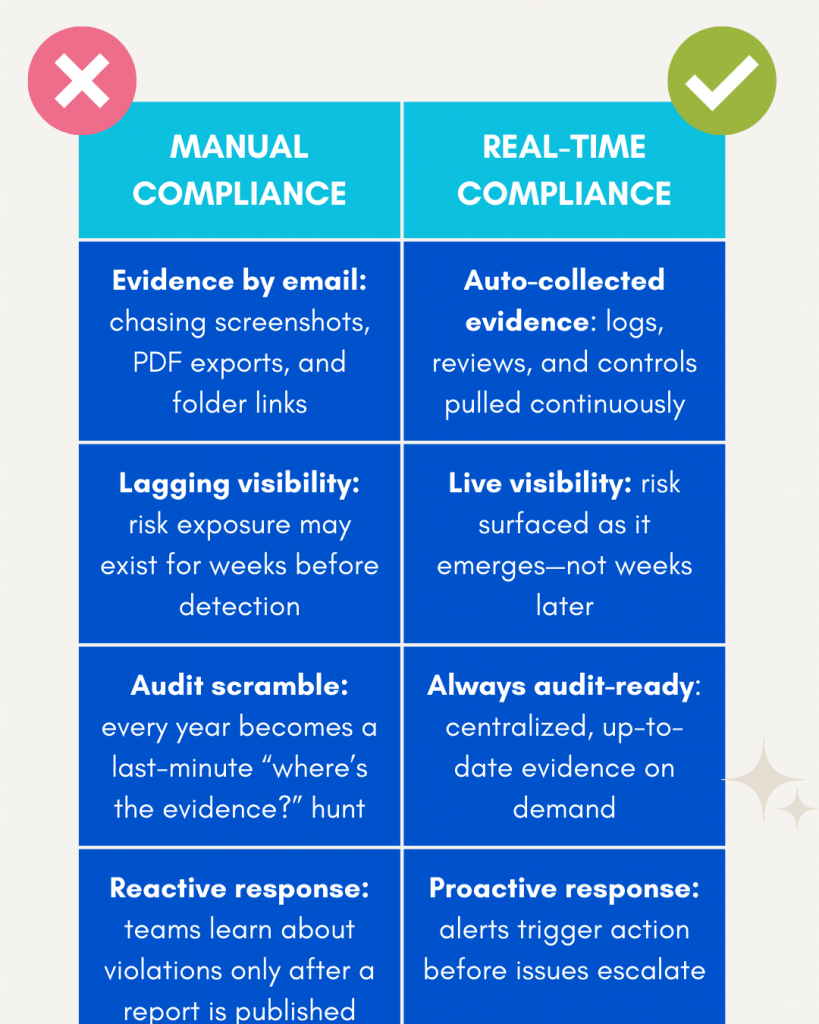
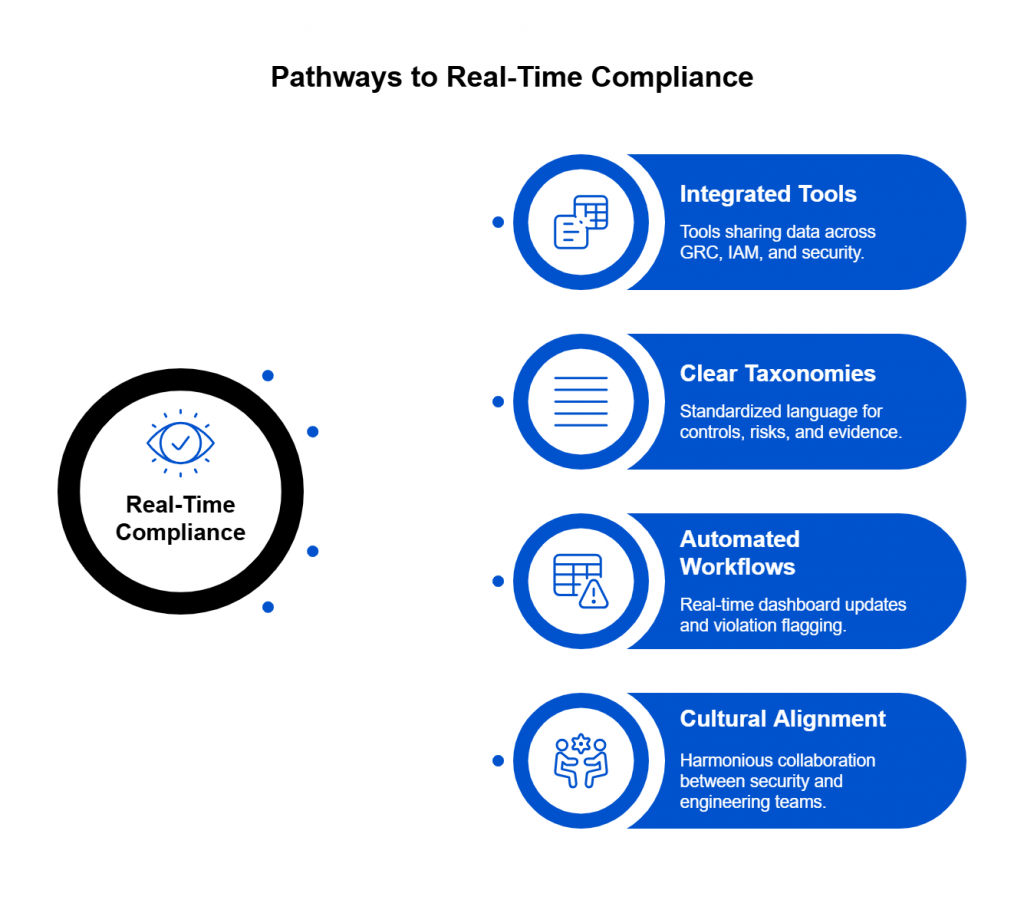
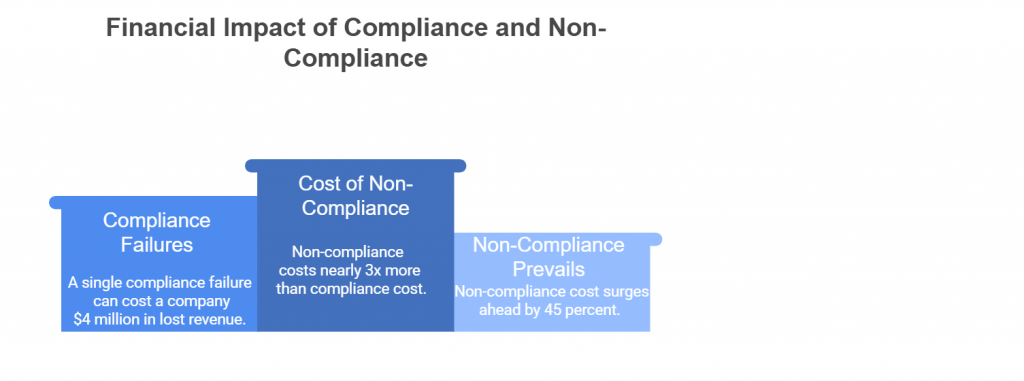
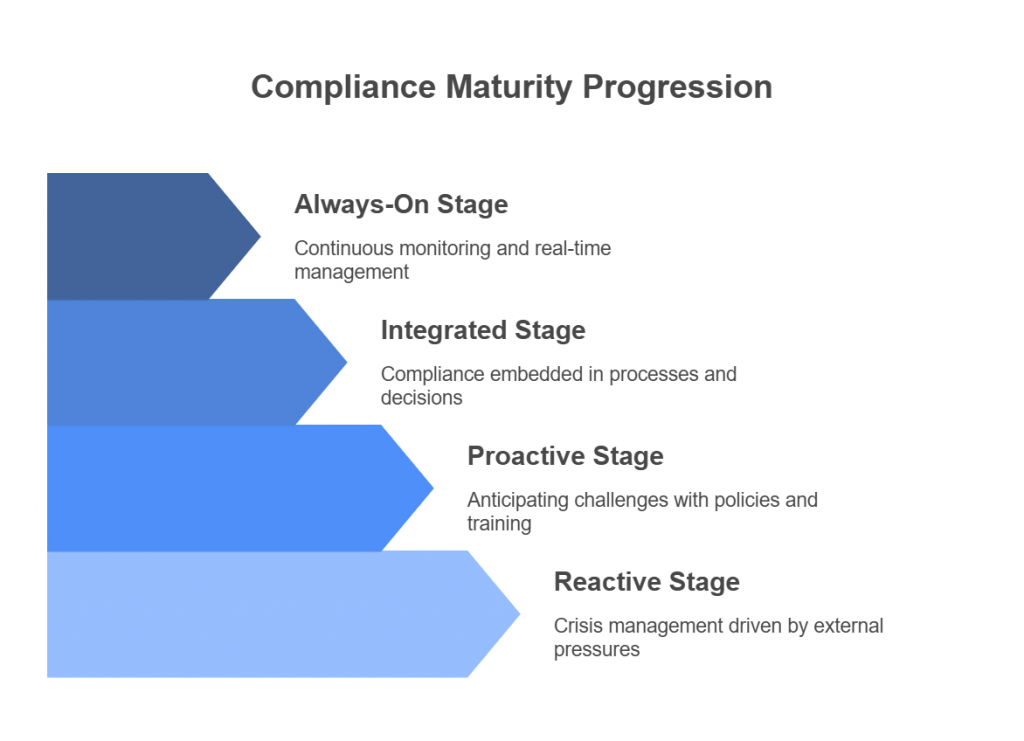
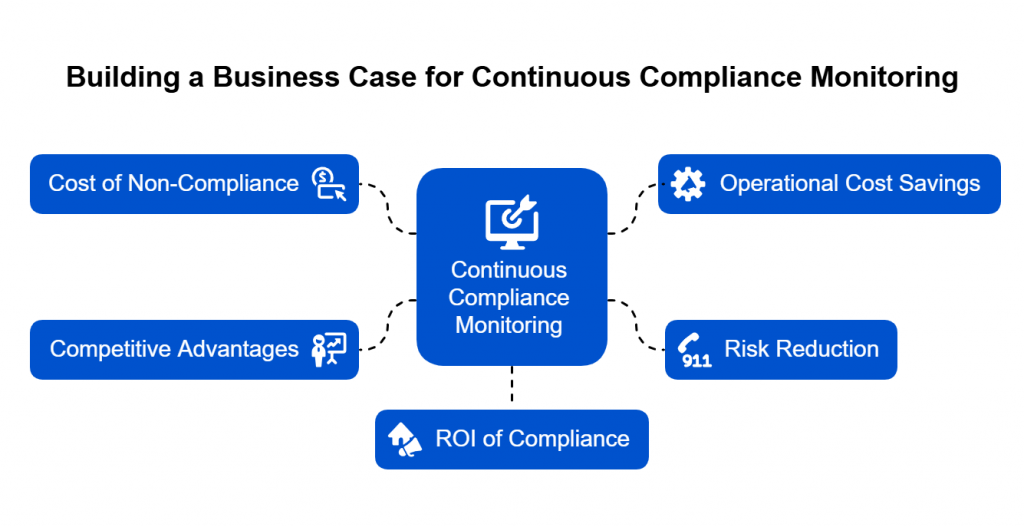
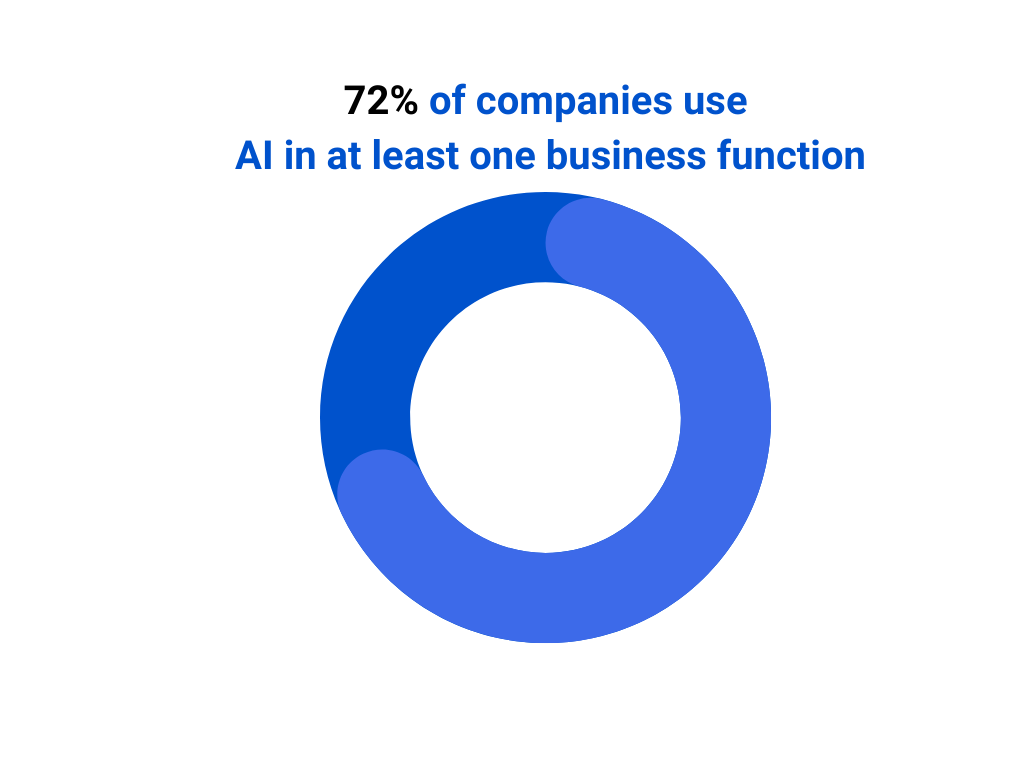
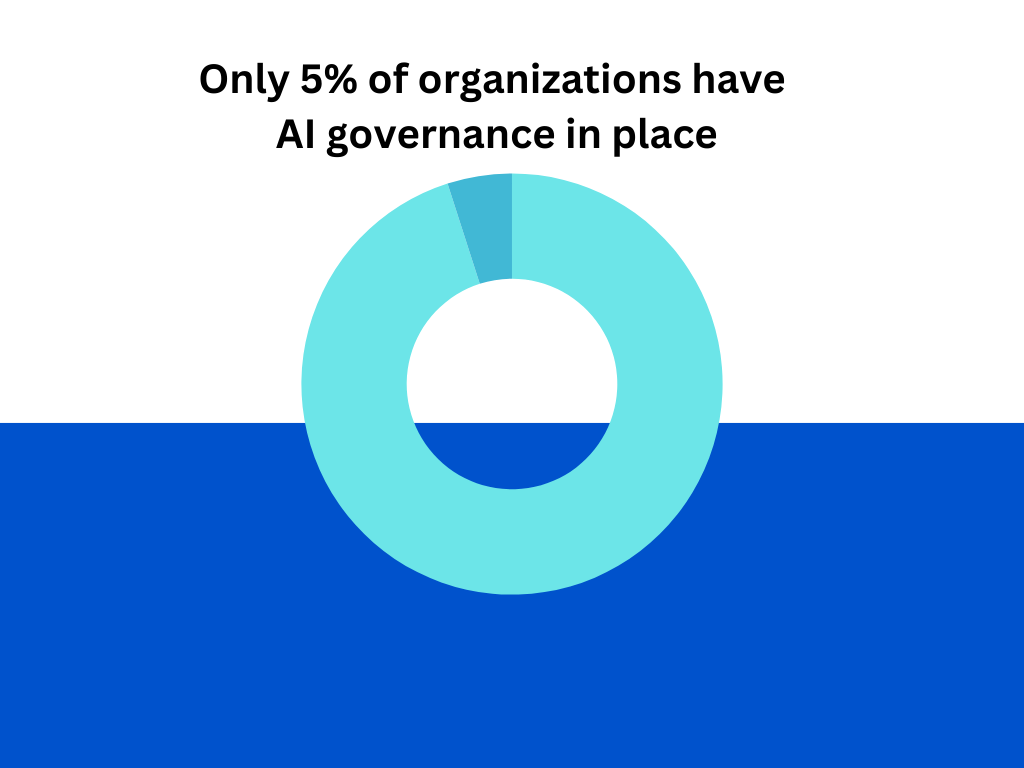
Introduction — When the Cloud Shakes, Compliance Crumbles
When AWS’s US-east-1 region went dark, so did thousands of companies. These weren’t reckless startups or poorly managed systems; they were organizations that had passed every audit, ticked every compliance box, and still couldn’t stay online.
The irony is hard to miss: compliance frameworks meant to assure availability failed to prevent unavailability. And that’s not because the standards are meaningless — it’s because we’ve learned to treat them like checklists rather than capabilities.
