As India accelerates toward becoming a digital-first economy, regulatory frameworks are increasingly shaping how enterprises manage data, AI, and security operations. At the heart of this transformation lies the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023.
A landmark legislation establishing India’s first comprehensive privacy framework. It lays down clear expectations around privacy, consent, and accountability, positioning data protection as both a compliance necessity and a business differentiator.
The recently notified DPDP Rules 2025 mark the next milestone in this journey — translating legislative intent into operational practice. These Rules aim to define how organizations should obtain verifiable consent, manage user data, report breaches, and enable individuals to exercise their rights. They also clarify roles such as Data Protection Officers (DPOs) and Consent Managers, and lay the groundwork for the functioning of the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI).
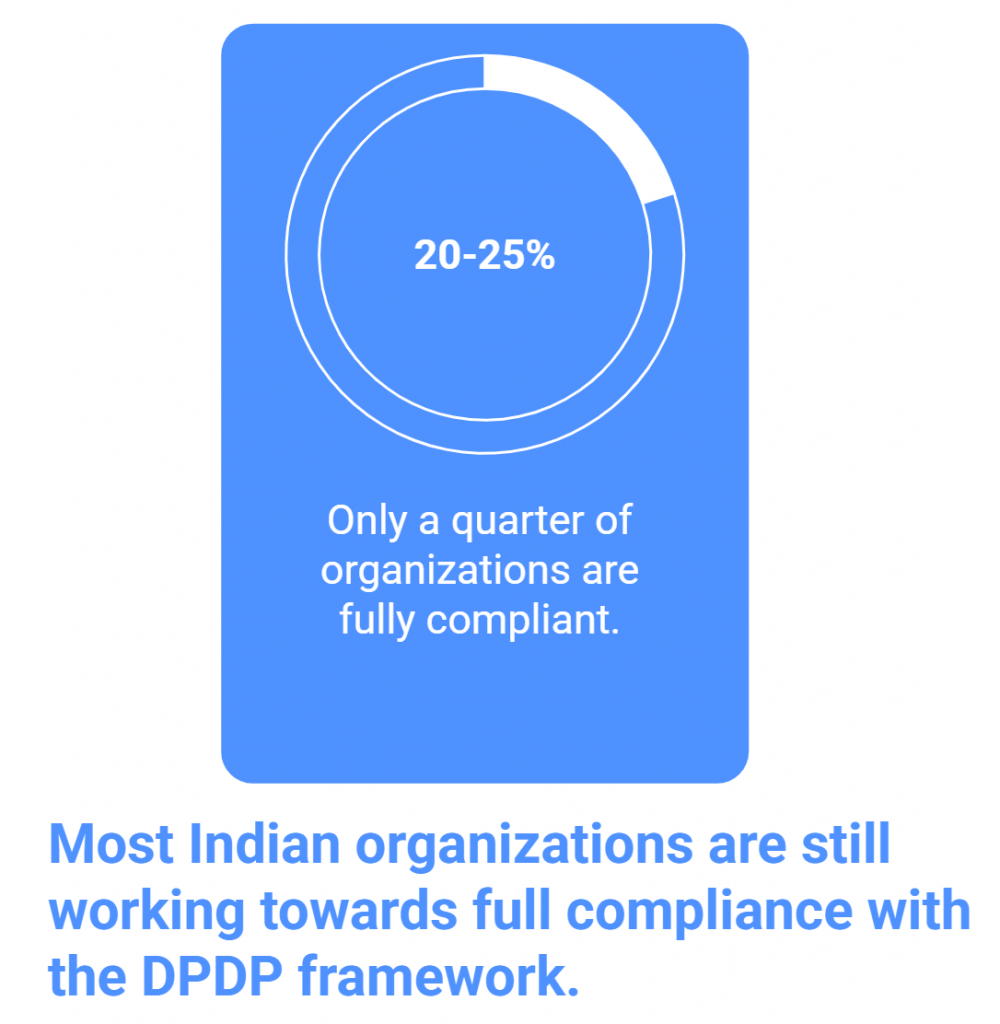
However, the road to compliance remains uneven. According to ETCISO Intelligence Cybersecurity Leadership Report 2025, a majority of Indian organizations describe themselves as either “work in progress” or “mostly compliant but with gaps,” while only about 20–25% claim to be fully compliant with the DPDP framework.
This mirrors the early stages of GDPR compliance in Europe, where achieving full readiness was a multi-year process rather than a one-time project.
Here’s a DPDP act compliance readiness checklist in alignment with the latest draft rules, including all the changes.
The Road to 2025: From Act to Rules
The journey from the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 to the DPDP Rules 2025 has been one of iterative consultation, sectoral debate, and mounting regulatory urgency. The Act, passed in August 2023, laid a foundational legal framework for how personal data should be collected, processed, and protected in India. Yet, it intentionally left much of the “how” to subsequent rules — a necessary but challenging choice given the country’s diverse digital ecosystem.

From Legislative Framework to Operational Clarity
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) spent much of 2024 conducting multi-stakeholder consultations, engaging with industry bodies, civil society groups, legal experts, and technology associations. Draft Rules were circulated in late 2024, with feedback spanning from requests for clearer consent mechanisms to leniency in reporting obligations for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). By mid-2025, the government notified the finalized DPDP Rules, bringing long-anticipated structure to data governance obligations.
These Rules seek to translate broad legal principles into enforceable standards — defining the roles and responsibilities of Data Fiduciaries, Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs), and Consent Managers. They outline procedural details for grievance redress, breach notification, cross-border data transfers, and data retention. Importantly, they also operationalize the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI), setting in motion the institutional mechanism for oversight and enforcement.
Global Context and Strategic Timing
The timing of the Rules is strategic. With India’s digital economy projected to cross USD 1 trillion by 2030, and with the growing integration of AI and machine learning models in enterprise operations, the government needed a robust governance framework to sustain both innovation and public trust. The Rules thus arrive not in isolation, but as part of a broader regulatory convergence — aligning privacy, cybersecurity, and AI oversight under a shared policy vision of “trust through transparency.”
Yet, this regulatory maturity also brings complexity. For enterprises already navigating frameworks like the Information Technology Rules (2021), CERT-In directives, and sectoral data guidelines issued by regulators such as the RBI and IRDAI, the DPDP Rules add another compliance layer. How these frameworks will coexist — or conflict — remains one of the biggest questions as India operationalizes its new data protection regime.
Key Changes Introduced by the DPDP Rules 2025
The DPDP Rules 2025 transform the high-level commitments of the 2023 Act into concrete, operational mandates for organizations handling personal data. They seek to standardize compliance practices, strengthen individual rights, and streamline enforcement through the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI). While they bring much-needed structure, several provisions are still evolving in interpretation and practical application.
1. Consent and Notice Framework
Perhaps the most significant area of elaboration lies in how consent must be obtained, verified, and managed.
The Rules specify that consent must be:
- Informed, through clear, concise, and easily understandable notices in multiple Indian languages;
- Specific, indicating the precise purpose and category of data being collected;
- Verifiable, ensuring that the data principal’s identity is authenticated at the point of consent; and
- Revocable, with equally simple mechanisms for withdrawal.
The introduction of Consent Managers—independent entities registered with MeitY—marks a new governance layer. These intermediaries are tasked with managing consent lifecycle operations between data principals and data fiduciaries, ensuring transparency in both granting and withdrawing consent.
The Rules also operationalize the concept of “deemed consent”, allowing limited data processing without explicit consent in cases such as national interest, employment purposes, or emergencies. However, the absence of strict boundaries for such exemptions continues to be a concern among privacy advocates.
2. Rights of Data Principals
For individuals, the DPDP Rules detail the procedures for exercising rights—including access, correction, erasure, and grievance redress. Data fiduciaries must:
- Respond to user requests within 30 days, extendable under exceptional circumstances;
- Provide standardized templates for submitting such requests; and
- Maintain transparent logs of all data access and correction activities.
The Rules also require fiduciaries to inform data principals about automated decision-making, wherever applicable—a nod to the growing use of AI-driven systems in processing personal data. However, the lack of explicit definitions for “profiling” or “automated decision” could create interpretational challenges.