Availability, as defined by frameworks like SOC 2 and ISO 27001, is often reduced to a static control:
“Are you hosted in multiple availability zones?”
“Do you replicate data across regions?”
These are good questions, but they’re not proof of resilience. They’re proof of intent, not evidence of execution.
When a region-wide outage strikes, documentation doesn’t fail over. Systems do. And unless those systems are continuously tested, monitored, and automated, your compliance report is just a well-formatted illusion of control.
True resilience isn’t a checkbox. It’s a behavior — one your systems must demonstrate under pressure.
The Availability Mirage in Compliance Frameworks
On paper, frameworks like SOC 2 and ISO 27001 appear to take availability seriously. They reference “system uptime,” “continuity,” and “disaster recovery readiness.” But in practice, these requirements are often interpreted in ways that prioritize audit comfort over operational truth.
Most organizations approach availability controls as architectural posture, not operational capability. During an audit, it’s enough to say:
- “We’re hosted in multiple Availability Zones.”
- “Our data is replicated across regions.”
- “We have a Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BC/DR) plan on file.”
Each of these statements checks a box — but none of them guarantee uptime when failure actually happens.
Having multiple regions doesn’t help if your failover process requires manual intervention. Replicating data doesn’t ensure continuity if your application stack can’t gracefully reroute users. A DR plan in a document repository doesn’t help when engineers are scrambling to execute it under pressure.