3. Data Fiduciary Obligations
The 2025 Rules codify a layered compliance framework based on the organization’s scale and data sensitivity:
- Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs)—those processing large volumes or sensitive data—must conduct periodic Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) based in India, and undergo annual data audits.
- All fiduciaries must implement reasonable security safeguards, including encryption, anonymization, and access control measures aligned with industry standards.
- Data retention must be purpose-bound—organizations are expected to delete personal data once the purpose of processing has been fulfilled, unless legally mandated otherwise.
This risk-based approach aligns with global best practices, yet organizations—especially MSMEs—have raised concerns about the cost and resource implications of implementing these controls.
4. Data Breach Notification and Reporting
In line with international norms, the Rules introduce a 72-hour reporting window for data breaches once detected. Organizations must notify both the Data Protection Board of India and affected individuals, specifying the nature of the breach, data categories compromised, and remedial actions taken.
The DPBI may issue directions for corrective actions or initiate investigations in severe cases. However, what qualifies as a “material breach” remains loosely defined—potentially leading to over-reporting or inconsistent enforcement across sectors.
5. Cross-Border Data Transfers
One of the most anticipated elements of the DPDP Rules is the mechanism for cross-border data transfers. The Rules adopt a “whitelist-based” approach, where transfers are permitted only to countries or territories notified by the Central Government as “trusted jurisdictions.”
While this model is intended to simplify compliance, it introduces uncertainty for global enterprises operating across multiple jurisdictions. The Rules are silent on whether standard contractual clauses (SCCs) or binding corporate rules (BCRs)—commonly used in GDPR compliance—will be recognized in India.
This ambiguity could hinder multinational corporations and Indian startups that rely on cross-border cloud infrastructure, particularly in sectors like ITES, BFSI, and healthcare.
6. Data Protection Board: Procedural Powers and Enforcement
The Rules formally establish the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI) as a quasi-judicial body empowered to investigate, mediate, and impose penalties for non-compliance. They outline procedures for:
- Registration of grievances,
- Preliminary inquiry and evidence collection, and
- Issuance of penalty orders or corrective directions.
Penalties under the DPDP framework can extend up to ₹250 crore per violation, depending on the severity and recurrence. Yet, the Rules remain vague on appeal procedures and independence safeguards, prompting concerns about institutional autonomy and due process.
7. Sectoral Integration and Alignment
Recognizing India’s complex regulatory landscape, the Rules call for coordination with sectoral regulators such as the RBI, IRDAI, and TRAI to ensure consistency in enforcement. However, this coordination remains aspirational at present—there is no defined mechanism for cross-regulatory harmonization, leaving businesses uncertain about overlapping obligations.
Who Needs to Comply with the DPDP Act — and What Non-Compliance Could Cost
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, along with its 2025 Rules, applies broadly across India’s digital and business ecosystem. Its scope extends not only to large corporations but also to startups, MSMEs, public bodies, and multinational entities that handle personal data of individuals within India. The law is deliberately technology-agnostic and sector-neutral, recognizing that data flows underpin virtually every modern enterprise — from e-commerce and fintech to healthcare, education, and government services.

Who Falls Under the DPDP Framework
The DPDP Act applies to:
- Data Fiduciaries – any person, company, or entity that determines the purpose and means of processing personal data.
- Examples: Banks, insurance firms, telecom providers, healthcare institutions, e-commerce platforms, and digital marketing agencies.
- Examples: Banks, insurance firms, telecom providers, healthcare institutions, e-commerce platforms, and digital marketing agencies.
- Data Processors – entities that process data on behalf of a fiduciary, such as IT vendors, SaaS platforms, or cloud service providers.
- Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs) – large organizations identified by the Central Government based on factors such as:
- Volume and sensitivity of data processed,
- Risk to data principals’ rights,
- Potential impact on national or public interests, and
- Use of new technologies such as AI, biometric analytics, or algorithmic profiling.
- Volume and sensitivity of data processed,
- Foreign Entities – companies operating outside India that process the personal data of Indian residents in connection with offering goods or services.
- This extraterritorial scope mirrors the GDPR’s global reach, ensuring that Indian citizens’ data is protected regardless of where it is processed.
- This extraterritorial scope mirrors the GDPR’s global reach, ensuring that Indian citizens’ data is protected regardless of where it is processed.
The inclusion of public authorities and government departments further underscores the Act’s intent to ensure uniform standards across both private and public data ecosystems.
Exemptions and Special Categories
Certain exemptions apply for:
- Data processed for national security, law enforcement, or public order purposes;
- Research, archiving, or statistical analysis, subject to anonymization safeguards; and
- Small entities handling minimal data volumes, which may receive simplified compliance obligations under MeitY notifications.
However, even exempted entities must adhere to reasonable security practices and are not absolved from accountability in the event of gross negligence or misuse of personal data.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
The DPDP Act introduces one of the strictest penalty regimes in Asia, emphasizing deterrence and accountability. The Data Protection Board of India (DPBI) is empowered to investigate violations and impose monetary penalties based on severity, intent, and recurrence.
Key penalty slabs include:
| Violation | Penalty (up to) |
| Failure to take reasonable security safeguards leading to data breach | ₹250 crore |
| Non-fulfilment of data principal rights (access, correction, erasure, grievance redress) | ₹200 crore |
| Non-notification of data breach to DPBI or affected individuals | ₹150 crore |
| Violation of obligations by Significant Data Fiduciaries (e.g., DPIA, audits, DPO appointment) | ₹150 crore |
| Non-compliance with orders of the DPBI | ₹50 crore |
| Failure of Consent Manager to fulfil obligations | ₹10 crore |
(Source: DPDP Act, 2023, Schedule on Financial Penalties)
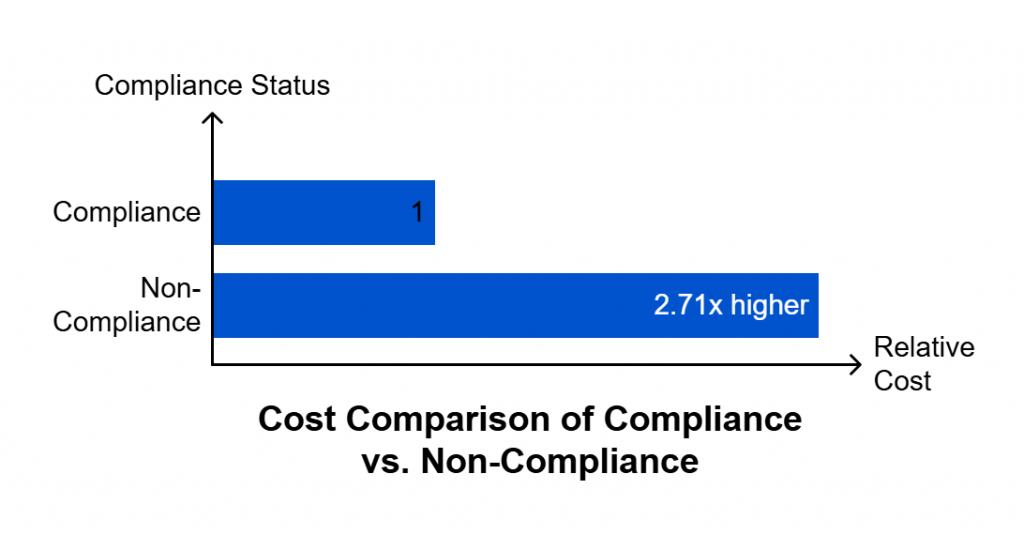
Beyond financial penalties, the Board can direct entities to cease data processing, delete unlawfully collected data, or suspend operations in severe cases. Such actions could have reputational and operational consequences far beyond monetary loss — particularly for global companies relying on India’s data flows.
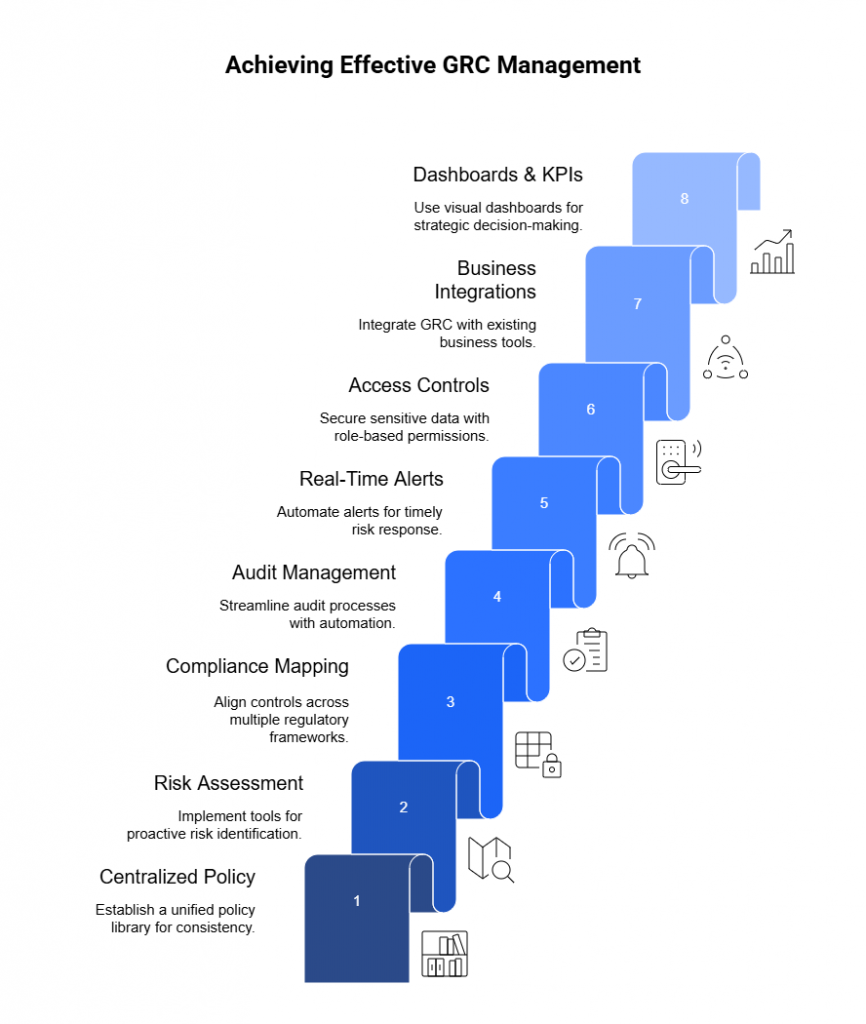
DPDP Act Compliance Readiness Checklist
Many organizations are still in the early stages of remediation — conducting privacy policy reviews, redrafting contracts with vendors, and appointing independent consent managers or DPOs.
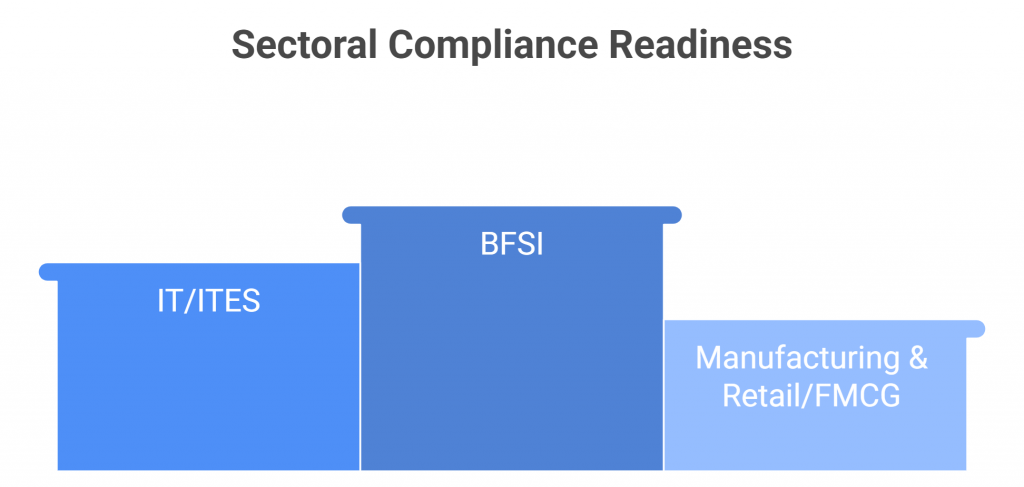
In fact, sectoral trends reveal that regulated industries such as banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) are among the most proactive, with the majority reporting partial or near-complete compliance. The IT/ITES sector follows suit, adopting regulations quickly. By contrast, the manufacturing and Retail & FMCG sectors lag behind, citing complexities in data flow mapping, cross-border transfers, and third-party vendor alignment.
The following checklist translates the Act and the 2025 Rules into practical steps for Chief Privacy Officers (CPOs), Data Protection Officers (DPOs), CISOs, and compliance leaders tasked with building a privacy-first organization.
5.1 Governance and Accountability
✅ Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
- Mandatory for all Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs).
- The DPO must be based in India and act as the primary contact for both data principals and the DPBI.
- Define roles and escalation paths for data privacy incidents.
✅ Constitute a Data Protection Committee or Working Group
- Include representatives from legal, IT security, HR, and product teams.
- Conduct regular reviews of compliance reports and privacy risk dashboards.
✅ Board-Level Oversight
- Ensure that senior management receives quarterly privacy compliance reports.
- Integrate data protection into enterprise risk management (ERM) frameworks.
5.2 Data Mapping and Inventory Management
✅ Conduct End-to-End Data Mapping
- Identify all personal and sensitive data collected, processed, and shared.
- Document how data flows across internal systems, vendors, and cloud platforms.
✅ Create a Centralized Data Register
- Maintain an inventory of processing activities (purpose, legal basis, retention).
- Keep updated logs available for DPBI audits or inspections.
5.3 Consent and Notice Management
✅ Deploy Verifiable Consent Frameworks
- Provide multi-language consent notices in plain language.
- Record explicit user actions (e.g., OTP or digital signature) as proof of consent.
- Enable consent withdrawal via a simple, mirrored process.
✅ Register or Partner with a Consent Manager
- Engage a MeitY-approved Consent Manager for consent lifecycle management.
- Ensure all consent and revocation actions are synchronized with processors.
✅ Review Privacy Policies
- Update policies to align with DPDP definitions and user rights.
- Include contact details of the DPO and specify grievance timelines (30 days).
5.4 Data Security and Breach Management
✅ Implement “Reasonable Security Practices”
- Encryption at rest and in transit; zero-trust access models.
- Periodic Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT).
✅ Develop a Breach Response Plan
- Create templates for notifying the DPBI and affected individuals.
- Establish a 72-hour breach reporting protocol per the DPDP Rules.
- Maintain detailed incident response logs for audit purposes.
5.5 Data Principal Rights Management
✅ Build User Rights Interfaces
- Enable data principals to access, correct, or erase their data easily.
- Track requests to ensure response within 30 days.
✅ Maintain Transparency Logs
- Record all user interactions and grievance redress outcomes.
5.6 Data Retention and Purpose Limitation
✅ Implement a Purpose-Bound Retention Schedule
- Retain personal data only as long as necessary for the stated purpose.
- Automate deletion or anonymization post-fulfillment.
- Maintain legal justification for any extended retention period.
5.7 Vendor and Processor Management
✅ Audit Vendor Contracts
- Include DPDP-compliant clauses covering data use, security, and breach notification.
- Require vendors to align with the fiduciary’s data protection standards.
✅ Manage Cross-Border Transfers
- Allow transfers only to whitelisted countries approved by the Central Government.
- Use standardized contractual clauses for additional safeguards.
5.8 Audits, Training, and Continuous Monitoring
✅ Conduct Regular Audits and DPIAs
- Annual independent data protection audits for SDFs.
- Record outcomes and corrective actions.
✅ Implement Organization-Wide Privacy Training
- Mandatory onboarding sessions for employees handling personal data.
- Specialized training for developers, HR teams, and marketing functions.