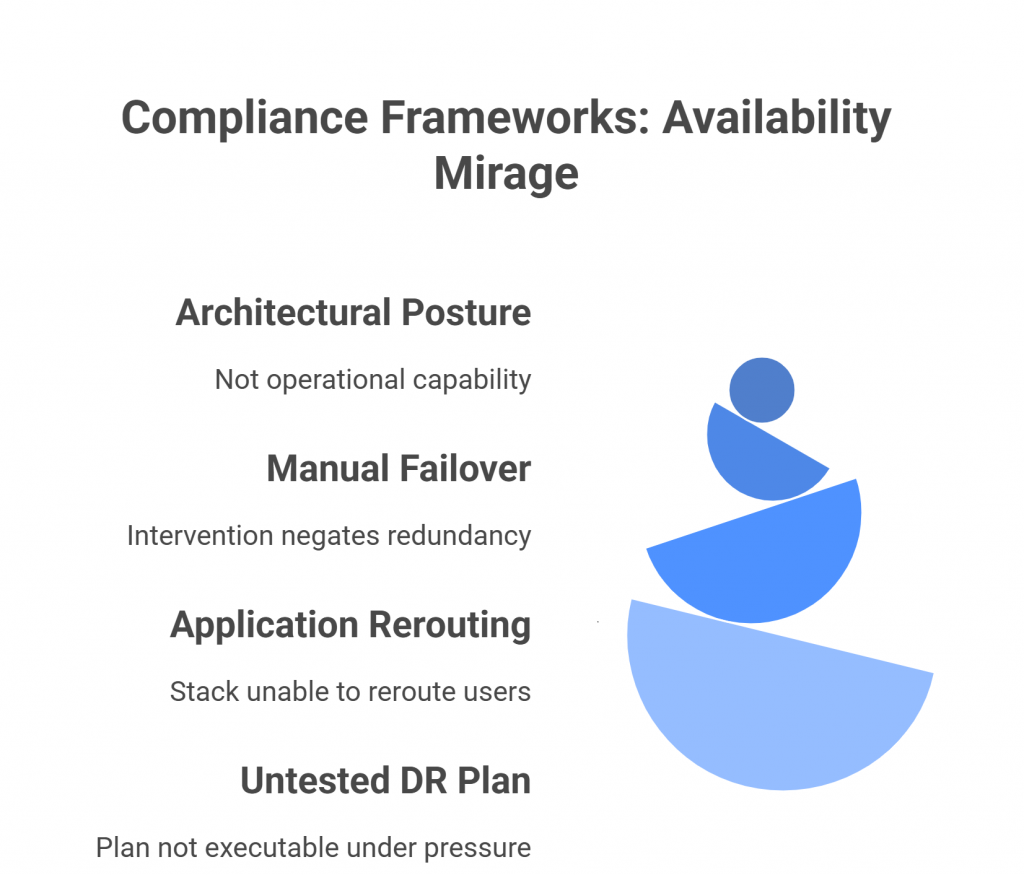
This is the availability mirage — the comforting illusion that infrastructure redundancy equals resilience. Compliance frameworks unintentionally fuel this illusion because their assessments focus on design, not execution.
As long as your policies look sound, and you can show evidence of documentation, you pass.
But systems don’t care about paperwork. When a critical dependency like AWS US-east-1 goes down, only automation, tested failovers, and operational discipline determine whether your company stays online.
Real-World Failures of “Compliant” Systems
In December 2021, when Fastly, one of the world’s largest content delivery networks (CDNs), experienced a configuration bug that triggered a massive global outage, dozens of high-profile websites — from The New York Times to GitHub and Reddit — went offline. These were organizations with mature security postures, rigorous change management processes, and clean audit reports.
None of that mattered when a single misconfigured update rippled across their infrastructure.
Every one of those companies had change-control policies, redundant systems, and disaster recovery procedures that looked impeccable during audits. Yet, when the outage hit, the dependency chain was too interconnected — automated rollbacks didn’t trigger as expected, and manual mitigation took hours.
That event exposed the same truth the AWS us-east-1 outage did: compliance can’t predict real-world behavior. Systems that are architecturally compliant can still be operationally fragile.
This isn’t a criticism of SOC 2 or ISO 27001 — both were designed for assurance, not simulation. But it highlights the fundamental gap between documented controls and tested outcomes.
Failover diagrams look great in audits. But in practice, resilience depends on how systems behave under failure conditions — latency spikes, API throttling, cascading restarts, or DNS propagation delays.
These are operational realities no auditor observes, because traditional audits test policy existence, not system response.
So whether it’s a global CDN glitch or a regional cloud outage, one principle remains:
You can’t certify resilience — you have to prove it in production.
The Audit Gap: What Auditors Check vs. What Systems Do
Here’s where the disconnect becomes painfully clear. Auditors are trained to evaluate documentation, not simulate disasters. Their job is to confirm that controls exist, are approved, and appear to function based on static evidence — screenshots, logs, or policy statements.
That process works for verifying access reviews or encryption standards. But when it comes to availability, it falls dramatically short.
An auditor might ask, “Do you have a DR plan?” or “Is your infrastructure deployed across multiple regions?” If the answers are “yes,” and the evidence — an architecture diagram, a failover runbook, a signed policy — looks legitimate, the box gets checked. The system passes.
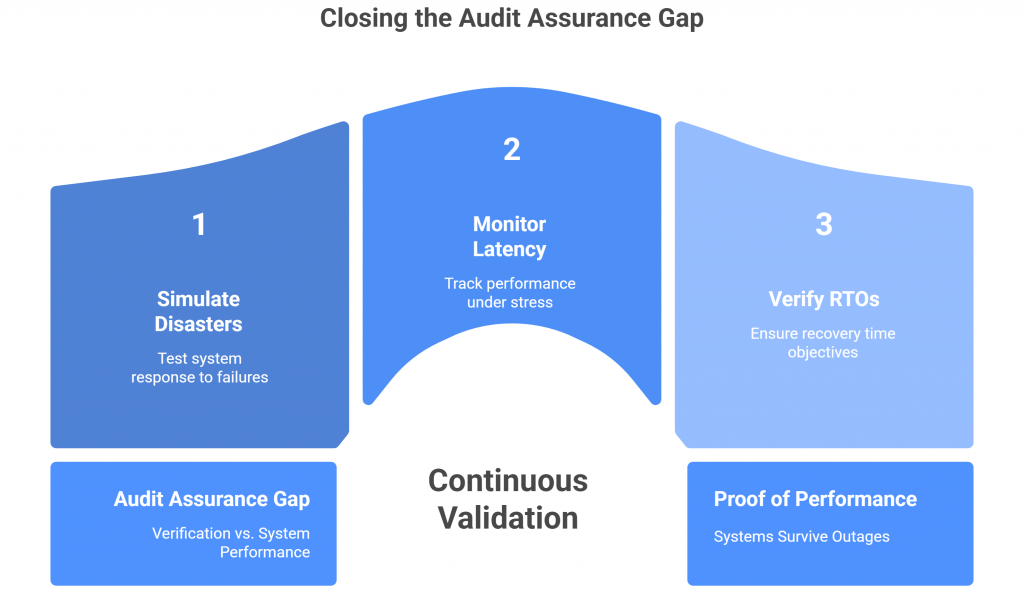
But real resilience isn’t observable on paper. It’s revealed only through behavior — through how systems respond when dependencies break, networks partition, or load spikes unpredictably.