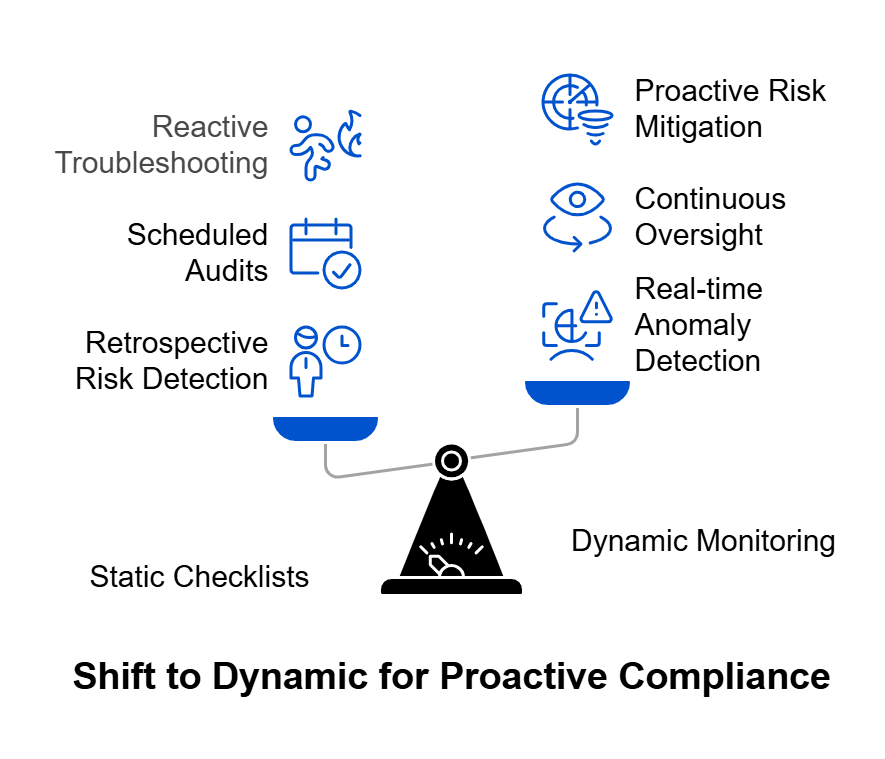
✅ Continuous Compliance Monitoring
- Deploy dashboards for breach tracking, consent logs, and audit trails.
- Review metrics quarterly to assess organizational maturity.
5.9 Voluntary Disclosures and Transparency
✅ Publish an Annual Privacy and Accountability Report
- Summarize compliance performance, data breach incidents, and audit findings.
- Share highlights publicly or with regulators to build stakeholder trust.
Readiness Snapshot
| Category | Action Required | Status |
| Governance & DPO Appointment | Establish accountability structure | ☐ |
| Data Mapping & Inventory | Identify all personal data flows | ☐ |
| Consent & Notice Management | Deploy verifiable consent tools | ☐ |
| Security & Breach Response | Implement 72-hour reporting protocol | ☐ |
| User Rights | Launch rights management portal | ☐ |
| Vendor Compliance | Review contracts & cross-border transfers | ☐ |
| Training & Audits | Conduct annual data privacy audits | ☐ |
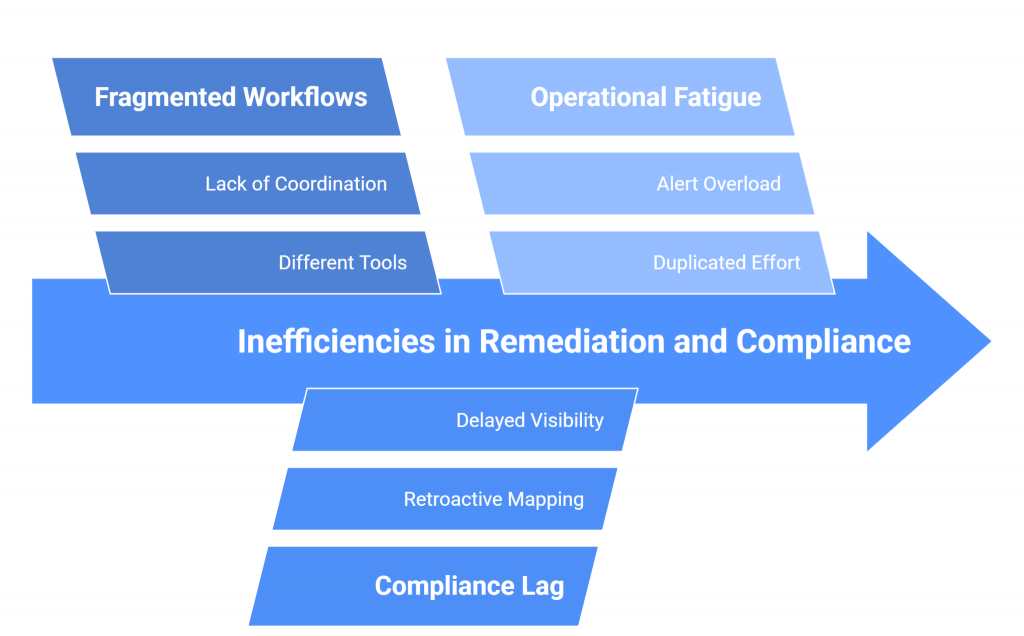
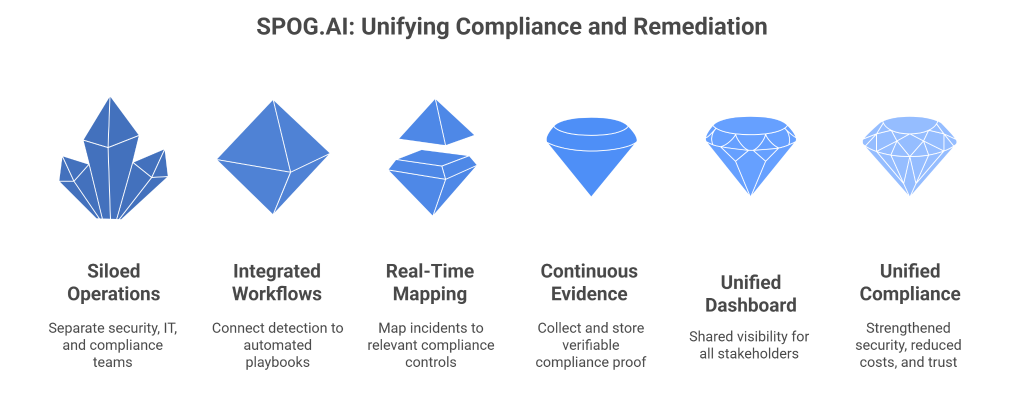