In most compliance audits, no one is pulling the plug on a live server to see if the failover kicks in. No one is monitoring latency under stress or verifying that RTOs (Recovery Time Objectives) are achieved in practice. That kind of assurance can’t come from screenshots; it requires continuous validation.
This creates what can only be described as an “assurance gap” — the space between what audits verify and what systems do. Organizations are rewarded for evidence of preparedness rather than proof of performance.
The result? A compliance culture that’s unintentionally optimized for passing audits, not surviving outages. And until that gap is closed, companies will continue to mistake documentation for durability.
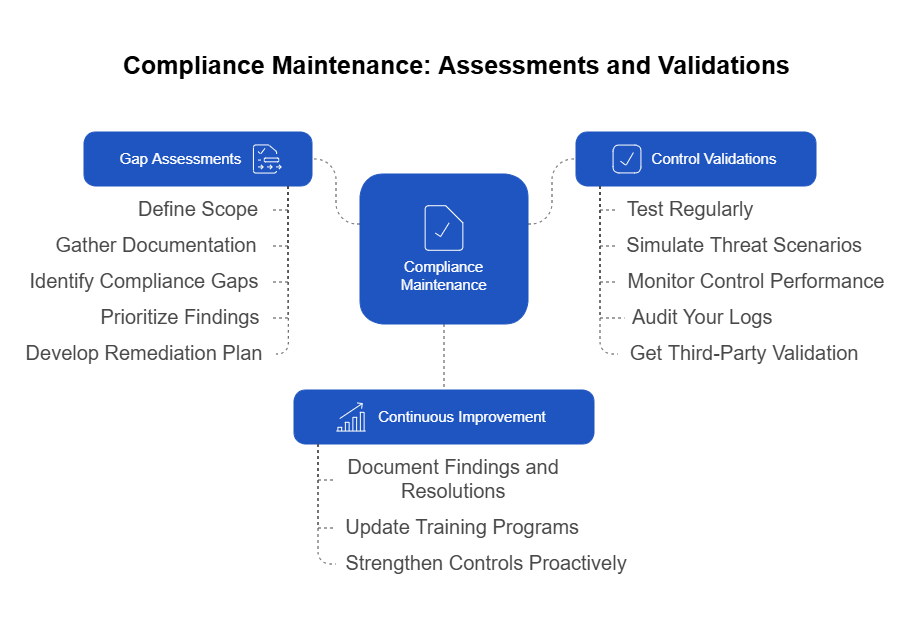
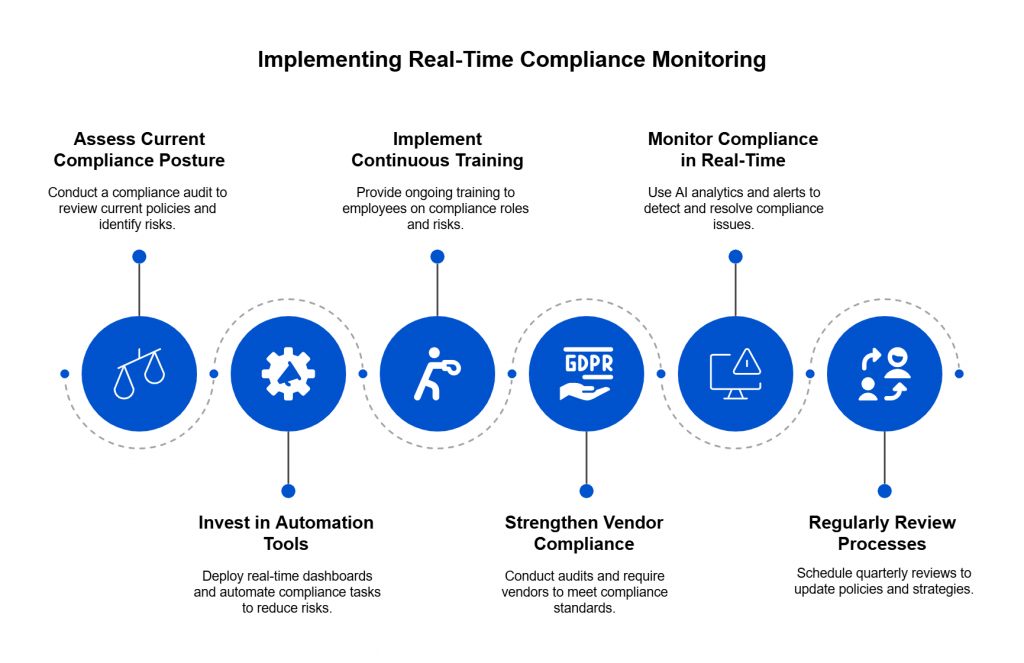
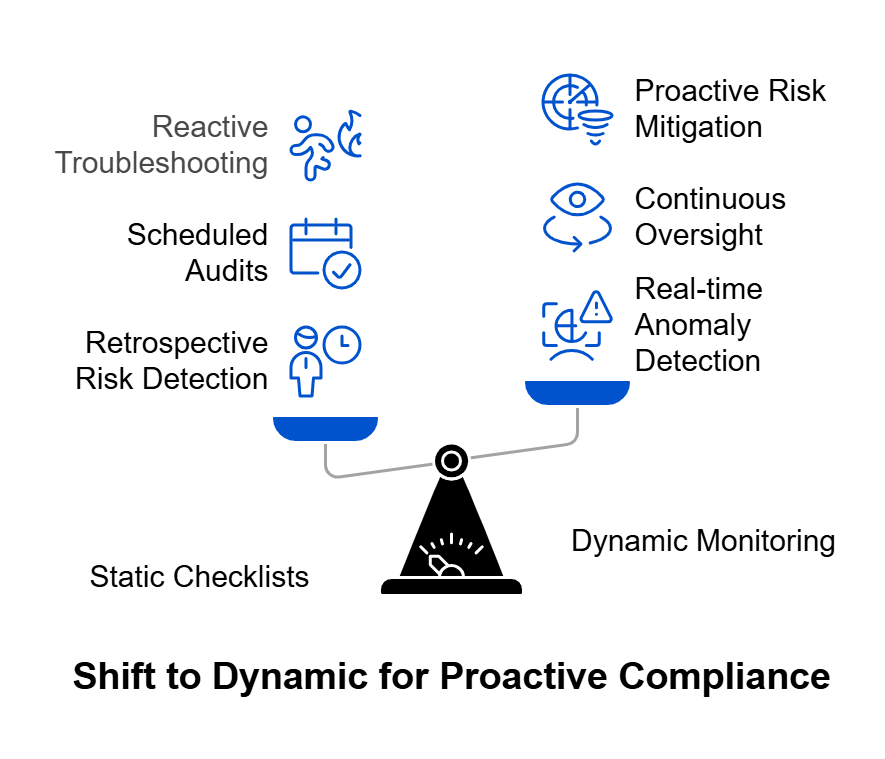
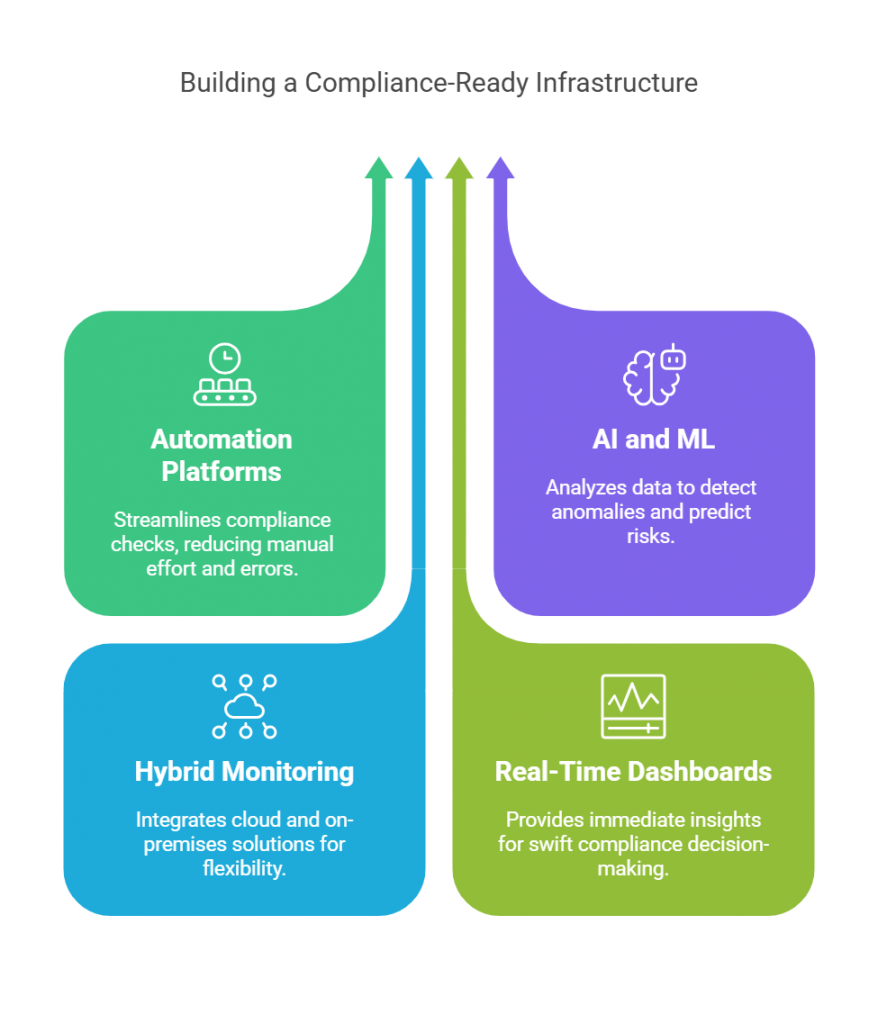
From Checklists to Continuous Assurance
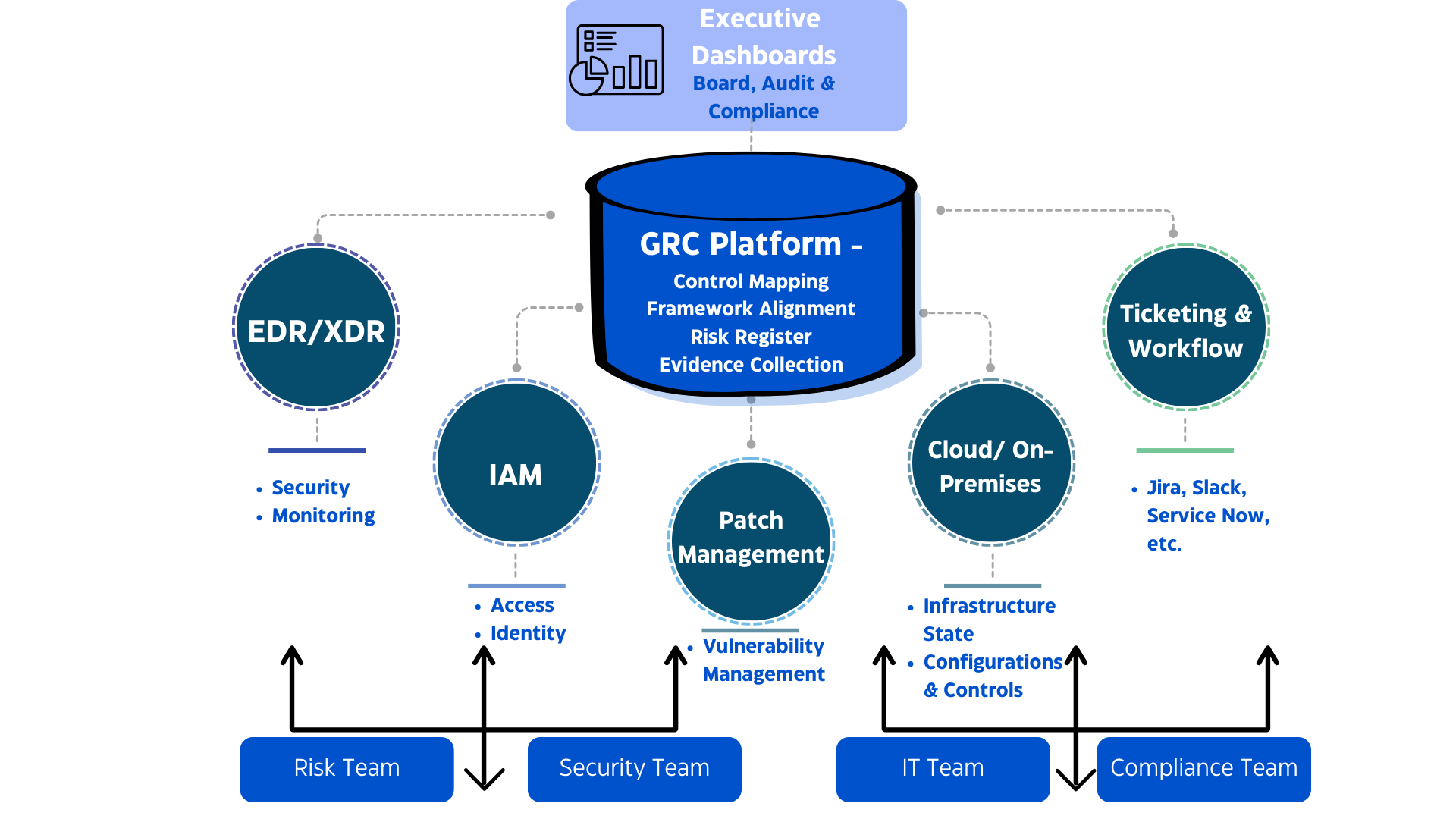
If traditional audits create an assurance gap, GRC automation is how we close it. It transforms governance from a retrospective exercise into a real-time feedback loop — one that continuously validates whether resilience controls are actually working, not just documented.