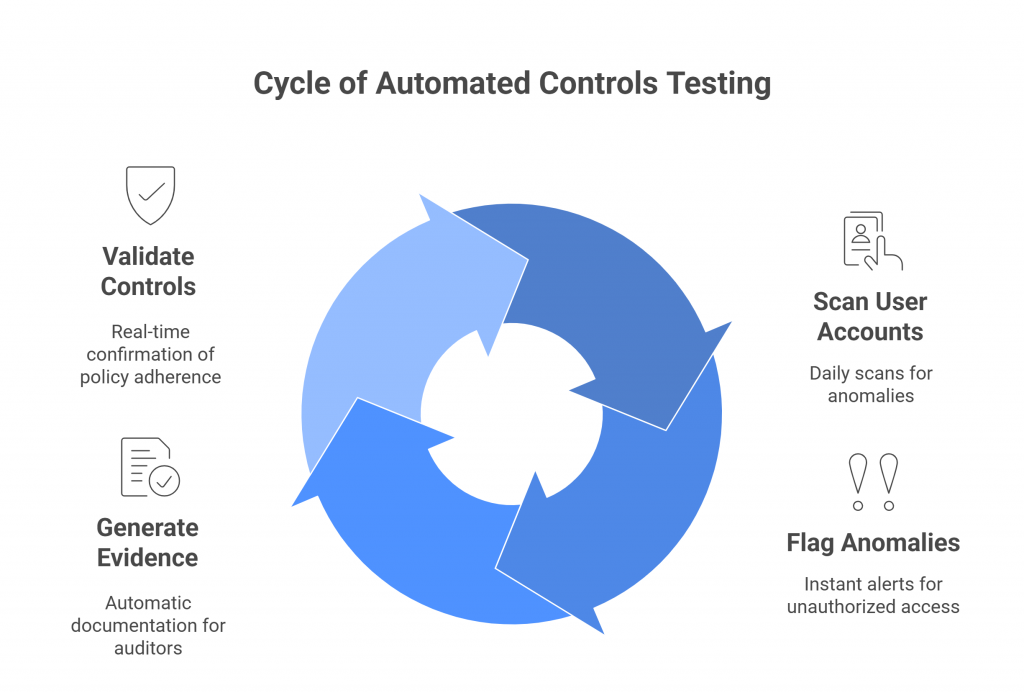
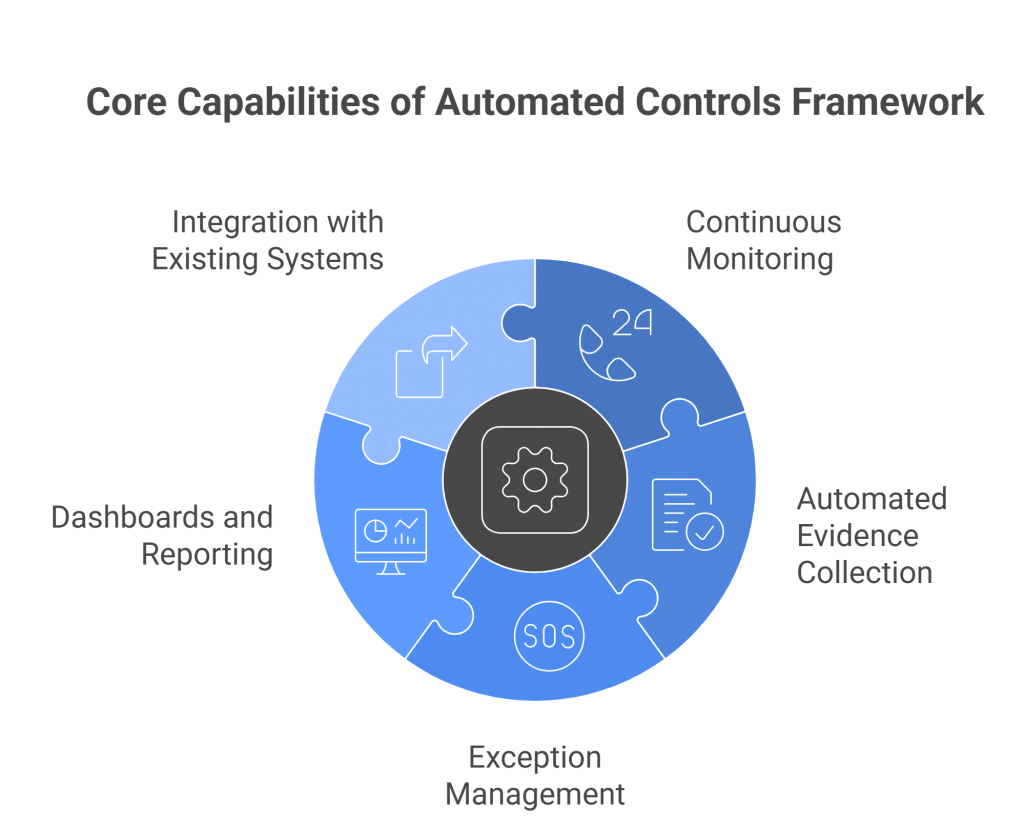
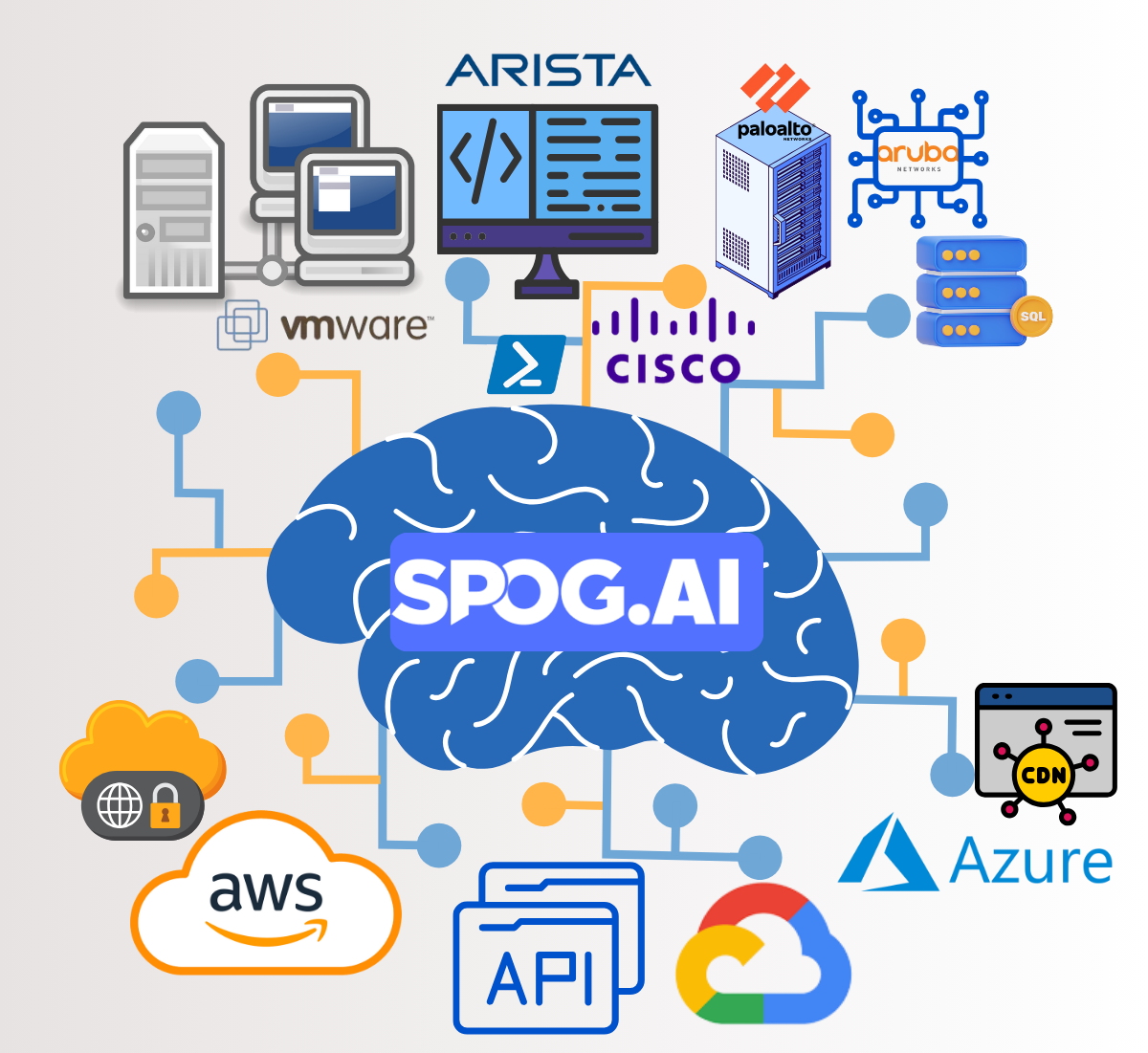
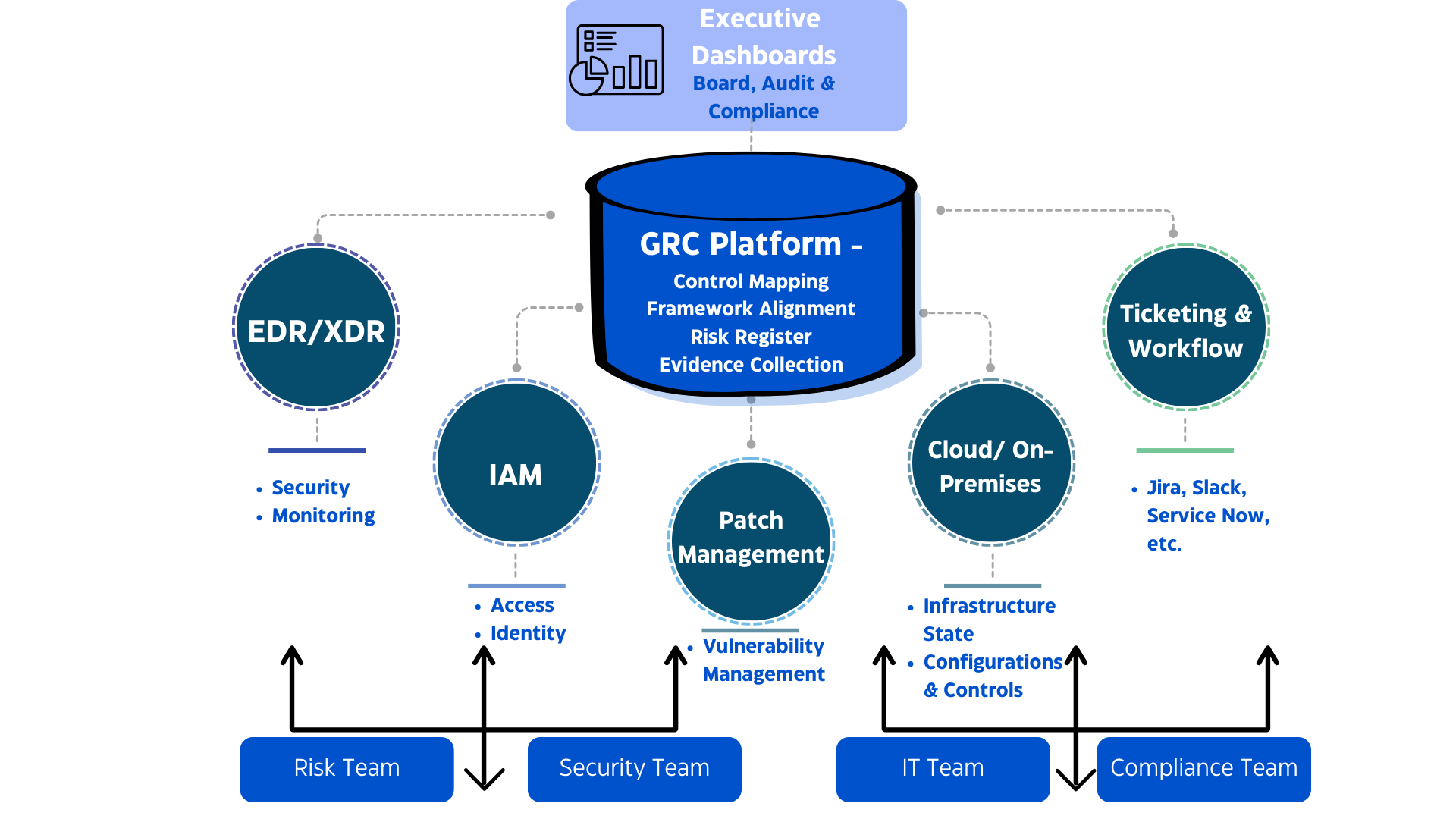
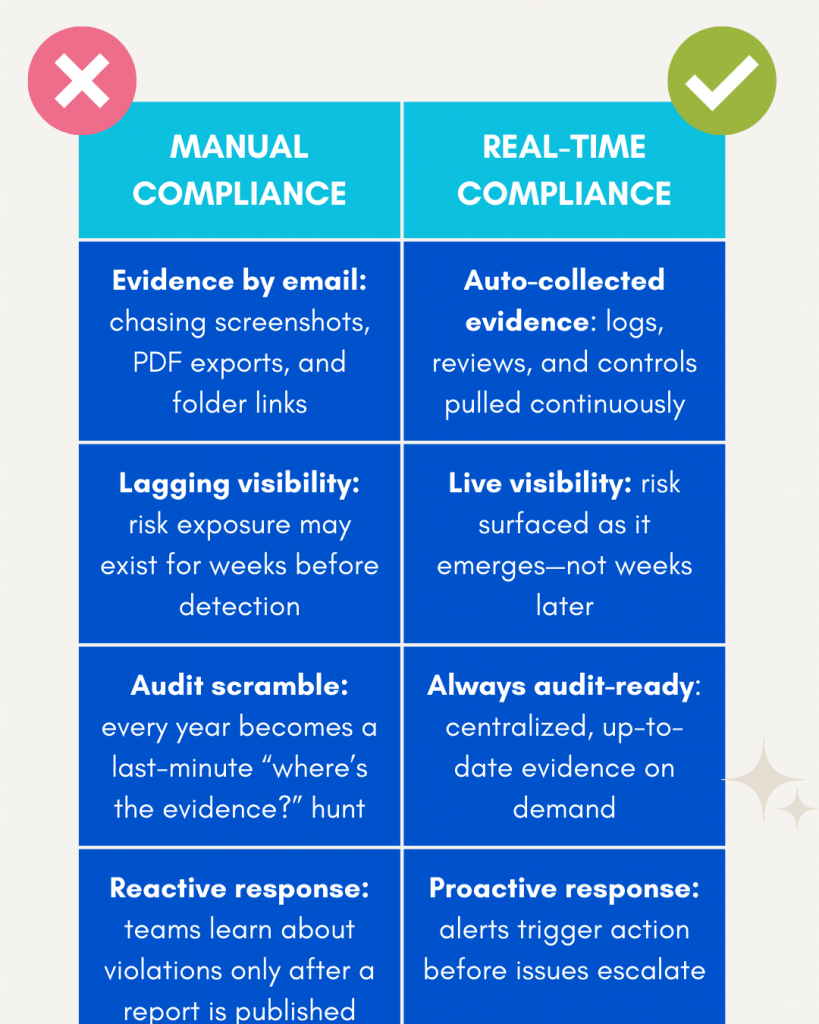
How SPOG.AI Helps You Strengthen DPDP Act Compliance
According to ETCISO Intelligence, nearly 60% of CISOs and compliance leaders believe that DPDPA readiness will take another 12–18 months for full-scale implementation, particularly in large and mid-sized organizations with legacy systems and complex vendor networks.