In the traditional model, evidence is static: screenshots of monitoring dashboards, copies of policies, or timestamps from last quarter’s DR drill. But in a world where cloud environments change by the hour, those artifacts go stale fast. By the time an auditor reviews them, the system has already evolved.
GRC automation flips that model. Instead of relying on one-off attestations, it integrates directly with infrastructure, cloud services, and monitoring tools to collect live evidence — continuously.
For example:
- Failover validation: Automated workflows can periodically trigger regional failovers to ensure systems recover within defined RTO/RPO thresholds.
- BC/DR monitoring: Real-time telemetry can confirm that backup systems are available, current, and accessible — not just configured.
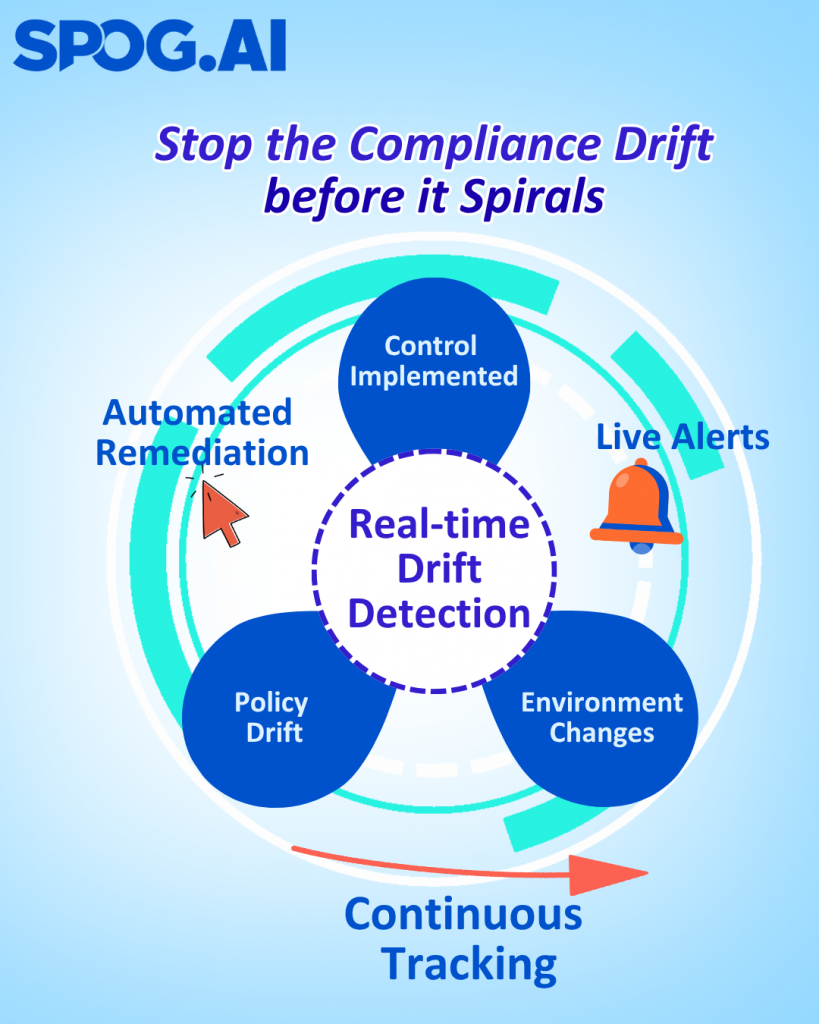
- Control drift detection: Automated checks can flag when an environment deviates from approved configurations, giving teams a chance to remediate before resilience is compromised.
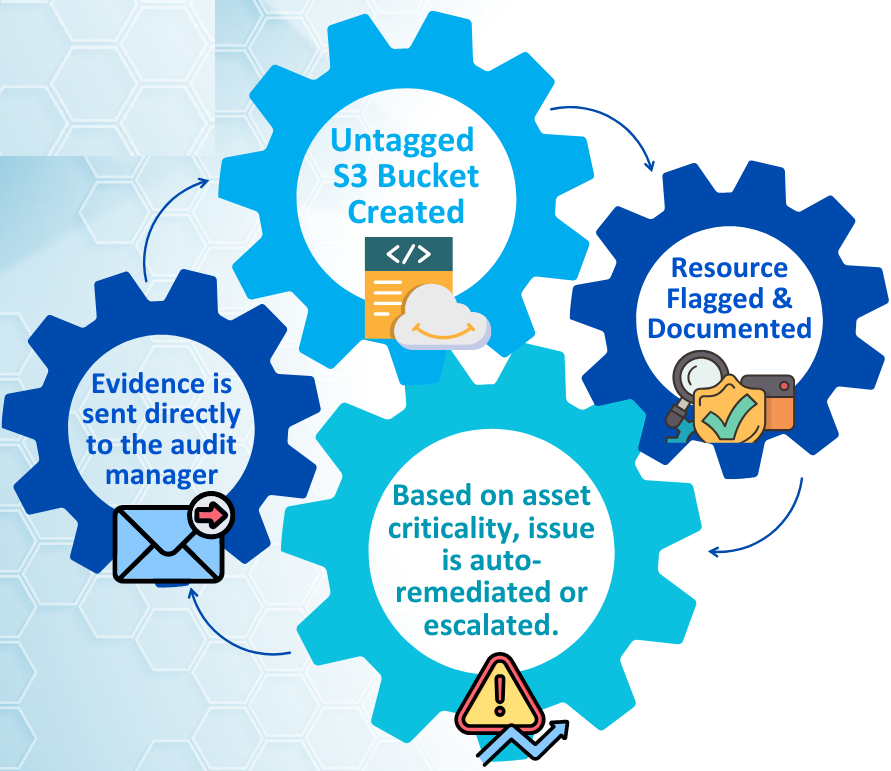
This approach turns compliance from a snapshot into a stream — where availability isn’t something you claim once a year but prove every day.