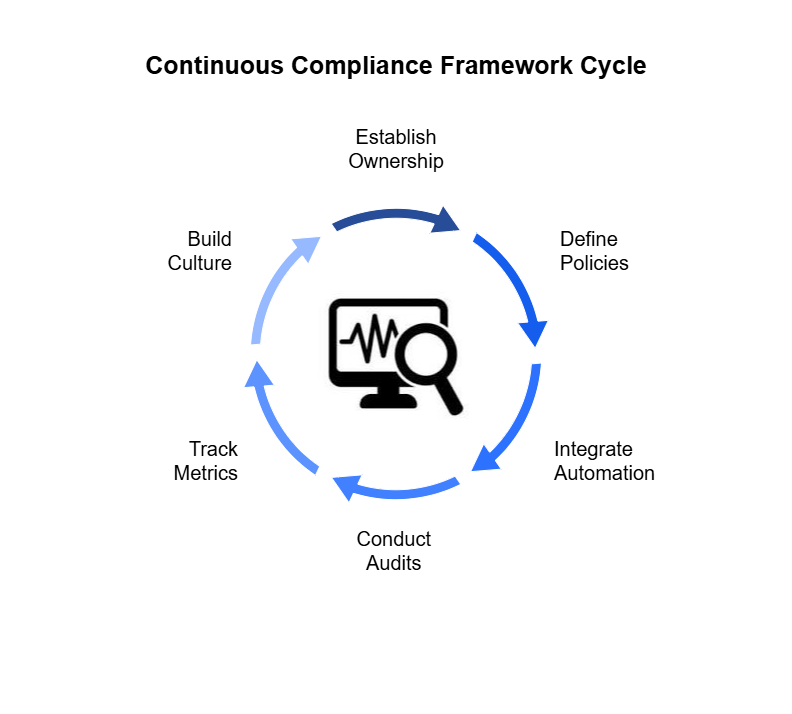
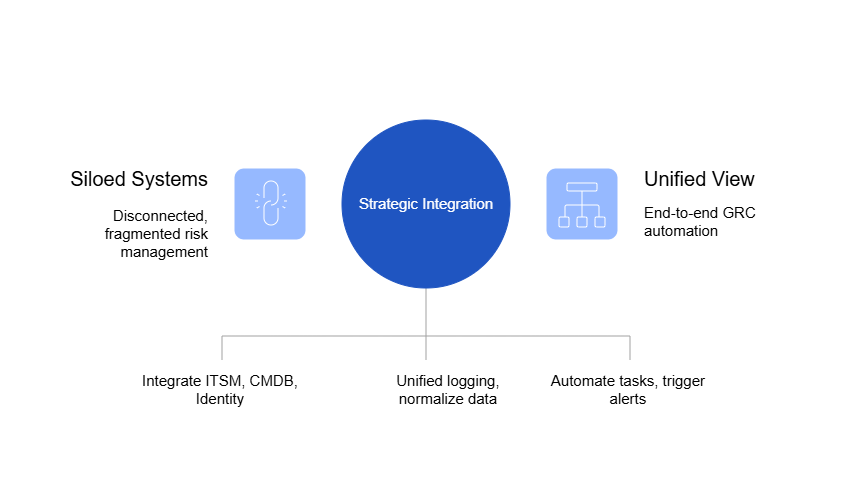
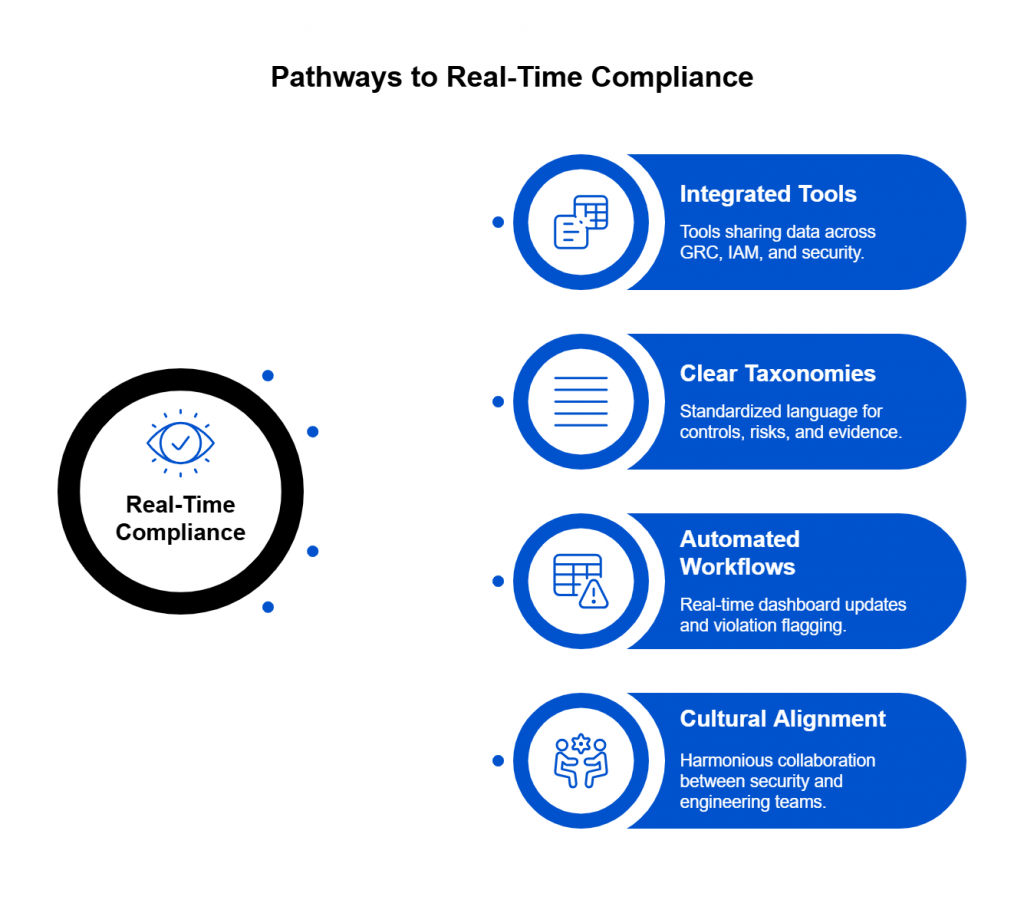
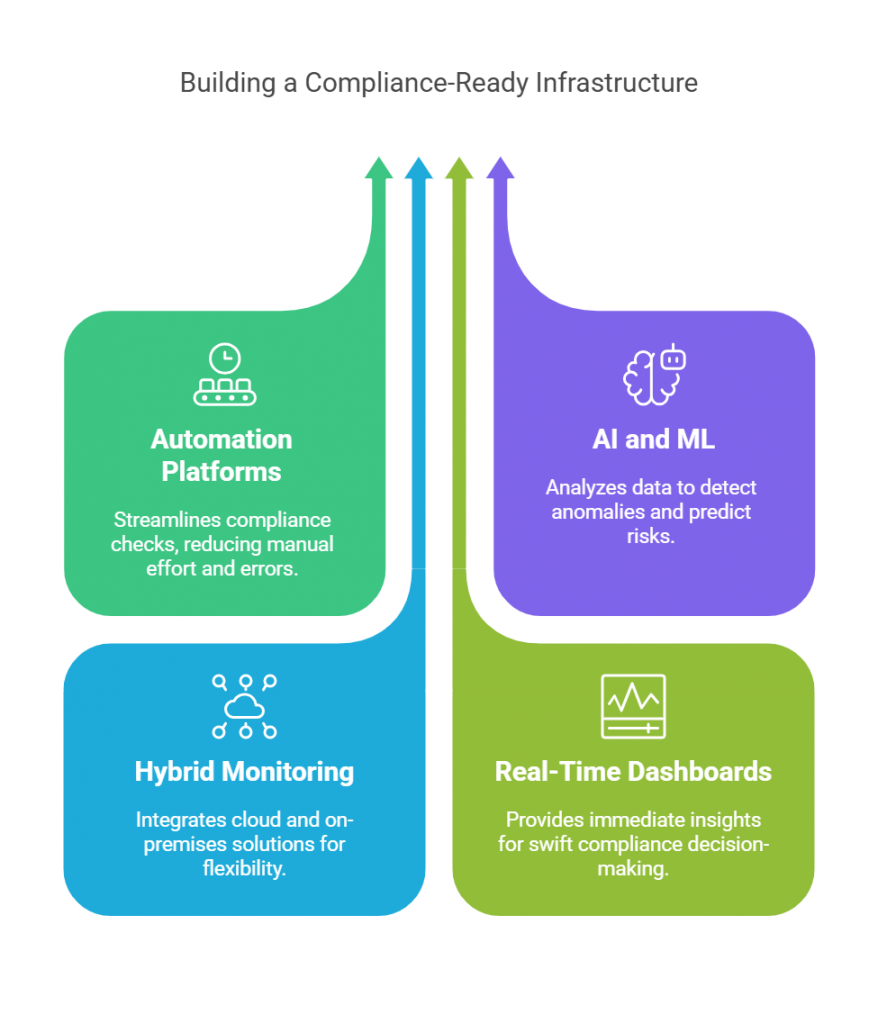
The DPDP Rules 2025 demand more than documentation, they demand real-time evidence of accountability. SPOG.AI provides that foundation by connecting privacy, security, and governance workflows into a single, intelligent fabric.
In a landscape where penalties can reach ₹250 crore per violation and reputational damage can be irreversible, SPOG.AI enables organizations to move from compliance anxiety to compliance confidence — with clarity, automation, and measurable control.