In essence, GRC automation operationalizes trust. It allows organizations to show auditors — and customers — that resilience isn’t theoretical. It’s observable, measurable, and constantly verified by the systems themselves.
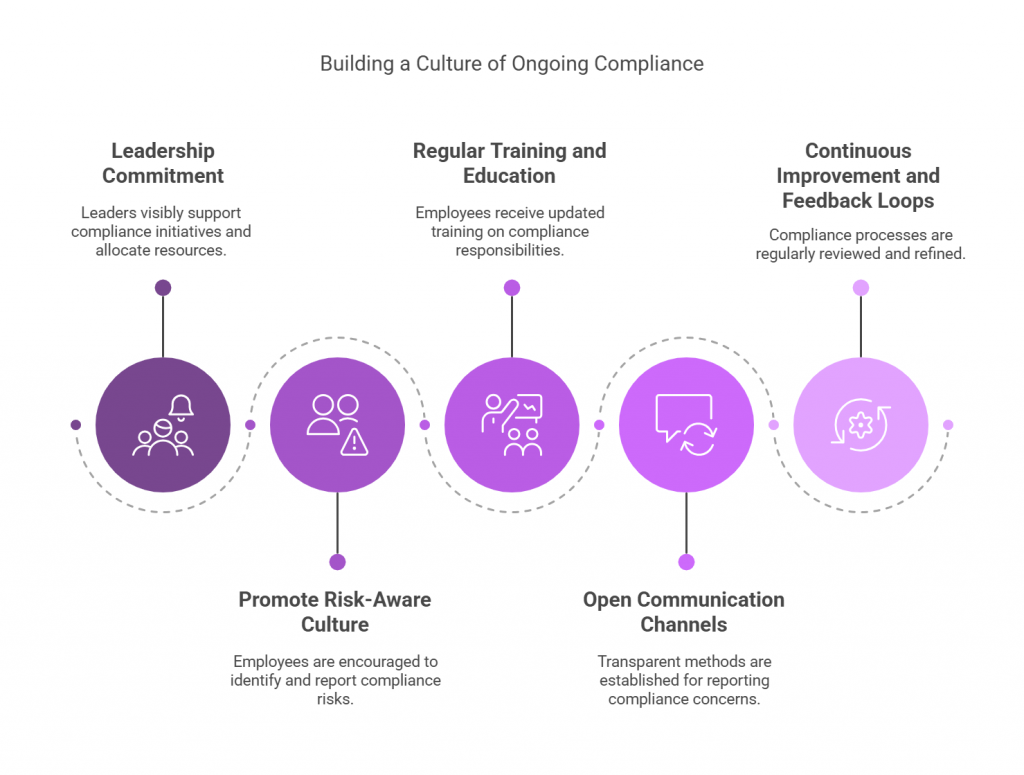
Because the truth is simple: a resilient organization doesn’t wait for audits to find out if its controls work. It knows, every minute, that they do.
Resilience for Modern Cloud Systems
For decades, “availability” has been defined in terms of infrastructure — redundant servers, replicated databases, and multi-region deployments. But in today’s cloud-native, API-driven, microservice-heavy ecosystems, that definition is obsolete. True availability isn’t about where you host; it’s about how your systems behave under stress.
In modern architectures, resilience depends on automation, orchestration, and observability. A system that requires manual intervention to fail over isn’t resilient — it’s merely delayed in its failure. Likewise, a replicated database that isn’t automatically reconnected by the application during an outage isn’t available — it’s just mirrored downtime.
To move beyond the checkbox version of availability, organizations need to redefine the metric itself. Here’s what real availability assurance should include:
- Automated Failover Verification:
Don’t just document DR plans — continuously test them. Failovers should be automated, measurable, and triggered without human intervention. - Outcome-Based Metrics:
Instead of proving that backups exist, prove that they restore correctly within target RTO/RPO limits. Monitor uptime as a user experience metric, not just a server metric. - Resilience Through Chaos Testing:
Introduce failure deliberately — through chaos engineering or simulated outages — to confirm systems recover as expected. If resilience is never tested, it’s only theoretical. - Integrated Control Validation:
Pair operational telemetry with compliance evidence. For instance, GRC systems can automatically collect logs showing successful failovers, validating both uptime and control effectiveness.
This evolution requires a mindset shift. Availability is no longer a checkbox on an audit form; it’s a living system property — one that must be continuously proven through data.
Organizations that adopt this model move from compliant architectures to self-healing architectures. And in a world where one regional outage can ripple across the internet, that difference defines who stays online — and who disappears with the next cloud disruption.
Conclusion — The Future of Trust Is Live
A SOC 2 certificate or ISO 27001 badge may earn customer confidence, but it can’t guarantee uptime. Compliance frameworks were designed for assurance, not adaptation — and in a cloud-native world where systems evolve hourly, that distinction matters.
The future of trust won’t be defined by static reports or annual attestations. It will be measured in real time, through live control validation, self-healing infrastructure, and automated evidence that proves systems behave as intended — not just that they were designed to.
When resilience becomes a living, observable property, trust transforms from an outcome of paperwork into an outcome of performance. GRC automation is the bridge that makes this possible — turning governance into a continuous, data-driven system of truth.
Because at the end of the day, a clean audit report doesn’t keep your services online.
Automated resilience does.
Compliance may check the box — but only continuous assurance keeps the lights on.