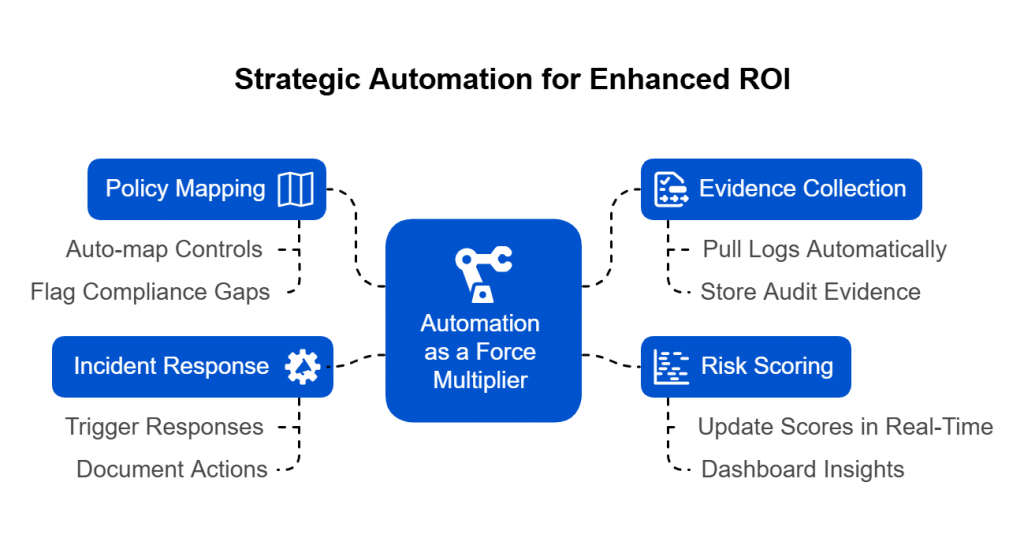
- Centralized Data Visibility:
Gain a unified view of personal data across systems, clouds, and vendors for complete traceability and audit readiness. - Impact-Based Risk Prioritization:
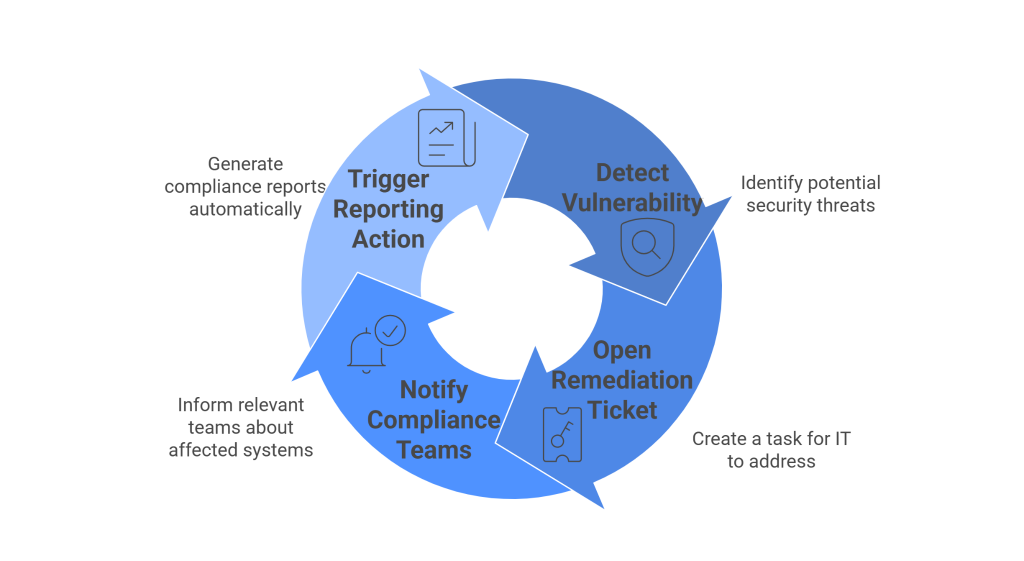
Automatically correlate alerts and vulnerabilities with data sensitivity to focus remediation where it matters most. - Automated Breach Response:
Detect, classify, and report data breaches within 72 hours using pre-built workflows aligned with DPDP Rules. - Third-Party & Vendor Oversight:
Continuously monitor vendor data access, cross-border transfers, and policy compliance through automated risk scoring. - Actionable Intelligence for DPOs:
Provide DPOs with real-time compliance dashboards, grievance tracking, and AI-generated readiness assessments. - Integrated Cyber & Privacy Controls:
Connect data protection with cybersecurity operations to identify compliance risks before they escalate. - Continuous Compliance Monitoring:
Replace manual reporting with real-time analytics and continuous assurance aligned to DPDP obligations. - Accelerated Readiness & Maturity:
Close the 12–18 month readiness gap by automating core compliance processes and standardizing governance practices. - Build a Culture of Trust:
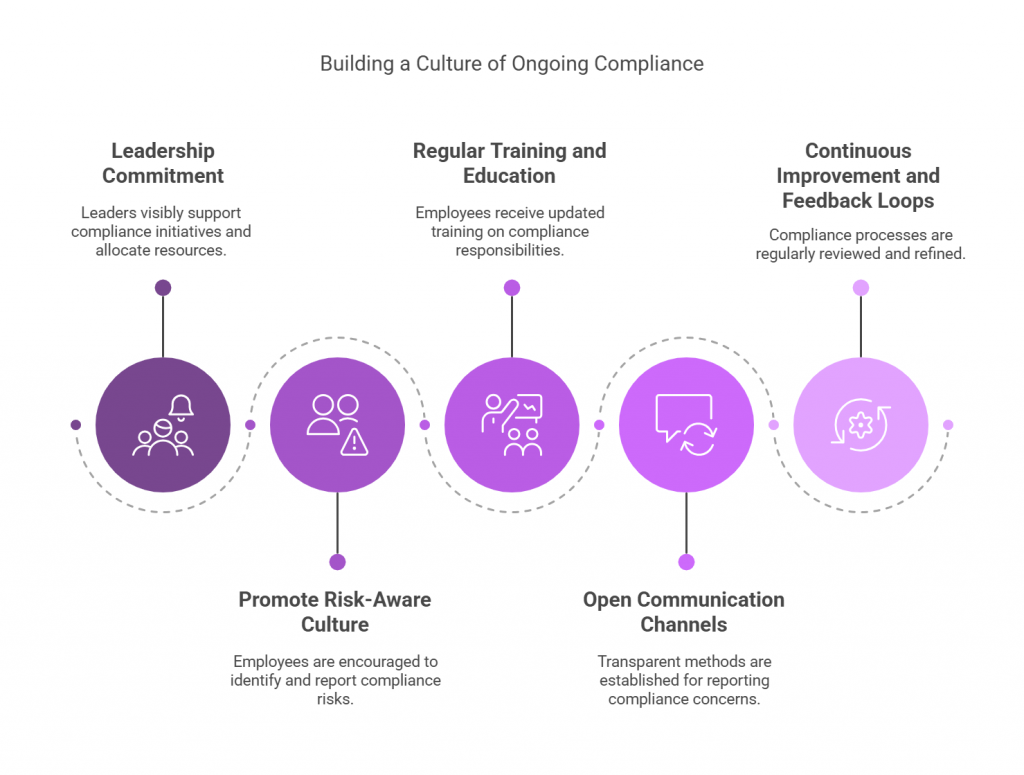
Turn DPDP compliance from a regulatory burden into a strategic differentiator — demonstrating transparency, accountability, and digital trust.
Conclusion
As India positions itself as a global data hub, the DPDP Rules 2025 will serve as both a compliance benchmark and a cultural inflection point. Whether they succeed depends not only on enforcement but also on how seriously organizations internalize the principle that privacy is not a cost — it’s a competitive advantage.
Yet, as multiple studies highlight, most organizations remain in the early or intermediate stages of readiness. Legacy infrastructure, fragmented data systems, and evolving interpretations of regulatory clauses continue to slow down implementation.
The real challenge, therefore, is not intent — it’s execution. Organizations need to bridge the gap between policy compliance and operational maturity, ensuring that privacy is not just documented but demonstrably practiced.
SPOG.AI can help organizations operationalize the DPDPA with unified governance, risk-based prioritization, and real-time compliance insights.
Ultimately, India’s data protection journey is just beginning. The success of the DPDP framework will depend not only on how strictly it is enforced, but also on how deeply it is embraced by businesses, regulators, and citizens alike.
Compliance must evolve into culture, and culture into trust.
Organizations that act early, invest in intelligent compliance infrastructure, and treat data protection as a strategic advantage rather than a legal burden will define the future of India’s trillion-dollar digital economy. One where privacy and innovation coexist by design, not by exception.